Abstract
Purpose
Down-regulation of let-7 microRNA (miRNA) plays an important role in the pathogenesis of lung cancer. k-Ras and c-Myc, two key oncogenes in lung cancer, have been found to be targeted by let-7 in vitro. However, the in vivo relevance of these findings is unknown. The aim of the present study is to determine the effect of let-7a, a member of let-7 family, on the growth of lung cancer in vivo and to investigate whether let-7-induced suppression of k-Ras and c-Myc is involved in lung cancer.
Methods
A549-let-7a cell line and A549-control cell line, two stable transfected cell lines over-expressing let-7a and the control miRNA, were established and preserved in our lab. A549, A549-control, and A549-let-7a cells were injected subcutaneously into nude mice, respectively. After 30 days, the mice were killed; the xenografts were excised and weighed. The expression of let-7a in tumor xenografts was assessed by real-time reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR). The expression of k-Ras and c-Myc in xenografts were determined by western blot and immunohistochemistry detection.
Results
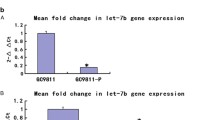
Real-time RT-PCR showed the expression of let-7a was increased significantly in A549-let-7a cells-injected group, compared with A549-control cells-injected group and A549 cells-injected group (P < 0.01). In the xenografts of A549-let-7a cells-injected group, a significant depression in tumor weight (P < 0.05) and significant decrease of k-Ras and c-Myc protein were observed (P < 0.01), compared to A549 cells-injected group and A549-control cells-injected group.
Conclusion
Overexpression of let-7a can inhibit the growth of lung cancer transplanted subcutaneously in nude mice by suppression of k-Ras and c-Myc.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431(7006):350–355
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M, Croce CM (2004) Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(9):2999–3004
Croce CM, Calin GA (2005) miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell 122(1):6–7
He X, Duan C, Chen J, Ou-Yang X, Zhang Z, Li C, Peng H (2009) Let-7a elevates p21(WAF1) levels by targeting NIRF and suppresses the growth of A549 lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett 583(21):3501–3507
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, Thun MJ (2008) (2008) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 58(2):71–96
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom M, Jarvis R, Cheng A, Labourier E, Reinert KL, Brown D, Slack FJ (2005) RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell 120(5):635–647
Johnson CD, Esquela-Kerscher A, Stefani G, Byrom M, Kelnar K, Ovcharenko D, Wilson M, Wang X, Shelton J, Shingara J, Chin J, Brown D, Slack FJ (2007) The let-7 microRNA represses cell proliferation pathways in human cells. Cancer Res 67(16):7713–7722
Koscianska E, Baev V, Skreka K, Oikonomaki K, Rusinov V, Tabler M, Kalantidis K (2007) Prediction and preliminary validation of oncogene regulation by miRNAs. BMC Mol Biol 8:79
Lee YS, Dutta A (2007) The tumor suppressor microRNA let-7 represses the HMGA2 oncogene. Genes Dev 21(9):1025–1030
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120(1):15–20
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, Downing JR, Jacks T, Horvitz HR, Golub TR (2005) MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435(7043):834–838
Mayr C, Hemann MT, Bartel DP (2007) Disrupting the pairing between let-7 and Hmga2 enhances oncogenic transformation. Science 315(5818):1576–1579
Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F, Martindale MQ, Kuroda MI, Maller B, Hayward DC, Ball EE, Degnan B, Müller P, Spring J, Srinivasan A, Fishman M, Finnerty J, Corbo J, Levine M, Leahy P, Davidson E, Ruvkun G (2000) Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 408(6808):86–89
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, Rougvie AE, Horvitz HR, Ruvkun G (2000) The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 403(6772):901–906
Robinson LA, Smith LJ, Fontaine MP, Kay HD, Mountjoy CP, Pirruccello SJ (1995) c-myc antisense oligodeoxyribonucleotides inhibit proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 60(6):1583–1591
Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, Osada H, Endoh H, Harano T, Yatabe Y, Nagino M, Nimura Y, Mitsudomi T, Takahashi T (2004) Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res 64(11):3753–3756
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30800534).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Xy., Chen, Jx., Zhang, Z. et al. The let-7a microRNA protects from growth of lung carcinoma by suppression of k-Ras and c-Myc in nude mice. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136, 1023–1028 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-009-0747-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-009-0747-5