Abstract
Purpose
To determine the interrelationships of p53, MDM2, and p14ARF protein expression in primary esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and their prognostic value in ESCC.
Methods
In total, 119 patients treated for ESCC with esophagectomy were enrolled in this study. Demographic and clinical data including gender, age, depth of tumor invasion, lymph node involvement, and 5-year survival rate were collected by chart review. p53, MDM2, and p14ARF were detected immunohistochemically in the resected tumors to evaluate their usefulness as biomarkers of clinical outcome.
Results
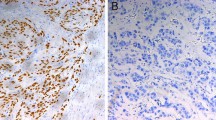
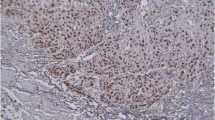
p53, MDM2, and p14ARF were expressed in 61 (51.3%), 34 (28.6%), and 22 (18.5%) of 119 tumor specimens, respectively. Overall, p53 protein expression was positively correlated with MDM2 (P = 0.024) and p14ARF expression (P = 0.026). In addition, p14ARF expression was most often found in specimens that were positive for both p53 and MDM2. Changes in the p53, MDM2, and p14ARF protein levels were not correlated with 5-year survival rate.
Conclusions
Expression of p53 protein correlates with increased MDM2 and p14ARF protein levels in ESCC. In addition, status of p53 (wild-type versus mutant) rather than expression level of p53, MDM2, or p14ARF is likely to be the more critical determinant of clinical outcome.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal A, Yang J, Murphy RF, Agrawal DK (2006) Regulation of the p14ARF-Mdm2-p53 pathway: an overview in breast cancer. Exp Mol Pathol 81:115–122. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2006.07.001
Arora S, Mathew R, Mathur M, Chattopadhayay TK, Ralhan R (2001) Alterations in MDM2 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: relationship with p53 status. Pathol Oncol Res 7:203–208
Capoulade C, Bressac-de Paillerets B, Lefrere I, Ronsin M, Feunteun J, Tursz T, Wiels J (1998) Overexpression of MDM2, due to enhanced translation, results in inactivation of wild-type p53 in Burkitt’s lymphoma cells. Oncogene 16:1603–1610. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201702
Cordon-Cardo C, Latres E, Drobnjak M, Oliva MR, Pollack D, Woodruff JM, Marechal V, Chen J, Brennan MF, Levine AJ (1994) Molecular abnormalities of mdm2 and p53 genes in adult soft tissue sarcomas. Cancer Res 54:794–799
Culjkovic B, Topisirovic I, Skrabanek L, Ruiz-Gutierrez M, Borden KL (2006) eIF4E is a central node of an RNA regulon that governs cellular proliferation. J Cell Biol 175:415–426. doi:10.1083/jcb.200607020
Fahn HJ, Wang LS, Huang BS, Huang MH, Chien KY (1994) Tumor recurrence in long-term survivors after treatment of carcinoma of the esophagus. Ann Thorac Surg 57:677–681
Gallagher S, Kefford RF, Rizos H (2005) Enforced expression of p14ARF induces p53-dependent cell cycle arrest but not apoptosis. Cell Cycle 4:465–472
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz A, Balch CM, Haller DG, Morrow M (2002) AJCC cancer staging manual. Springer, New York
Harris SL, Levine AJ (2005) The p53 pathway: positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene 24:2899–2908. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208615
Higashiyama M, Doi O, Kodama K, Yokouchi H, Kasugai T, Ishiguro S, Takami K, Nakayama T, Nishisho I (1997) MDM2 gene amplification and expression in non-small-cell lung cancer: immunohistochemical expression of its protein is a favourable prognostic marker in patients without p53 protein accumulation. Br J Cancer 75:1302–1308
Honda R, Tanaka H, Yasuda H (1997) Oncoprotein MDM2 is a ubiquitin ligase E3 for tumor suppressor p53. FEBS Lett 420:25–27. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(97)01480-4
Hsu HS, Wang YC, Tseng RC, Chang JW, Chen JT, Shih CM, Chen CY (2004) 5′ cytosine-phospho-guanine island methylation is responsible for p14ARF inactivation and inversely correlates with p53 overexpression in resected non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10:4734–4741. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0704
Ikeda G, Isaji S, Chandra B, Watanabe M, Kawarada Y (1999) Prognostic significance of biologic factors in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Cancer 86:1396–1405. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19991015)86:8<1396::AID-CNCR3>3.0.CO;2-H
Ikeguchi M, Ueda T, Fukuda K, Yamaguchi K, Tsujitani S, Kaibara N (2002) Expression of the murine double minute gene 2 oncoprotein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma as a novel marker for lack of response to chemoradiotreatment. Am J Clin Oncol 25:454–459. doi:10.1097/00000421-200210000-00006
Landers JE, Cassel SL, George DL (1997) Translational enhancement of mdm2 oncogene expression in human tumor cells containing a stabilized wild-type p53 protein. Cancer Res 57:3562–3568
Leach FS, Tokino T, Meltzer P, Burrell M, Oliner JD, Smith S, Hill DE, Sidransky D, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1993) p53 Mutation and MDM2 amplification in human soft tissue sarcomas. Cancer Res 53:2231–2234
Lianes P, Orlow I, Zhang ZF, Oliva MR, Sarkis AS, Reuter VE, Cordon-Cardo C (1994) Altered patterns of MDM2 and TP53 expression in human bladder cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 86:1325–1330. doi:10.1093/jnci/86.17.1325
Mandard AM, Hainaut P, Hollstein M (2000) Genetic steps in the development of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Mutat Res 462:335–342. doi:10.1016/S1383-5742(00)00019-3
Matsumoto M, Furihata M, Kurabayashi A, Araki K, Sasaguri S, Ohtsuki Y (2003) Association between inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and p53 status in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncology 64:90–96. doi:10.1159/000066519
Momand J, Zambetti GP, Olson DC, George D, Levine AJ (1992) The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell 69:1237–1245. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-R
Nathan CO, Sanders K, Abreo FW, Nassar R, Glass J (2000) Correlation of p53 and the proto-oncogene eIF4E in larynx cancers: prognostic implications. Cancer Res 60:3599–3604
Robert V, Michel P, Flaman JM, Chiron A, Martin C, Charbonnier F, Paillot B, Frebourg T (2000) High frequency in esophageal cancers of p53 alterations inactivating the regulation of genes involved in cell cycle and apoptosis. Carcinogenesis 21:563–565. doi:10.1093/carcin/21.4.563
Rosa AR, Schirmer CC, Gurski RR, Meurer L, Edelweiss MI, Kruel CD (2003) Prognostic value of p53 protein expression and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in resected squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Dis Esophagus 16:112–118. doi:10.1046/j.1442-2050.2003.00309.x
Saito H, Tsujitani S, Oka S, Ikeguchi M, Maeta M, Kaibara N (2002) The expression of murine double minute 2 is a favorable prognostic marker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma without p53 protein accumulation. Ann Surg Oncol 9:450–456. doi:10.1007/BF02557267
Shibagaki I, Tanaka H, Shimada Y, Wagata T, Ikenaga M, Imamura M, Ishizaki K (1995) p53 mutation, murine double minute 2 amplification, and human papillomavirus infection are frequently involved but not associated with each other in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 1:769–773
Smeds J, Berggren P, Ma X, Xu Z, Hemminki K, Kumar R (2002) Genetic status of cell cycle regulators in squamous cell carcinoma of the oesophagus: the CDKN2A (p16(INK4a) and p14(ARF)) and p53 genes are major targets for inactivation. Carcinogenesis 23:645–655. doi:10.1093/carcin/23.4.645
Stott FJ, Bates S, James MC, McConnell BB, Starborg M, Brookes S, Palmero I, Ryan K, Hara E, Vousden KH, Peters G (1998) The alternative product from the human CDKN2A locus, p14(ARF), participates in a regulatory feedback loop with p53 and MDM2. EMBO J 17:5001–5014. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.17.5001
Volant A, Nousbaum JB, Giroux MA, Roue-Quintin I, Metges JP, Ferec C, Gouerou H, Robaszkiewicz M (1995) p53 protein accumulation in oesophageal squamous cell carcinomas and precancerous lesions. J Clin Pathol 48:531–534. doi:10.1136/jcp.48.6.531
Wang YC, Lin RK, Tan YH, Chen JT, Chen CY (2005) Wild-type p53 overexpression and its correlation with MDM2 and p14ARF alterations: an alternative pathway to non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:154–164. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.03.139
Weber JD, Taylor LJ, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ, Bar-Sagi D (1999) Nucleolar Arf sequesters Mdm2 and activates p53. Nat Cell Biol 1:20–26. doi:10.1038/8991
Xing EP, Nie Y, Song Y, Yang GY, Cai YC, Wang LD, Yang CS (1999) Mechanisms of inactivation of p14ARF, p15INK4b, and p16INK4a genes in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 5:2704–2713
Xue Q, Sano T, Kashiwabara K, Oyama T, Nakajima T (2001) Aberrant expression of pRb, p16, p14ARF, MDM2, p21 and p53 in squamous cell carcinomas of lung. Jpn J Cancer Res 92:285–292
Zhu N, Gu L, Findley HW, Zhou M (2005) Transcriptional repression of the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E gene by wild type p53. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 335:1272–1279. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.08.026
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by grants from the National Science Council of Taiwan to HS Hsu (NSC-96-2314-B-075-027) and TH Cheng (NSC-93-2320-B-010-063).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, TH., Hsu, PK., Li, A.FY. et al. Correlation of p53, MDM2 and p14ARF protein expression in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 135, 1577–1582 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-009-0605-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-009-0605-5