Abstract
Purpose
Malignant pleural effusion (MPE) is a common clinical problem in patients with advanced cancer. Evidence suggests that tumor-mediated angiogenesis and enhanced vascular permeability in the pleural wall are due to high levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which plays an important role in the pathogenesis of MPE. The present study was designed to test whether the recombinant adenovirus-mediated delivery of human endostatin (Ad-hEndo), one of the potent inhibitors of angiogenesis, would inhibit the formation and progression of MPE.
Methods
We developed a novel mouse model of MPE by injecting Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) cells directly into pleural cavity of C57BL/6 mice. To evaluate the therapeutic effects of endostatin in this MPE model, we injected the Ad-hEndo into the pleural cavity of MPE-bearing mice three times with the 3-day interval.
Results
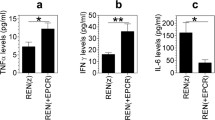
We found that this treatment resulted in significant reduction in pleural effusion volume, the number of pleural tumor foci, microvessel density, and vascular permeability, while it significantly prolonged the survival time. In addition, VEGF level of MPE in the group administered with the Ad-hEndo was obviously decreased as compared with that in the two control groups administered with null-adenovirus (Ad-null) or normal saline.
Conclusions
Our work provides a rationale for future studies toward evaluating the effectiveness of the adenovirus-based endostatin therapy for MPE.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antony VB, Loddenkemper R, Astoul P, Boutin C, Goldstraw P, Hott J et al (2000) Management of malignant pleural effusions. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 162:1987–2001
Burrows CM, Mathews WC, Colt HG (2000) Predicting survival in patients with recurrent symptomatic malignant pleural effusions. Chest 117:73–78. doi:10.1378/chest.117.1.73
Carmeliet P, Ferreira V, Breier G, Pollefeyt S, Kieckens L, Gertsenstein M et al (1996) Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single VEGF allele. Nature 380:435–439. doi:10.1038/380435a0
Ceyhan BB, Ozgun S, Celikel T, Yalcin M, Koc M (1996) IL-8 in pleural effusion. Respir Med 90:215–221. doi:10.1016/S0954-6111(96)90290-5
Cheng D, Lee YCG, Rogers JT, Perkett EA, Moyers JP, Rodriguez RM et al (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor level correlates with transforming growth factor-β isoform levels in pleural effusions. Chest 118:1747–1753. doi:10.1378/chest.118.6.1747
Dkhissi F, Lu H, Soria C, Opolon P, Griscelli F, Liu H et al (2003) Endostatin exhibits a direct antitumor effect in addition to its antiangiogenic activity in colon cancer cells. Hum Gene Ther 14:997–1008. doi:10.1089/104303403766682250
Ferrara N, Carver-Moore K, Chen H, Dowd M, Lu L, O’Shea KS et al (1996) Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the VEGF gene. Nature 380:439–442. doi:10.1038/380439a0
Folkman J (1995) Seminars in Medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston Clinical applications of research on angiogenesis. N Engl J Med 333:1757–1763. doi:10.1056/NEJM199512283332608
Gahéry-Ségard H, Juillard V, Gaston J, Lengagne R, Pavirani A, Boulanger P et al (1997) Humoral immune response to the capsid components of recombinant adenoviruses: routes of immunization modulate virus-induced Ig subclass shifts. Eur J Immunol 27:653–659. doi:10.1002/eji.1830270312
Hajitou A, Grignet C, Devy L, Berndt S, Blacher S, Deroanne CF et al (2002) The antitumoral effect of endostatin and angiostatin is associated with a down-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in tumor cells. FASEB J 16:1802–1804
Hamed EA, El-Noweihi AM, Mohamed AS, Mahmoud A (2004) Vasoactive mediators (VEGF and TNF-a) in patients with malignant and tuberculous pleural effusions. Respirology 9:81–86. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1843.2003.00529.x
Hampl M, Tanaka T, Albert PS, Lee J, Ferrari N, Fine HA (2001) Therapeutic effects of viral vector-mediated antiangiogenic gene transfer in malignant ascites. Hum Gene Ther 12:1713–1729. doi:10.1089/104303401750476221
Herbst RS, Fidler IJ (2000) Angiogenesis and lung cancer: potential for therapy. Clin Cancer Res 6:4604–4606
Herbst RS, Hess KR, Tran HT, Tseng JE, Mullani NA, Charnsangavej C et al (2002) Phase I study of recombinant human endostatin in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 20:3792–3803. doi:10.1200/JCO.2002.11.061
Huang BJ, Liu RY, Huang JL, Liang ZH, Gao GF, Wu JX et al (2007) Long-Term toxicity studies in Canine of E10A, an adenoviral vector for human endostatin gene. Hum Gene Ther 18:207–221. doi:10.1089/hum.2006.149
Leopold PL, Wendland RL, Vincent T, Crystal RG (2006) Neutralized adenovirus-immune complexes can mediate effective gene transfer via an Fc receptor-dependent infection pathway. J Virol 80:10237–10247. doi:10.1128/JVI.00512-06
Li G, Tian L, Hou JM, Ding ZY, He QM, Feng P et al (2005) Improved therapeutic effectiveness by combining recombinant CXC chemokine ligand 10 with Cisplatin in solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 11:4217–4224. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2117
Li L, Liu RY, Huang JL, Liu QC, Li Y, Wu PH et al (2006) Adenovirus-mediated intra-tumoral delivery of the human endostatin gene inhibits tumor growth in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer 118:2064–2071. doi:10.1002/ijc.21585
Light RW (2002) Talc for pleurodesis? Chest 122:1506–1508. doi:10.1378/chest.122.5.1506
Marx J (2003) Angiogenesis A boost for tumor starvation. Science 301:452–454. doi:10.1126/science.301.5632.452
Maskell NA, Lee YC, Gleeson FV, Hedley EL, Pengelly G, Davies RJ (2004) Randomized trials describing lung inflammation after pleurodesis with talc of varying particle size. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170:377–382. doi:10.1164/rccm.200311-1579OC
Matsumori Y, Yano S, Goto H, Nakataki E, Wedge SR, Ryan AJ et al (2006) ZD6474, an inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, inhibits growth of experimental lung metastasis and production of malignant pleural effusions in a non-small cell lung cancer model. Oncol Res 16:15–26
Momi H, Matsuyama W, Inoue K, Kawabata M, Arimura K, Fukunaga H et al (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor and proinflammatory cytokines in pleural effusions. Respir Med 96:817–822. doi:10.1053/rmed.2002.1364
O’Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Lane WS et al (1997) Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell 88:277–285. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81848-6
Sack U, Hoffman M, Zhao XJ, Chan KS, Hui DS, Gosse H et al (2005) Vascular endothelial growth factor in pleural effusions of different origin. Eur Respir J 25:600–604. doi:10.1183/09031936.05.00037004
Setoguchi Y, Jaffe HA, Chu CS, Crystal RG (1994) Intraperitoneal in vivo gene therapy to deliver alpha 1-antitrypsin to the systemic circulation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 10:369–377
Stathopoulos GT, Zhu Z, Everhart MB, Kalomenidis I, Lawson WE, Bilaceroglu S et al (2006) Nuclear factor-kappaB affects tumour progression in a mouse model of malignant pleural effusion. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 34:142–150. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2005-0130OC
Stathopoulos GT, Kollintza A, Moschos C, Psallidas I, Sherrill TP, Pitsinos EN et al (2007) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha promotes malignant pleural effusion. Cancer Res 67:9825–9834. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1064
Stathopoulos GT, Moschos C, Loutrari H, Kollintza A, Psallidas I, Karabela S et al (2008) Zoledronic acid is effective against experimental malignant pleural effusion. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 178(1):50–59
Sterman DH, Recio A, Vachani A, Sun J, Cheung L, DeLong P et al (2005) Long-term follow-up of patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma receiving high-dose adenovirus herpes simplex thymidine kinase/ganciclovir suicide gene therapy. Clin Cancer Res 11:7444–7453. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0405
Sterman DH, Recio A, Carroll RG, Gillespie CT, Haas A, Vachani A et al (2007) A phase I clinical trial of single-dose intrapleural IFN-beta gene transfer for malignant pleural mesothelioma and metastatic pleural effusions: high rate of antitumor immune responses. Clin Cancer Res 13:4456–4466. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0403
Strizzi L, Vianale G, Catalano A, Muraro R, Mutti L, Procopio A (2001) Basic fibroblast growth factor in mesothelioma pleural effusions: correlation with patient survival and angiogenesis. Int J Oncol 18:1093–1098
Thomas JP, Arzoomanian RZ, Alberti D, Marnocha R, Lee F, Friedl A et al (2003) Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of recombinant human endostatin in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 21:223–231. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.12.120
Tomimoto H, Yano S, Muguruma H, Kakiuchi S, Sone S (2007) Levels of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 are elevated in the exudative pleural effusions. J Med Invest 54:146–153. doi:10.2152/jmi.54.146
Van Ginkel FW, Liu C, Simecka JW, Dong JY, Greenway T, Frizzell RA et al (1995) Intratracheal gene delivery with adenoviral vector induces elevated systemic IgG and mucosal IgA antibodies to adenovirus and beta-galactosidase. Hum Gene Ther 6:895–903. doi:10.1089/hum.1995.6.7-895
Worgall S, Krause A, Qiu J, Joh J, Hackett NR, Crystal RG (2007) Protective immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa induced with a capsid-modified adenovirus expressing P. aeruginosa OprF. J Virol 81:13801–13808. doi:10.1128/JVI.01246-07
Wu Y, Yang L, Hu B, Liu JY, Su JM, Luo Y et al (2005) Synergistic anti-tumor effect of recombinant human endostatin adenovirus combined with gemcitabine. Anticancer Drugs 16:551–557. doi:10.1097/00001813-200506000-00011
Yanagawa H, Takeuchi E, Suzuki Y, Ohmoto Y, Bando H, Sone S (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor in malignant pleural effusion associated with lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 48:396–400. doi:10.1007/s002620050592
Yano S, Shinohara H, Herbst RS, Kuniyasu H, Bucana CD, Ellis LM et al (2000a) Production of experimental malignant pleural effusions is dependent on invasion of the pleura and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor by human lung cancer cells. Am J Pathol 157:1893–1903
Yano S, Herbst RS, Shinohara H, Knighton B, Bucana CD, Killion JJ et al (2000b) Treatment for malignant pleural effusion of human lung adenocarcinoma by inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylation. Clin Cancer Res 6:957–965
Yei S, Mittereder N, Wert S, Whitsett JA, Wilmott RW, Trapnell BC (1994) In vivo evaluation of the safety of adenovirus-mediated transfer of the human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator cDNA to the lung. Hum Gene Ther 5:731–744. doi:10.1089/hum.1994.5.6-731
Zebrowski BK, Yano S, Liu W, Shaheen RM, Hicklin DJ, Putnam JB Jr et al (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor levels and induction of permeability in malignant pleural effusions. Clin Cancer Res 5:3364–3368
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Chinese Key Basic Research Program (2004CB518807), the projects of National Natural Science Foundation of China, and National 973 Program. Since the area of Ad vector research is rapidly expending, it was impossible to cite all related references in this article. Our apologies are to all investigators whose work could not be cited.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no duality of interest that could be perceived to bias our work, acknowledging all financial support and any other personal connections.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
F. Fang, P. Chen and X. Wu have equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, F., Chen, P., Wu, X. et al. Therapeutic effects of recombinant human endostatin adenovirus in a mouse model of malignant pleural effusion. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 135, 1149–1157 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-009-0555-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-009-0555-y