Abstract
Purpose
CKS2 was identified as an upregulated gene in gastric cancer via our DNA microarray. This study was to verify the upregulation of CKS2 in many gastric cancer patients and to examine the CKS2-mediated cellular response.
Methods
CKS2 upregulation was analyzed using reverse transcriptase PCR, real-time PCR, and immunohistochemical and clinicopathological analyses. GFP-CKS2 or CKS2-siRNA was used to analyze the cellular localization and proliferation.
Results
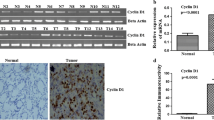
The strong upregulation of mRNA and protein levels of CKS2 was identified. In CKS2-overexpressing cells, tumor suppressor p53 and p21cip1 were downregulated and cell growth was increased. In contrast, CKS2-siRNA-transfected cells showed an increased tumor suppressor expression and decreased cell growth.
Conclusions
We showed that CKS2 was significantly upregulated in gastric cancers and a high level of CKS2 was highly correlated with histologic tumor differentiation and pathological grade of the tumor size, lymph node, and metastasis stage. We suggest that the cell cycle regulator CKS2 might be deeply involved in gastric cancer progression.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alhasan SA, Ensley JF, Sarkar FH (2000) Genistein induced molecular changes in a squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck cell line. Int J Oncol 16:333–338
Banerjee SK, Weston AP, Zoubine MN, Campbell DR, Cherian R (2000) Expression of cdc2 and cyclin B1 in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric MALT and MALT lymphoma: relationship to cell death, proliferation, and transformation. Am J Pathol 156:217–225
El-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1993) WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 75:817–825
El-Rifai W, Frierson HF Jr, Harper JC, Powell SM, Knuutila S (2001) Expression profiling of gastric adenocarcinoma using cDNA array. Int J Cancer 92:832–838
Ganoth D, Bornstein G, Ko TK, Larsen B, Tyers M, Pagano M, Hershko A (2001) The cell-cycle regulatory protein Cks1 is required for SCF (Skp2)-mediated ubiquitinylation of p27. Nat Cell Biol 3:321–324
Gostissa M, Hofmann TG, Will H, Del Sal G (2003) Regulation of p53 functions: let’s meet at the nuclear bodies. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:351–357
Haaber J, Abildgaard N, Knudsen LM, Dahl IM, Lodahl M, Thomassen M, Kerndrup GB, Rasmussen T (2008) Myeloma cell expression of 10 candidate genes for osteolytic bone disease. Only overexpression of DKK1 correlates with clinical bone involvement at diagnosis. Br J Haematol 140:25–35
Hansel DE, Dhara S, Huang RC, Ashfaq R, Deasel M, Shimada Y, Bernstein HS, Harmon J, Brock M, Forastiere A, Washington MK, Maitra A, Montgomery E (2005) CDC2/CDK1 expression in esophageal adenocarcinoma and precursor lesions serves as a diagnostic and cancer progression marker and potential novel drug target. Am J Surg Pathol 29:390–399
Hayles J, Aves S, Nurse P (1986a) suc1 is an essential gene involved in both the cell cycle and growth in fission yeast. Embo J 5:3373–3379
Hayles J, Beach D, Durkacz B, Nurse P (1986b) The fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2: isolation of a sequence suc1 that suppresses cdc2 mutant function. Mol Gen Genet 202:291–293
Kawakami K, Enokida H, Tachiwada T, Gotanda T, Tsuneyoshi K, Kubo H, Nishiyama K, Takiguchi M, Nakagawa M, Seki N (2006) Identification of differentially expressed genes in human bladder cancer through genome-wide gene expression profiling. Oncol Rep 16:521–531
Krause K, Wasner M, Reinhard W, Haugwitz U, Dohna CL, Mossner J, Engeland K (2000) The tumour suppressor protein p53 can repress transcription of cyclin B. Nucleic Acids Res 28:4410–4418
Krause K, Haugwitz U, Wasner M, Wiedmann M, Mossner J, Engeland K (2001) Expression of the cell cycle phosphatase cdc25C is down-regulated by the tumor suppressor protein p53 but not by p73. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284:743–750
Lan Y, Zhang Y, Wang J, Lin C, Ittmann MM, Wang F (2008) Aberrant expression of Cks1 and Cks2 contributes to prostate tumorigenesis by promoting proliferation and inhibiting programmed cell death. Int J Cancer 123:543–551
Li M, Lin YM, Hasegawa S, Shimokawa T, Murata K, Kameyama M, Ishikawa O, Katagiri T, Tsunoda T, Nakamura Y, Furukawa Y (2004) Genes associated with liver metastasis of colon cancer, identified by genome-wide cDNA microarray. Int J Oncol 24:305–312
Lin CC, Lin SY, Chung JG, Lin JP, Chen GW, Kao ST (2006) Down-regulation of cyclin B1 and upregulation of Wee1 by berberine promotes entry of leukemia cells into the G2/M-phase of the cell cycle. Anticancer Res 26:1097–1104
Lin HM, Chatterjee A, Lin YH, Anjomshoaa A, Fukuzawa R, McCall JL, Reeve AE (2007) Genome wide expression profiling identifies genes associated with colorectal liver metastasis. Oncol Rep 17:1541–1549
Lu X, Guo J, Hsieh TC (2003) PC-SPES inhibits cell proliferation by modulating p21, cyclins D, E and B and multiple cell cycle-related genes in prostate cancer cells. Cell Cycle 2:59–63
Martinsson-Ahlzen HS, Liberal V, Grunenfelder B, Chaves SR, Spruck CH, Reed SI (2008) Cyclin dependent kinase associated proteins Cks1 and Cks2 are essential during early embryogenesis and for cell cycle progression in somatic cells. Mol Cell Biol 28:5698–5709
Masuda TA, Inoue H, Nishida K, Sonoda H, Yoshikawa Y, Kakeji Y, Utsunomiya T, Mori M (2003) Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 gene expression is associated with poor prognosis in gastric carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 9:5693–5698
Medina R, van der Deen M, Miele-Chamberland A, Xie RL, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS (2007) The HiNF-P/p220NPAT cell cycle signaling pathway controls nonhistone target genes. Cancer Res 67:10334–10342
Pines J (1996) Cell cycle: reaching for a role for the Cks proteins. Curr Biol 6:1399–1402
Rivera A, Mavila A, Bayless KJ, Davis GE, Maxwell SA (2006) Cyclin A1 is a p53-induced gene that mediates apoptosis, G2/M arrest, and mitotic catastrophe in renal, ovarian, and lung carcinoma cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:1425–1439
Rother K, Johne C, Spiesbach K, Haugwitz U, Tschop K, Wasner M, Klein-Hitpass L, Moroy T, Mossner J, Engeland K (2004) Identification of Tcf-4 as a transcriptional target of p53 signaling. Oncogene 23:3376–3384
Rother K, Dengl M, Lorenz J, Tschop K, Kirschner R, Mossner J, Engeland K (2007) Gene expression of cyclin-dependent kinase subunit Cks2 is repressed by the tumor suppressor p53 but not by the related proteins p63 or p73. FEBS Lett 581:1166–1172
Roublevskaia IN, Polevoda BV, Ludlow JW, Haake AR (2000) Induced G2/M arrest and apoptosis in human epidermoid carcinoma cell lines by semisynthetic drug Ukrain. Anticancer Res 20:3163–3167
Scrideli CA, Carlotti CG Jr, Okamoto OK, Andrade VS, Cortez MA, Motta FJ, Lucio-Eterovic AK, Neder L, Rosemberg S, Oba-Shinjo SM, Marie SK, Tone LG (2008) Gene expression profile analysis of primary glioblastomas and non-neoplastic brain tissue: identification of potential target genes by oligonucleotide microarray and real-time quantitative PCR. J Neurooncol 88:281–291
Sherr CJ (1994) G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell 79:551–555
Singh SP, Lipman J, Goldman H, Ellis FH Jr, Aizenman L, Cangi MG, Signoretti S, Chiaur DS, Pagano M, Loda M (1998) Loss or altered subcellular localization of p27 in Barrett’s associated adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 58:1730–1735
Spruck C, Strohmaier H, Watson M, Smith AP, Ryan A, Krek TW, Reed SI (2001) A CDK-independent function of mammalian Cks1: targeting of SCF (Skp2) to the CDK inhibitor p27Kip1. Mol Cell 7:639–650
Spruck CH, de Miguel MP, Smith AP, Ryan A, Stein P, Schultz RM, Lincoln AJ, Donovan PJ, Reed SI (2003) Requirement of Cks2 for the first metaphase/anaphase transition of mammalian meiosis. Science 300:647–650
Stanbrough M, Bubley GJ, Ross K, Golub TR, Rubin MA, Penning TM, Febbo PG, Balk SP (2006) Increased expression of genes converting adrenal androgens to testosterone in androgen independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res 66:2815–2825
Uchikado Y, Inoue H, Haraguchi N, Mimori K, Natsugoe S, Okumura H, Aikou T, Mori M (2006) Gene expression profiling of lymph node metastasis by oligomicroarray analysis using laser microdissection in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol 29:1337–1347
Urbanowicz-Kachnowicz I, Baghdassarian N, Nakache C, Gracia D, Mekki Y, Bryon PA, Ffrench M (1999) ckshs expression is linked to cell proliferation in normal and malignant human lymphoid cells. Int J Cancer 82:98–104
Vousden KH, Lu X (2002) Live or let die: the cell’s response to p53. Nat Rev Cancer 2:594–604
Wiese AH, Auer J, Lassmann S, Nahrig J, Rosenberg R, Hofler H, Ruger R, Werner M (2007) Identification of gene signatures for invasive colorectal tumor cells. Cancer Detect Prev 31:282–295
Wong YF, Cheung TH, Tsao GS, Lo KW, Yim SF, Wang VW, Heung MM, Chan SC, Chan LK, Ho TW, Wong KW, Li C, Guo Y, Chung TK, Smith DI (2006) Genome-wide gene expression profiling of cervical cancer in Hong Kong women by oligonucleotide microarray. Int J Cancer 118:2461–2469
Xu K, Belunis C, Chu W, Weber D, Podlaski F, Huang KS, Reed SI, Vassilev LT (2003) Protein–protein interactions involved in the recognition of p27 by E3 ubiquitin ligase. Biochem J 371:957–964
Yun J, Chae HD, Choy HE, Chung J, Yoo HS, Han MH, Shin DY (1999) p53 negatively regulates cdc2 transcription via the CCAAT-binding NF-Y transcription factor. J Biol Chem 274:29677–29682
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by FG08-12-01 of the 21C Frontier Functional Human Genome Project from the Ministry of Science & Technology in Korea, and by the KRIBB Research Initiative Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Min Ah Kang and Jong-Tae Kim contributed equally to the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, M.A., Kim, JT., Kim, J.H. et al. Upregulation of the cycline kinase subunit CKS2 increases cell proliferation rate in gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 135, 761–769 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-008-0510-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-008-0510-3