Abstract
Purpose
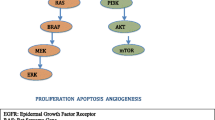
The efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been linked to activating mutations in the EGFR gene. So far these mutations have been extensively characterized in established cell lines. The aim of this study was to determine the effects of EGFR mutations on downstream signaling in human tumor specimens.
Methods
We have looked for mutations of the EGFR gene in specimens of 67 patients with NSCLC and correlated these with EGFR phosphorylation and the activity of its three main downstream signaling cascades Akt, MAPK and Stat3 by immunohistochemistry.
Results
We show that the phosphorylation of tyrosine residues 922 and 1173, but not 1068, are primarily affected by the activating EGFR mutations. Akt activity was significantly higher in patients with EGFR mutations but we found no difference in Stat3 or MAPK phosphorylation. Our results suggest that EGFR mutations not only increase receptor activity, but also alter responses of downstream signaling cascades in human NSCLCs and that these finding differ from results obtained in cell lines.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- Akt:
-
Protein kinase B
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen activated protein kinase
- Stat:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription protein
- TKI:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- PLCγ:
-
Phospholipase C-gamma
- DAG:
-
1,2-Diacylglycerol
- IP3 :
-
Inositol 1,3,5-triphosphate
- Grb:
-
Growth factor receptor-bound protein
- Sos:
-
Son of sevenless
- SH2:
-
Src homology 2
- GDP/GTP:
-
Guanosine di-/tri-phosphate
- Erk:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinases
- PI3-K Ia:
-
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase class Ia
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
References
Alvarez JV, Greulich H, Sellers WR, Meyerson M, Frank DA (2006) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is required for the oncogenic effects of non-small-cell lung cancer-associated mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Res 66:3162–3168. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3757
Atkins D, Reiffen KA, Tegtmeier CL, Winther H, Bonato MS, Storkel S (2004) Immunohistochemical detection of EGFR in paraffin-embedded tumor tissues: variation in staining intensity due to choice of fixative and storage time of tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem 52:893–901. doi:10.1369/jhc.3A6195.2004
Batzer AG, Rotin D, Urena JM, Skolnik EY, Schlessinger J (1994) Hierarchy of binding sites for Grb2 and Shc on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol 14:5192–5201
Bishnupuri KS, Luo Q, Murmu N, Houchen CW, Anant S, Dieckgraefe BK (2006) Reg IV activates the epidermal growth factor receptor/Akt/AP-1 signaling pathway in colon adenocarcinomas. Gastroenterology 130:137–149. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2005.10.001
Brambilla E, Travis WD, Colby TV, Corrin B, Shimosato Y (2001) The new World Health Organization classification of lung tumours. Eur Respir J 18:1059–1068. doi:10.1183/09031936.01.00275301
Brognard J, Clark AS, Ni Y, Dennis PA (2001) Akt/protein kinase B is constitutively active in non-small cell lung cancer cells and promotes cellular survival and resistance to chemotherapy and radiation. Cancer Res 61:3986–3997
Cao Z, Liu L, Van Winkle DM (2005) Met5-enkephalin-induced cardioprotection occurs via transactivation of EGFR and activation of PI3K. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288:H1955–H1964. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00256.2004
Cappuzzo F, Magrini E, Ceresoli GL, Bartolini S, Rossi E, Ludovini V, Gregorc V, Ligorio C, Cancellieri A, Damiani S, Spreafico A, Paties CT et al (2004) Akt phosphorylation and gefitinib efficacy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:1133–1141
Chattopadhyay A, Vecchi M, Ji Q, Mernaugh R, Carpenter G (1999) The role of individual SH2 domains in mediating association of phospholipase C-gamma1 with the activated EGF receptor. J Biol Chem 274:26091–26097. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.37.26091
Cheng JQ, Ruggeri B, Klein WM, Sonoda G, Altomare DA, Watson DK, Testa JR (2001) Amplification of AKT2 in human pancreatic cells and inhibition of AKT2 expression and tumorigenicity by antisense RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:3636–3641. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.8.3636
Ciardiello F, Tortora G (2001) A novel approach in the treatment of cancer: targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. Clin Cancer Res 7:2958–2970
Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, Tamura T, Nakagawa K, Douillard JY, Nishiwaki Y, Vansteenkiste J, Kudoh S, Rischin D, Eek R, Horai T et al (2003) Multi-institutional randomized phase II trial of gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial) [corrected]. J Clin Oncol 21:2237–2246. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.10.038
Haura EB, Zheng Z, Song L, Cantor A, Bepler G (2005) Activated epidermal growth factor receptor-Stat-3 signaling promotes tumor survival in vivo in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:8288–8294. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0827
Heukamp LC, Fischer HP, Schirmacher P, Chen X, Breuhahn K, Nicolay C, Buttner R, Gutgemann I (2006) Podocalyxin-like protein 1 expression in primary hepatic tumours and tumour-like lesions. Histopathology 49:242–247. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2006.02489.x
Hirsch FR, Varella-Garcia M, Bunn PA Jr, Di Maria MV, Veve R, Bremmes RM, Baron AE, Zeng C, Franklin WA (2003) Epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small-cell lung carcinomas: correlation between gene copy number and protein expression and impact on prognosis. J Clin Oncol 21:3798–3807. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.11.069
Hirsch FR, Varella-Garcia M, Bunn PA Jr, Franklin WA, Dziadziuszko R, Thatcher N, Chang A, Parikh P, Pereira JR, Ciuleanu T, von Pawel J, Watkins C et al (2006) Molecular predictors of outcome with gefitinib in a phase III placebo-controlled study in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:5034–5042. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.06.3958
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ (2007) Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin 57:43–66
Johnson GL, Vaillancourt RR (1994) Sequential protein kinase reactions controlling cell growth and differentiation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 6:230–238. doi:10.1016/0955-0674(94)90141-4
Jorissen RN, Walker F, Pouliot N, Garrett TP, Ward CW, Burgess AW (2003) Epidermal growth factor receptor: mechanisms of activation and signalling. Exp Cell Res 284:31–53. doi:10.1016/S0014-4827(02)00098-8
Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS, Lynch TJ Jr, Prager D, Belani CP, Schiller JH, Kelly K, Spiridonidis H, Sandler A, Albain KS, Cella D et al (2003) Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA 290:2149–2158. doi:10.1001/jama.290.16.2149
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, Louis DN, Christiani DC et al (2004) Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 350:2129–2139. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa040938
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, Naoki K, Sasaki H et al (2004) EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 304:1497–1500. doi:10.1126/science.1099314
Parra HS, Cavina R, Latteri F, Zucali PA, Campagnoli E, Morenghi E, Grimaldi GC, Roncalli M, Santoro A (2004) Analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor expression as a predictive factor for response to gefitinib (‘Iressa’, ZD1839) in non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 91:208–212
Rotin D, Margolis B, Mohammadi M, Daly RJ, Daum G, Li N, Fischer EH, Burgess WH, Ullrich A, Schlessinger J (1992) SH2 domains prevent tyrosine dephosphorylation of the EGF receptor: identification of Tyr992 as the high-affinity binding site for SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma. Embo J 11:559–567
Selvaggi G, Novello S, Torri V, Leonardo E, De Giuli P, Borasio P, Mossetti C, Ardissone F, Lausi P, Scagliotti GV (2004) Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression correlates with a poor prognosis in completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 15:28–32. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdh011
Sobol RE, Astarita RW, Hofeditz C, Masui H, Fairshter R, Royston I, Mendelsohn J (1987) Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in human lung carcinomas defined by a monoclonal antibody. J Natl Cancer Inst 79:403–407
Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA, Settleman J (2004) Gefitinib-sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science 305:1163–1167. doi:10.1126/science.1101637
Stoscheck CM, King LE Jr (1986) Role of epidermal growth factor in carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 46:1030–1037
Sturla LM, Amorino G, Alexander MS, Mikkelsen RB, Valerie K, Schmidt-Ullrichr RK (2005) Requirement of Tyr-992 and Tyr-1173 in phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by ionizing radiation and modulation by SHP2. J Biol Chem 280:14597–14604. doi:10.1074/jbc.M413287200
Vasko V, Saji M, Hardy E, Kruhlak M, Larin A, Savchenko V, Miyakawa M, Isozaki O, Murakami H, Tsushima T, Burman KD, De Micco C et al (2004) Akt activation and localisation correlate with tumour invasion and oncogene expression in thyroid cancer. J Med Genet 41:161–170. doi:10.1136/jmg.2003.015339
Vega QC, Cochet C, Filhol O, Chang CP, Rhee SG, Gill GN (1992) A site of tyrosine phosphorylation in the C terminus of the epidermal growth factor receptor is required to activate phospholipase C. Mol Cell Biol 12:128–135
Yuan ZQ, Sun M, Feldman RI, Wang G, Ma X, Jiang C, Coppola D, Nicosia SV, Cheng JQ (2000) Frequent activation of AKT2 and induction of apoptosis by inhibition of phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase/Akt pathway in human ovarian cancer. Oncogene 19:2324–2330. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203598
Acknowledgments
We thank Ellen Paggen for technical help with DNA sequencing and Christiane Esch for support with the immunohistochemistry. L.C.H. was supported by the BONFOR research council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure 6
Percent of tumors staining positive in EGFR, P-Tyr-992, P-Tyr-1068, P-Tyr-1173, P-Stat3, P-Akt and P-MAPK immunohistochemistry with regard to specific EGFR mutations. The EGFR subgroups were compared to EGFR-WT samples and the P-values are illustrated. The EGFR-M group and the EGFR-M subgroups display the same pattern in receptor phosphorylation and activity of downstream signaling cascades. (EPS 438 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zimmer, S., Kahl, P., Buhl, T.M. et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in non-small cell lung cancer influence downstream Akt, MAPK and Stat3 signaling. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 135, 723–730 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-008-0509-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-008-0509-9