Abstract
Introduction
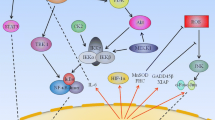
Nuclear factor-κB pathway (NF-κB) is activated in many breast cancers. NF-кB has interactions with other pathways such as the nerve growth factor (NGF) pathway, which is involved in the survival and proliferation of breast cancer cells. NGF treatment of breast cancer cells activates NF-κB resulting in the inhibition of ceramide-induced apoptosis. NGF effects on apoptosis and cell proliferation are mediated through p75NTR and p140TrkA receptors, respectively. In this study we investigate the NGF/NF-κB pathway as a therapeutic target in breast cancer.
Results
We demonstrate that p75NTR inhibitor Pep5, p140TrkA inhibitor K-252a, and NF-κB inhibitor BAY11-7085 have pro-apoptotic and anti-proliferation activities in breast cancer cells. We also show a synergy in combining the NGF receptor inhibitors with the conventional breast cancer treatments tamoxifen and taxol.
Conclusion
These data suggest that NGF/NF-κB pathway is a potential therapeutic target in breast cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriaenssens E, Vanhecke E, Saule P et al (2008) Nerve growth factor is a potential therapeutic target in breast cancer. Cancer Res 68(2):346–351. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1183
Biswas DK, Shi Q, Baily S et al (2004) NF-B activation in human breast cancer specimens and its role in cell proliferation and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(27):10137–10142. doi:10.1073/pnas.0403621101
Boehm JS, Zhao JJ, Yao J et al (2007) Integrative genomic approaches identify IKBKE as a breast cancer oncogene. Cell 129(6):1065–1079. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.03.052
de Graffenried LA, Chandrasekar B, Friedrichs WE et al (2004) NF-kappa B inhibition markedly enhances sensitivity of resistant breast cancer tumor cells to tamoxifen. Ann Oncol 15(6):885–890
Descamps S, Toillon RA, Adriaenssens E et al (2001) Nerve growth factor stimulates proliferation and survival of human breast cancer cells through two distinct signalling pathways. J Biol Chem 276(21):17864–17870
Dolle L, Adriaenssens E, El Yazidi-Belkoura I et al (2004) Nerve growth factor receptors and signaling in breast cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 4(6):463–470
Dolle L, Oliveira MJ, Bruyneel E et al (2005) Nerve growth factor mediates its pro-invasive effect in parallel with the release of a soluble E-cadherin fragment from breast cancer MCF-7/AZ cells. J Dairy Res 72 Spec No:20–26
El Yazidi-Belkoura I, Adriaenssens E, Dolle L et al (2003) Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated death domain protein is involved in the neurotrophin receptor-mediated antiapoptotic activity of nerve growth factor in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 278(19):16952–16956
Naderi A, Teschendorff AE, Beigel J et al (2007) BEX2 is overexpressed in a subset of primary breast cancers and mediates nerve growth factor/nuclear factor-kappaB inhibition of apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 67(14):6725–6736
Oh I, Ozaki K, Sato K et al (2007) Interferon-gamma and NF-kappaB mediate nitric oxide production by mesenchymal stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 335(4):956–962
Pratt MA, Bishop TE, White D et al (2003) Estrogen withdrawal-induced NF-kappaB activity and bcl-3 expression in breast cancer cells: roles in growth and hormone independence. Mol Cell Biol 19:6887–6900
Reddel RR, Sutherland RL (1984) Tamoxifen stimulation of human breast cancer cell proliferation in vitro: a possible model for tamoxifen tumour flare. Euro J Cancer Clin Oncol 20(11):1419–1424
Riggins RB, Zwart A, Nehra R et al (2005) The nuclear factor kappa B inhibitor parthenolide restores ICI 182, 780 (Faslodex; fulvestrant)-induced apoptosis in antiestrogen-resistant breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 4(1):33–41
Singh S, Shi Q, Bailey ST et al (2007) Nuclear factor-B activation: a molecular therapeutic target for estrogen receptor–negative and epidermal growth factor receptor family receptor–positive human breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 6(7):1973–1982
Yamashita T, Tohyama M (2003) The p75 receptor acts as a displacement factor that releases Rho from Rho-GDI. Nat Neurosci 6(5):461–467
Acknowledgements
This study is funded by Fund & Friends of Addenbrookes Charity and Diamantina Institute for Cancer, Immunology and Metabolic Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naderi, A., Hughes-Davies, L. Nerve growth factor/nuclear factor-κB pathway as a therapeutic target in breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 135, 211–216 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-008-0455-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-008-0455-6