Abstract
Purpose
Primary chemotherapy brings the opportunity for an early and accurate assessment of response and offers an ideal model to search for new predictors of response. HER-2/neu is one of the most studied genes for this purpose.
Patients and methods
Her-2/neu was tested in a non-randomized series of 300 patients with operable breast carcinomas treated with primary CMF. Response was assessed by mammography. Disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) were calculated after a mean follow-up of 116 months. Statistical analysis was performed to study the association between HER-2/neu status and response to CMF.
Results
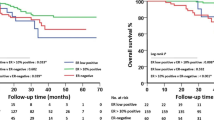
Overexpression/amplification was found in 23.66% cases. Univariate analysis showed that response was similar in HER-2/neu positive and negative tumors (51.38 vs. 47.36%, P = 0.6). Triple negative tumors (ER, PR and HER-2/neu negative) presented the highest response rate (64.9%). By multivariate analysis, response was significantly correlated to higher nuclear grade and negative estrogen receptor status (P = 0.02 and 0.007, respectively). Patients with HER-2/neu positive tumors presented shorter survival rates (P = 0.06). Patients with response to CMF showed a better survival over non-responders independent of Her-2/neu status. Patients with the combination of response to CMF and Her-2/neu negative tumors presented the best outcome. On the other hand, the association of no response to CMF and positive Her-2/neu score was statistically related to poor DFS and OS.
Conclusions
CMF indication is independent of Her-2/neu status.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allred DC, Clark GM, Tandon AK et al (1992) HER-2/neu in node-negative breast cancer: prognostic significance of overexpression influenced by the presence of in situ carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 10:599–605
Bargmann CI, Hung MC, Weinberg (1986) The neu oncogene encodes an epidermal growth factor receptor-related protein. Nature 319:226–230
Baselga J, Seidman AD, Rosen PP et al (1997) HER2 overexpression and paclitaxel sensitivity in breast cancer: therapeutic implications. Oncology 11:43–48
Bonadonna G, Valagussa P, Brambilla C et al (1998) Primary chemotherapy in operable breast cancer: eight-year experience at the Milan Cancer Institute. J Clin Oncol 16:93–100
Buchholz TA, Huang EH, Berry D et al (2004) HER2/neu positive disease does not increase risk of locorregional recurrence for patients treated with neoadjuvant doxorrubicin-based chemotherapy, mastectomy, and radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:1337–1342
Falo C, Moreno A, Lloveras B et al (2003) Algorithm for the diagnosis of HER-2/neu status in breast infiltrating carcinomas. Am J Clinical Oncol 26:465–470
Falo C, Moreno A, Benito E et al (2005) Primary chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and 5-fluorouracil in operable breast carcinoma. Cancer 12:657–663
Fisher B, Bryant J, Wolmark N et al (1998) Effect of preoperative chemotherapy on the outcome of women with operable breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 16:2672–2685
Goldhirsch A, Glick JH, Gelber RD et al (2005) Meeting Highlights: International Expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2005. Ann of Oncol 16:1569–1583
Gusterson BA, Gelber RD, Goldhirsch A et al (1992) Prognostic importance of c-erbB-2 expression in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 10:1049–1056
Haffty BG, Brown F, Carter D et al (1996) Evaluation of HER-2/neu oncoprotein expression as a prognostic indicator of local recurrence in conservatively treated breast cancer: a case-control study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 35:751–757
Konecny GE, Thomssen Ch, Lück HJ et al (2004) HER-2/neu gene amplification and response to paclitaxel in patients with metastatic breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:1141–1151
Martin M, Pienkowski T, Mackey J et al (2005) Adjuvant docetaxel for node-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med 352:2302–2313
Ménard S, Valagussa P, Pilotti S et al (2001) Response to cyclophosphamide, methrotrexate and fluorouracil in lymph node-positive breast cancer according to HER-2 overexpression and other tumor biologic variables. J Clin Oncol 19:329–335
Miles DW, Harris WH, Gillett CE et al (1999) Effect of c-erbB(2) and estrogen receptor status on survival of women with primary breast cancer treated with adjuvant cyclophosphamide/methotrexate/fluorouracil. Int J Cancer 84:354–359
Moreno A, Lloveras B, Figueras A et al (1997) Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast: correlation between histologic classifications and biologic markers. Mod Pathol 10(11):1088–1092
Moreno A, Escobedo A, Benito E, Serra JM, Guma A, Riu F (2002) Pathologic changes related to CMF primary chemotherapy in breast cancer. Pathological evaluation of response predicts clinical outcome. Breast Cancer Res Treat 75(2):119–125
Muss HB, Thor AD, Berry DA et al (1994) C-erbB-2 expression and response to adjuvant therapy in women with node-positive early breast cancer. N Engl J Med 330:1260–1266
Paik S, Hazan R, Fisher ER et al (1990) Pathologic findings from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project: prognostic significance of c-erbB-2 protein overexpression in primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 8:103–112
Paik S, Bryant J, Tan-Chiu E et al (2000) HER2 and choice of adjuvant chemotherapy for invasive breast cancer: National Surgical Adjuvant Breast And Bowel Project Protocol B-15. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:1991–1998
Reed W, Hannisdal E, Boehler PJ et al (2000) The prognostic value of p53 and c-erbB-2 immunostaining is overrated for patients with lymph node negative breast carcinoma: a multivariate analysis of prognostic factors in 613 patients with a follow-up of 14–30 years. Cancer 88:804–813
Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG et al (1987) Human breast cancer. Correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 235:177–182
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R et al (2001) Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10869–10874
Van de Vijver MJ, Peterse JL, Mooi WJ et al (1988) Neu-protein overexpression in breast cancer. Association with comedo-type ductal carcinoma in situ and limited prognostic value in stage II breast cancer. N Engl J Med 319:1239–1245
van’t Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ et al (2002) Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature (Lond) 415:530–536
Wright C, Nicholson S, Angus B et al (1992) Relationship between c-erB-2 protein product expression and response to endocrine therapy in advanced breast cancer. Br J Cancer 65:118–121
Yang W, Klos Ks, Zhou X et al (2003) ErbB2 overexpression in human breast carcinoma is correlated with p21Cip1 up-regulation and tyrosine-15 hyperphosphorilation of p34Cdc2: poor responsiveness to chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and 5-fluorouracil is associated with ErbB2 overexpression and with p21Cip1 overexpression. Cancer 98:1123–1130
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
We have not received any financial support for the development of this study. The authors thank Edurne Arriola for the assistance in the correction of the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Falo, C., Moreno, A., Varela, M. et al. HER-2/neu status and response to CMF: retrospective study in a series of operable breast cancer treated with primary CMF chemotherapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 133, 423–429 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-006-0176-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-006-0176-7