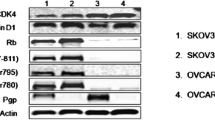
Abstract
Purpose: A low proliferating fraction in solid tumors limits the effectiveness of cell-cycle-dependent chemotherapeutic agents. To understand the molecular basis of such resistance, we examined the expression of the cyclin-dependent kinases inhibitor p27, and relationship with drug resistance and P-gp expression in ovarian cancer multicellular spheroids. Methods: We cultured ovarian cancer cells (A2780 and CAOV3) as multicellular spheroids and examined the expression of p27 and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) by western blot, flow cytometry and confocal. We also analyzed the cell-cycle distribution by flow cytometry. In addition, trypan blue exclusion testing and cell apoptosis analysis were used to detect the sensitivity to Taxol. Results: When transferred from monolayer to three-dimensional culture, a consistent upregulation of p27 protein and P-gp protein was observed in ovarian cancer cell lines. Compared with monolayer cells, there was a significant increase of G0-G1 phase cells and decrease of S and G2-M phase cells in spheroid cells. Aggregates of cells showed higher cell viability than monolayer cells. Antisense oligodeoxynucleotide (ASON) -mediated downregulation of p27 reduced intercellular adhesion, increased cell proliferation, downregulated P-gp expression and sensitized cells to Taxol. Conclusions: Our results implicate that p27 serves as a regulator of drug resistance in ovarian tumors. ASON-mediated alteration of p27 reverses resistance of ovarian cancer to anticancer agents that are associated with increased sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agents.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MCS:
-
Multicellular spheroids
- ASON:
-
Antisense oligodeoxynucleotide
- SON:
-
Sense oligodeoxynucleotide
- SON/monolayer:
-
Monolayer cells treated with SON
- ASON/monolayer:
-
Monolayer cells treated with ASON
- SON/MCS:
-
Spheroid cells treated with SON
- ASON/MCS:
-
Spheroid cells treated with ASON
- P-gp:
-
P-glycoprotein
- MDR:
-
Multidrug resistance
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
References
Alkarain A, Slingerland J (2004) Deregulation of p27 by oncogenic signaling and its prognostic significance in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 6:13–21
Arguello F, Alexander M, Sterry JA, Tudor G, Smith EM, Kalavar NT, Greene JF, Koss W, Morgan CD, Stinson SF, Siford TJ, Alvord WG, Klabansky RL, Sausville EA (1998) Flavopiridol induces apoptosis of normal lymphoid cells, causes immunosuppression, and has potent antitumor activity in vivo against human leukemia and lymphoma xenografts. Blood 91:1482–2409
Ashton AW, Watanabe G, Albanese C, Harrington EO, Ware JA, Pestell RG (1999) Protein kinase C and inhibition of S-phase transition in capillary endothelial cells involves the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27. J Biol Chem 274:20805–20811
Barnes A, Pinder SE, Bell JA, Paish EC, Wencyk PM, Robertson JF, Elston CW, Ellis IO (2003) Expression of p27kip1 in breast cancer and its prognostic significance. J Pathol 201:451–459
Drewinko B, Patchen M, Yang LY, Barlogie B (1981) Differential killing efficacy of twenty antitumor drugs on proliferating and nonproliferating human tumor cells. Cancer Res 41:2328–2333
Dusek J, Scudla V, Kolar Z, Rihakova P, Hlobilova A (2000) Biological characteristics of multiple myeloma. Cesk Patol 36:111–115
Fero ML, Rivkin M, Tasch M, Porter P, Carow CE, Fripo E, Polyak K, Tsai LH, Broudy V, Perlmutter RM, Kaushansky K, Roberts JM (1996) A syndrome of multiorgan hyperplasia with features of didactism, tumorigenesis, and female sterility in p27(Kip1)-deficient mice. Cell 85:733–744
Jirstrom K, Ringberg A, Ferno M, Anagnostaki L, Landberg G (2003) Tissue microarray analyses of G1/S-regulatory proteins in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast indicate that low cyclin D1 is associated with local recurrence. Brit J Cancer 89:1920–1926
Kiyokawa H, Koff A (1998) Roles of cyclin- dependent kinase inhibitors: lessons from knockout mice. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 227:105–120
LaRue KE, Khalil M, Freyer JP (2004) Microenvironmental regulation of proliferation in multicellular spheroids is mediated through differential expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res 64:1621–1631
Martin C, Walker J, Rothnie A, Callaghan R (2003) The expression of P-glycoprotein does influence the distribution of novel fluorescent compounds in solid tumour models. Brit J Cancer 89:1581–1589
Masciullo V, Sgambato A, Pacilio C, Pucci B, Farrandina G, Juan P, Arnaldo C, Achille C, Salvatore M, Giovanni S, Antonio G (1999) Frequent loss of expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 59:3790–3794
Mengst L, Dulic V, Slingerland JM, Lees E, Reed SI (1994) A cell cycle- regulated inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci 91:5291–5295
Morgan DO (1995) Principies of CDK regulation. Nature 374:131–134
Nakayama K (1996) Mice lacking p27 display increased body size, multiple-organ hyperplasia, retinal dysplasia, and pituitary tumors. Cell 85:707–720
Nho RS, Sheaff RJ (2003) p27kip1 contributions to cancer. Prog Cell Cycle Res 5:249–259
Peng JP, Liu LT, Chang HC, Hung WC (2003) Enhancement of chemotherapeutic drug-induced apoptosis by a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor in hypopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 201:157–163
Polyak K, Kato J, Solomon MJ, Sherr CJ, Massague J, Roberts JM, Koff A (1994) p27kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitior, links transforming growth factor-βand contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Genes Dev 8:9–22
Ricardo VL, Lori A, Erickson, LJ, Elzbieta K, Xiang Q, John CC, Bernd WS (1999) p27: A multifunctional cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with prognostic significance in humen cancers. Am J Pathol 154:313–323
Rivard N, Boucher MJ, Asselin C, L’Allemain G (1999) MAP kinase cascade is required for p27 downregulation and S phase entry in fibroblasts and epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 277:652–654
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM (1999) CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev 13:1501–1512
Shiohara M (1994) Absence of WAF1 mutations in a variety of human malignancies. Blood 84:3781–3784
Sougioultzis S, Foukas PG, Tzivras M, Kourtessas D, Gorgoulis VG, Davaris P, Archimandritis AJ (2003) Alterations in the proliferating compartment of gastric mucosa during Helicobacter pylori infection: the putative role of epithelial cells expressing p27(kip1). Mod Pathol 16:1076–1085
Spirin KS (1996) p27/Kip1 mutation found in breast cancer. Cancer Res 56:2400–2404
St Croix B, Florenes VA, Rak JW, Flanagan M, Bhattacharya N, Silingerland JM, Kerbel RS (1996) Impact of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 on resistance of tumor cells to anticancer agents. Nature Med 2:1204–1210
Sunters A, Thomas DP, Yeudall WA, Grigoriadis AE (2004) Accelerated cell cycle progression in osteoblasts overexpressing the c-fos proto-oncogene: induction of cyclin A and enhanced CDK2 activity. J Biol Chem 279:9882–9891
Sutherland LaRue KE, Khalil M, Freyer JP (2004) Microenvironmental regulation of proliferation in multicellular spheroids is mediated through differential expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res 64:1621–1631
Tannock IF (1994) Principles of cell proliferation: cell kinetics, in current cancer therapeutics. Princeton Academic Press, Princeton New Jersey, pp 3–13
Tatjana V, Achenbach M, Emily PS (2000) Synergistic antitumor effect of chemotherapy and antisense-mediated ablation of the cell cycle inhibitor p27. Clin Cancer Res 6:3006–3014
Walker J, Martin C, Callaghan R (2004) Inhibition of P-glycoprotein function by XR9576 in a solid tumour model can restore anticancer drug efficacy. Eur J Cancer 40:594–605
Wartenberg M, Fischer K, Hescheler J, Sauer H, Redox (2000) Regulation of p-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in multicellular prostate tumor spheroids. Int J Cancer 85:267–274
Wartenberg M, Fischer K, Hescheler J, Sauer H (2002) Modulation of intrinsic P-glycoprotein expression in multicellular prostate tumor spheroids by cell cycle inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta 1589:49–62
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Science Foundation of China (No. 39870765) and ‘973’ program of China (No. 2002CB513100)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hui Xing and Shixuan Wang have contributed equally in this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, H., Wang, S., Hu, K. et al. Effect of the cyclin-dependent kinases inhibitor p27 on resistance of ovarian cancer multicellular spheroids to anticancer chemotherapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 131, 511–519 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-005-0677-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-005-0677-9