Abstract
Purpose
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) represents the prototype of an angiogenic tumor. Recently, the continuous low-dose scheduling of chemotherapeutic drugs in combination with an inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) has been suggested as a novel anti-angiogenic approach. The aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and activity of continuous low-dose temozolomide (TMZ) plus the COX-2 inhibitor rofecoxib in patients with newly diagnosed GBM.
Methods
In vitro, endothelial cells were characterized by a tenfold higher sensitivity to TMZ than glioma cells. Consequently, a subgroup of patients with incompletely resected GBM (n=13) was divided into three groups aiming at a dose escalation to 1/10 of the daily MTD for TMZ: (A) TMZ 10 mg/m2 every third day and rofecoxib 25 mg/d; (B) TMZ 10 mg/m2/d and rofecoxib 25 mg/d; (C) TMZ 5 mg/m2 twice a day and rofecoxib 12.5 mg twice a day. COX-2, VEGF, VEGF Receptor-2, and CD34 were assessed immunohistochemically, in the clinical setting.
Results
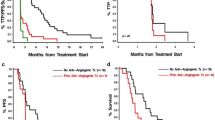
The mean follow-up period was 15 months. We observed no severe toxicity attributable to the therapy. Quality of life was not impaired. For the whole study population, median time to progression and overall survival were 8 months and 16 months, respectively. Immunohistochemistry suggested that tumors with higher vessel densities were characterized by a significantly better control than those with lower vessel densities.
Conclusions
Continuous low-dose TMZ plus rofecoxib is feasible, safe, and maintains good quality of life. This study is indicative of an anti-angiogenic efficacy of continuous low-dose TMZ plus rofecoxib in GBMs, especially in those tumors that are characterized by a high angiogenic activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adini A, Kornaga T, Firoozbakht F, Benjamin LE (2002) Placental growth factor is a survival factor for tumor endothelial cells and macrophages. Cancer Res 62:2749–2752
Bello L, Carrabba G, Giussani C, Lucini V, Cerutti F, Scaglione F, Landre J, Pluderi M, Tomei G, Villani R, Carroll RS, Black PM, Bikfalvi A (2001) Low-dose chemotherapy combined with an antiangiogenic drug reduces human glioma growth in vivo. Cancer Res 61:7501–7506
Benjamin LE, Golijanin D, Itin A, Pode D, Keshet E (1999) Selective ablation of immature blood vessels in established human tumors follows vascular endothelial growth factor withdrawal. J Clin Invest 103:159–165
Bernsen HJ, van der Kogel AJ (1999) Antiangiogenic therapy in brain tumor models. J Neurooncol 45:247–255
Bocci G, Nicolaou KC, Kerbel RS (2002) Protracted low-dose effects on human endothelial cell proliferation and survival in vitro reveal a selective antiangiogenic window for various chemotherapeutic drugs. Cancer Res 62:6938–6943
Brada M, Hoang-Xuan K, Rampling R, Dietrich PY, Dirix LY, Macdonald D, Heimans JJ, Zonnenberg BA, Bravo-Marques JM, Henriksson R, Stupp R, Yue N, Bruner J, Dugan M, Rao S, Zaknoen S (2001) Multicenter phase II trial of temozolomide in patients with glioblastoma multiforme at first relapse. Ann Oncol 12:259–266
Brem S, Tsanaclis AM, Gately S, Gross JL, Herblin WF (1992) Immunolocalization of basic fibroblast growth factor to the microvasculature of human brain tumors. Cancer 70:2673–2680
Brock CS, Newlands ES, Wedge SR, Bower M, Evans H, Colquhoun I, Roddie M, Glaser M, Brampton MH, Rustin GJ (1998) Phase I trial of temozolomide using an extended continuous oral schedule. Cancer Res 58:4363–4367
Browder T, Butterfield CE, Kraling BM, Shi B, Marshall B, O’Reilly MS, Folkman J (2000) Antiangiogenic scheduling of chemotherapy improves efficacy against experimental drug-resistant cancer. Cancer Res 60:1878–1886
Burger PC, Dubois PJ, Schold SC Jr, Smith KR Jr, Odom GL, Crafts DC, Giangaspero F (1983) Computerized tomographic and pathologic studies of the untreated, quiescent, and recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurosurg 58:159–169
Clements MK, Jones CB, Cumming M, Daoud SS (1999) Antiangiogenic potential of camptothecin and topotecan. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 44:411–416
Crombet-Ramos T, Rak J, Perez R, Viloria-Petit A (2002) Antiproliferative, antiangiogenic and proapoptotic activity of h-R3: a humanized anti-EGFR antibody. Int J Cancer 101:567–575
Curran WJ Jr, Scott CB, Horton J, Nelson JS, Weinstein AS, Fischbach AJ, Chang CH, Rotman M, Asbell SO, Krisch RE (1993) Recursive partitioning analysis of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group malignant glioma trials. J Natl Cancer Inst 85:704–710
Daniel TO, Liu H, Morrow JD, Crews BC, Marnett LJ (1999) Thromboxane A2 is a mediator of cyclooxygenase-2-dependent endothelial migration and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 59:4574–4577
Deininger MH, Weller M, Streffer J, Mittelbronn M, Meyermann R (1999) Patterns of cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 expression in human gliomas in vivo. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 98:240–244
Dicker AP (2003) COX-2 Inhibitors and cancer therapeutics: potential roles for inhibitors of COX-2 in combination with cytotoxic therapy: reports from a symposium held in conjunction with the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group June 2001 meeting. Am J Clin Oncol 26:S46–47
Dormond O, Foletti A, Paroz C, Ruegg C (2001) NSAIDs inhibit alpha V beta 3 integrin-mediated and Cdc42/Rac-dependent endothelial-cell spreading, migration and angiogenesis. Nat Med 7:1041–1047
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285:1182–1186
Fujiwaki R, Iida K, Kanasaki H, Ozaki T, Hata K, Miyazaki K (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in endometrial cancer: correlation with microvessel count and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and thymidine phosphorylase. Hum Pathol 33:213–219
Gallo O, Masini E, Bianchi B, Bruschini L, Paglierani M, Franchi A (2002) Prognostic significance of cyclooxygenase-2 pathway and angiogenesis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Hum Pathol 33:708–714
Gately S, Kerbel R (2001) Antiangiogenic scheduling of lower dose cancer chemotherapy. Cancer J 7:427–436
Gately S, Kerbel R (2003) Therapeutic potential of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in the management of tumor angiogenesis. Prog Exp Tumor Res 37:179–192
Gorski DH, Beckett MA, Jaskowiak NT, Calvin DP, Mauceri HJ, Salloum RM, Seetharam S, Koons A, Hari DM, Kufe DW, Weichselbaum RR (1999) Blockage of the vascular endothelial growth factor stress response increases the antitumor effects of ionizing radiation. Cancer Res 59:3374–3378
Grobholz R, Bohrer MH, Siegsmund M, Junemann KP, Bleyl U, Woenckhaus M (2000) Correlation between neovascularisation and neuroendocrine differentiation in prostatic carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract 196:277–284
Hernandez GL, Volpert OV, Iniguez MA, Lorenzo E, Martinez-Martinez S, Grau R, Fresno M, Redondo JM (2001) Selective inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated angiogenesis by cyclosporin A: roles of the nuclear factor of activated T cells and cyclooxygenase 2. J Exp Med 193:607–620
Hida T, Kozaki K, Muramatsu H, Masuda A, Shimizu S, Mitsudomi T, Sugiura T, Ogawa M, Takahashi T (2000) Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor induces apoptosis and enhances cytotoxicity of various anticancer agents in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 6:2006–2011
Jaffe EA, Nachman RL, Becker CG, Minick CR (1973) Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest 52:2745–2756
Jones MK, Wang H, Peskar BM, Levin E, Itani RM, Sarfeh IJ, Tarnawski AS (1999) Inhibition of angiogenesis by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: insight into mechanisms and implications for cancer growth and ulcer healing. Nat Med 5:1418–1423
Kakeji Y, Teicher BA (1997) Preclinical studies of the combination of angiogenic inhibitors with cytotoxic agents. Invest New Drugs 15:39–48
Kerbel RS, Klement G, Pritchard KI, Kamen B (2002) Continuous low-dose anti-angiogenic/metronomic chemotherapy: from the research laboratory into the oncology clinic. Ann Oncol 13:12–15
Klement G, Baruchel S, Rak J, Man S, Clark K, Hicklin DJ, Bohlen P, Kerbel RS (2000) Continuous low-dose therapy with vinblastine and VEGF receptor-2 antibody induces sustained tumor regression without overt toxicity. J Clin Invest 105:R15–24
Klement G, Huang P, Mayer B, Green SK, Man S, Bohlen P, Hicklin D, Kerbel RS (2002) Differences in therapeutic indexes of combination metronomic chemotherapy and an anti-VEGFR-2 antibody in multidrug-resistant human breast cancer xenografts. Clin Cancer Res 8:221–232
Kunkel P, Ulbricht U, Bohlen P, Brockmann MA, Fillbrandt R, Stavrou D, Westphal M, Lamszus K (2001) Inhibition of glioma angiogenesis and growth in vivo by systemic treatment with a monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. Cancer Res 61:6624–6628
Kurzen H, Schmitt S, Naher H, Mohler T (2003) Inhibition of angiogenesis by non-toxic doses of temozolomide. Anticancer Drugs 14:515–522
Laird AD, Vajkoczy P, Shawver LK, Thurnher A, Liang C, Mohammadi M, Schlessinger J, Ullrich A, Hubbard SR, Blake RA, Fong TA, Strawn LM, Sun L, Tang C, Hawtin R, Tang F, Shenoy N, Hirth KP, McMahon G, Cherrington JM (2000) SU6668 is a potent antiangiogenic and antitumor agent that induces regression of established tumors. Cancer Res 60:4152–4160
Laird AD, Christensen JG, Li G, Carver J, Smith K, Xin X, Moss KG, Louie SG, Mendel DB, Cherrington JM (2002) SU6668 inhibits Flk-1/KDR and PDGFRbeta in vivo, resulting in rapid apoptosis of tumor vasculature and tumor regression in mice. Faseb J 16:681–690
Leon SP, Folkerth RD, Black PM (1996) Microvessel density is a prognostic indicator for patients with astroglial brain tumors. Cancer 77:362–372
Man S, Bocci G, Francia G, Green SK, Jothy S, Hanahan D, Bohlen P, Hicklin DJ, Bergers G, Kerbel RS (2002) Antitumor effects in mice of low-dose (metronomic) cyclophosphamide administered continuously through the drinking water. Cancer Res 62:2731–2735
Masferrer JL, Leahy KM, Koki AT, Zweifel BS, Settle SL, Woerner BM, Edwards DA, Flickinger AG, Moore RJ, Seibert K (2000) Antiangiogenic and antitumor activities of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Cancer Res 60:1306–1311
Miller KD, Sweeney CJ, Sledge GW Jr (2001) Redefining the target: chemotherapeutics as antiangiogenics. J Clin Oncol 19:1195–1206
Pennacchietti S, Michieli P, Galluzzo M, Mazzone M, Giordano S, Comoglio PM (2003) Hypoxia promotes invasive growth by transcriptional activation of the met protooncogene. Cancer Cell 3:347–361
Plate KH, Risau W (1995) Angiogenesis in malignant gliomas. Glia 15:339–347
Polverini PJ, Novak RF (1986) Inhibition of angiogenesis by the antineoplastic agents mitoxantrone and bisantrene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 140:901–907
Ruegg C, Zaric J, Stupp R (2003) Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and COX-2 inhibitors as anti-cancer therapeutics: hypes, hopes and reality. Ann Med 35:476–487
Saleh M, Stacker SA, Wilks AF (1996) Inhibition of growth of C6 glioma cells in vivo by expression of antisense vascular endothelial growth factor sequence. Cancer Res 56:393–401
Schneider F, Meziani F, Chartier C, Alt M, Jaeger A (2002) Fatal allergic vasculitis associated with celecoxib. Lancet 359:852–853
Stupp R, Mason WP, Van Den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn A, Brandes A, Cairncross G, Lacombe D, Mirimanoff RO (2004) Concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide (TMZ) and radiotherapy (RT) for newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). Conclusive results of a randomized phase III trial by the EORTC Brain & RT groups and NCIC Clinical Trials Group. Presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Society for Clinical Oncology 2004 (assessed July 14 2004, through http://www.asco.org/ac/1,1003,_12-002511-00_18-0026-00_19-009670-00_21-00106,00.asp)
Teicher BA, Sotomayor EA, Huang ZD (1992) Antiangiogenic agents potentiate cytotoxic cancer therapies against primary and metastatic disease. Cancer Res 52:6702–6704
Tortora G, Caputo R, Damiano V, Melisi D, Bianco R, Fontanini G, Veneziani BM, De Placido S, Bianco AR, Ciardiello F (2003) Combination of a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 and protein kinase A antisense causes cooperative antitumor and antiangiogenic effect. Clin Cancer Res 9:1566–1572
Vajkoczy P, Menger MD, Vollmar B, Schilling L, Schmiedek P, Hirth KP, Ullrich A, Fong TA (1999) Inhibition of tumor growth, angiogenesis, and microcirculation by the novel Flk-1 inhibitor SU5416 as assessed by intravital multi-fluorescence videomicroscopy. Neoplasia 1:31–41
Weller M, Muller B, Koch R, Bamberg M, Krauseneck P, Neuro-Oncology Working Group of the German Cancer Society (2003) Neuro-Oncology Working Group 01 trial of nimustine plus teniposide versus nimustine plus cytarabine chemotherapy in addition to involved-field radiotherapy in the first-line treatment of malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 21:3276–3284
Yung WK, Prados MD, Yaya-Tur R, Rosenfeld SS, Brada M, Friedman HS, Albright R, Olson J, Chang SM, O’Neill AM, Friedman AH, Bruner J, Yue N, Dugan M, Zaknoen S, Levin VA (1999) Multicenter phase II trial of temozolomide in patients with anaplastic astrocytoma or anaplastic oligoastrocytoma at first relapse. Temodal Brain Tumor Group. J Clin Oncol 17:2762–2771
Yung WK, Albright RE, Olson J, Fredericks R, Fink K, Prados MD, Brada M, Spence A, Hohl RJ, Shapiro W, Glantz M, Greenberg H, Selker RG, Vick NA, Rampling R, Friedman H, Phillips P, Bruner J, Yue N, Osoba D, Zaknoen S, Levin VA (2000) A phase II study of temozolomide vs procarbazine in patients with glioblastoma multiforme at first relapse. Br J Cancer 83:588–593
Acknowledgements
We thank Violetta Powajbo and Alexandra Kappeler for excellent technical assistance. We are grateful to Ralf Weigel and Michael Diepers for their help with the volumetric analysis of MRI images. This study was supported by grants from the German Research Foundation (DFG VA151/4–2 and UL 60/4–2) and the 5th framework of the European Union (BMH4-CT95–0875).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tuettenberg, J., Grobholz, R., Korn, T. et al. Continuous low-dose chemotherapy plus inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 as an antiangiogenic therapy of glioblastoma multiforme. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 131, 31–40 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-004-0620-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-004-0620-5