Abstract
Background
The number of axillary lymph-node metastases is not only a function of disease progression in primary breast cancer, but is also influenced by the intra-mammary location of the tumor. Nevertheless, the prognostic role of the tumor site is discussed controversially. The objective of this study was to analyze the impact of primary-tumor location on axillary lymph-node involvement, relapse, and mortality risk by univariate and multivariate analysis, in patients both with and without systemic and loco-regional treatment.
Method
Retrospective analysis was conducted on 2,414 patients at the I. Frauenklinik, Ludwig-Maximilians University, Munich and Berlin-Charlottenburg, who underwent R0 resection of the primary tumor and systematic axillary lymph-node dissection (at least five lymph nodes resected) for UICC I-III-stage breast cancer. Patients with unknown tumor site, multifocal tumor spread, central tumor location, or tumor location within 15° of the border between outer and inner quadrants were excluded from the study. Median observation time was 6.7 years.
Results
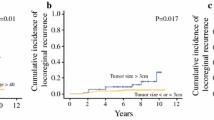
The primary tumor site was within or between the medial quadrants of the breast in 33.6% of the patients (n=810) and in the lateral hemisphere of the breast in 66.4% (n=1,604). Tumor size, histopathological grading, and estrogen receptor status were balanced between patients with lateral and medial tumor location. Metastatic axillary lymph-node involvement was significantly associated with a lateral tumor location (P<0.0001). The mean number of axillary lymph-node metastases was increased by 29% in cases with lateral tumor location (2.2 vs 1.7, P=0.003). In a multivariate logistic regression analysis allowing for tumor location, estrogen receptor status, grading and tumor size, tumor location was confirmed as a significant risk factor (P=0.02) for axillary lymph-node involvement. Tumor location, however, did not correlate with either disease-free survival (DFS) or overall survival (OS), by univariate (DFS: P=0.41; OS: P=0.57) or by multivariate analysis (DFS: P=0.16; OS: P=0.98).
Conclusion
We conclude that there is no sufficient evidence to support any independent prognostic significance of intra-mammary tumor location in early breast cancer. However, medial tumor location may lead to the underestimation of axillary lymph-node involvement.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bevilacqua JL, Gucciardo G, Cody HS, MacDonald KA, Sacchini V, Borgen PI, Van Zee KJ (2002) A selection algorithm for internal mammary sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 28:603–614
Bloom HJG, Richardson WW (1957) Histologic grading and prognosis in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 15:359–377
Blum JL, Jones SE, Fay JW, Senzer N, Mennel RG (1997) Guidelines for systemic therapy of early stage breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 43:259–276
Cascinelli N, Greco M, Bufalino R, Clemente C, Galluzzo D, delle-Donne V, de Lellis R, Sacchini V, Veronesi U (1987) Prognosis of breast cancer with axillary node metastases after surgical treatment only. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 23:795–799
Cody HS III, Urban JA (1995) Internal mammary node status: a major prognosticator in axillary node-negative breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2:32–37
Cox DR (1972) Regression models and life tables. J R Stat Soc B 34:187–220
Fisher B, Bauer M, Wickerham DL, Redmond CK, Fisher ER, Cruz AB, Foster R, Gardner B, Lerner H, Margolese R, et al. (1983) Relation of number of positive axillary nodes to the prognosis of patients with primary breast cancer. An NSABP update. Cancer 52:1551–1557
Fisher B, Redmond C, Fisher ER, Bauer M, Wolmark N, Wickerham DL, Deutsch M, Montague E, Margolese R, Foster R (1985) Ten-year results of a randomized clinical trial comparing radical mastectomy and total mastectomy with or without radiation. N Engl J Med 312:674–681
Fowble B, Solin LJ, Schultz DJ, Weiss MC (1992) Breast recurrence and survival related to primary tumor location in patients undergoing conservative surgery and radiation for early-stage breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 23:933–939
Fowble B, Hanlon A, Freedman G, Nicolaou N, Hoffman J, Sigurdson E, Boraas M, Torosian M, Goldstein L (2000) Internal mammary node irradiation neither decreases distant metastases nor improves survival in stage I and II breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:883–894
Gaffney DK, Tsodikov A, Wiggins CL (2003) Diminished survival in patients with inner versus outer quadrant breast cancers. J Clin Oncol 21:467–472
Gaglia P, Bussone R, Caldarola B, Lai M, Jayme A, Caldarola L (1987) The correlation between the spread of metastases by level in the axillary nodes and disease-free survival in breast cancer. A multifactorial analysis. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 23:849–854
Goldhirsch A, Glick JH, Gelber RD, Senn HJ (1998) Meeting highlights: International Consensus Panel on the Treatment of Primary Breast Cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 90:1601–1608
Goldhirsch A, Glick JH, Gelber RD, Coates AS, Senn HJ (2001) Meeting highlights: International Consensus Panel on the Treatment of Primary Breast Cancer. Seventh International Conference on Adjuvant Therapy of Primary Breast Cancer. J Clin Oncol 19:3817–3827
Jatoi I, Hilsenbeck SG, Clark GM, Osborne CK (1999) Significance of axillary lymph node metastasis in primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 17:2334–2340
Johnson N, Soot L, Nelson J, Franzini MD, Vea H, Gruner S, Kulawiak L, Young K (2000) Sentinel node biopsy and internal mammary lymphatic mapping in breast cancer. Am J Surg 179:386–388
Kambouris AA (1996) Axillary node metastases in relation to size and location of breast cancers: analysis of 147 patients. Am Surg 62:519–524
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Krause A, Dunkelmann S, Makovitzky J, Kuchenmeister I, Schumichen C, Reimer T, Friese K, Gerber B (2000) Detection of atypical site of "sentinel lymph nodes" by lymph drainage scintigraphy in patients with breast carcinoma. Zentralbl Gynakol 122:514–518
Lacour J, Bucalossi P, Cacers E, Jacobelli G, Koszarowski T, Le M, Rumeau-Rouquette C, Veronesi U (1976) Radical mastectomy versus radical mastectomy plus internal mammary dissection. Five-year results of an international cooperative study. Cancer 37:206–214
Langlands AO, Prescott RJ, Hamilton T (1980) A clinical trial in the management of operable cancer of the breast. Br J Surg 67:170–174
Le DV, Tubiana HM, Friedman S, Hacene K, Spyratos F, Brunet M (1989) Prognostic value of histologic grade nuclear components of Scarff-Bloom-Richardson (SBR). An improved score modification based on a multivariate analysis of 1262 invasive ductal breast carcinomas. Cancer 64:1914–1921
Lohrisch C, Jackson J, Jones A, Mates D, Olivotto IA (2000) Relationship between tumor location and relapse in 6,781 women with early invasive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 18:2828–2835
Noguchi M, Taniya T, Koyasaki N, Miyazaki I (1992) A multivariate analysis of en bloc extended radical mastectomy versus conventional radical mastectomy in operable breast cancer. Int Surg 77:48–54
Noguchi M, Ohta N, Thomas M, Kitagawa H, Miyazaki I (1993) Risk of internal mammary lymph node metastases and its prognostic value in breast cancer patients. J Surg Oncol 52:26–30
Recht A, Edge SB, Solin LJ, Robinson DS, Estabrook A, Fine RE, Fleming GF, Formenti S, Hudis C, Kirshner JJ, Krause DA, Kuske RR, Langer AS, Sledge GW, Whelan TJ, Pfister DG (2001) Postmastectomy radiotherapy: clinical practice guidelines of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol 19:1539–1569
Schnitt SJ, Connolly JL, Harris JR, Hellman S, Cohen RB (1984) Pathologic predictors of early local recurrence in stage I and II breast cancer treated by primary radiation therapy. Cancer 53:1049–1057
Sobin LH, Fleming ID (1997) TNM classification of malignant tumors, 5th edn. Union Internationale Contre le Cancer and the American Joint Committee on Cancer. Cancer 80:1803–1804
Veronesi U, Valagussa P (1981) Inefficacy of internal mammary nodes dissection in breast cancer surgery. Cancer 47:170–175
Veronesi U, Cascinelli N, Bufalino R, Morabito A, Greco M, Galluzzo D, delle-Donne V, de Lellis R, Piotti P, Sacchini V, et al. (1983) Risk of internal mammary lymph node metastases and its relevance on prognosis of breast cancer patients. Ann Surg 198:681–684
Veronesi U, Luini A, Galimberti V, Marchini S, Sacchini V, Rilke F (1990) Extent of metastatic axillary involvement in 1446 cases of breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 16:127–133
Veronesi U, Marubini E, Mariani L, Valagussa P, Zucali R (1999) The dissection of internal mammary nodes does not improve the survival of breast cancer patients. 30-year results of a randomised trial. Eur J Cancer 35:1320–1325
Vitucci C, Tirelli C, Graziano F, Santoro E (2000) Results of conservative surgery for limited-sized infiltrating breast cancer: analysis of 962 tested patients: 24 years of experience. J Surg Oncol 74:108–115
Zucali R, Mariani L, Marubini E, Kenda R, Lozza L, Rilke F, Veronesi U (1998) Early breast cancer: evaluation of the prognostic role of the site of the primary tumor. J Clin Oncol 16:1363–1366
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Friedrich-Baur Stiftung, Münich, Germany. The authors are sincerely grateful to David and Sally Gray for their editorial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janni, W., Rack, B., Sommer, H. et al. Intra-mammary tumor location does not influence prognosis but influences the prevalence of axillary lymph-node metastases. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 129, 503–510 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-003-0465-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-003-0465-3