Abstract
Purpose
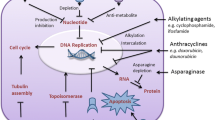
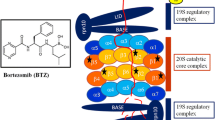
In this study, we investigated the effects of cell-permeable proteasome inhibitors MG-132, MG-262, PSI, and lactacystin on multiple myeloma cell lines OPM-2, U266, RPMI 8226-S, freshly isolated plasma cells with or without deletion of chromosome 13 from patients with multiple myeloma and plasma cell leukemia, and CD34+ human hematopoietic stem cells. The effects of proteasome inhibitors on cell cycle progression, cell growth, and apoptosis were determined.
Methods
MTT-assay was used to examine the cytotoxicity, and annexin-V staining to quantify apoptosis. Cell cycle analyses were performed using 7-ADD and Ki-67 staining by flow cytometry.
Results
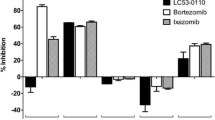
PSI was the most potent proteasome inhibitor among those tested with a half maximal cytotoxicity (IC50) of 5.7 nM, followed by MG-262, MG-132, and lactacystin. Growth inhibition occurred irrespective of chromosome 13 status. Cell cycle arrest occurred in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Low, subapoptotic dosages led to a partial loss of Ki-67 antigen, whereas apoptotic dosages led to reduced Ki-67 levels. Apoptosis was partially dependent on activation of caspase-3, since Ac-DEVD-cho, a caspase-3 inhibitor, could reduce apoptosis significantly. The cytotoxicity of the four proteasome inhibitors tested was significantly lower in human hematopoietic stem cells than in myeloma cells.
Conclusions
Our results show that proteasome inhibitors induce time- and dose-dependent cell cycle alterations, growth inhibition, and apoptosis in human myeloma cells irrespective of chromosome 13 deletion.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams J, Behnke M, Chen S, Cruickshank AA, Dick LR, Grenier L, Klunder JM, Ma YT, Plamondon L, Stein RL (1998) Potent and selective inhibitors of the proteasome: dipeptidyl boronic acids. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 8:333–338
Adams J, Palombella VJ, Sausville EA, Johnson J, Destree A, Lazarus DD, Maas J, Pien CS, Prakash S, Elliott PJ (1999) Proteasome inhibitors: a novel class of potent and effective antitumor agents. Cancer Res 59:2615–2622
Adams J, Palombella VJ, Eliott PJ (2000) Proteasome inhibition: a new strategy in cancer treatment. Invest New Drugs 18:109–121
Blagosklonny MV, Wu GS, Omura S, El-Deiry WS (1996) Proteasome-dependent regulation of p21WAF1/CIP1 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Com 227:564–569
Boyer SN, Wazer DE, Band V (1996) E7 protein of human papilloma virus-16 induces degradation of retinoblastoma protein through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Cancer Res 56:4620–4624
Casaccia-Bonnefil P, Tikoo R, Kiyokawa H, Friedrich V Jr, Chao MV, Koff A (1997) Oligodendrocyte precusor differentiation is preturbed in the absence of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1. Genes Dev 11:2335–2346
Dick LR, Cruickshank AA, Grenier L, Melandri FD, Nunes SL, Stein RL (1996) Mechanistic studies on the inactivation of the proteasome by lactacystin: a central role for clasto-lactacystin beta-lactone. J Biol Chem 271:7273–7276
Dick LR, Cruikshank AA, Destree AT, Grenier L, McCormack TA, Melandri FD, Nunes SL, Palombella VJ, Parent LA, Plamondon L, Stein RL (1997) Mechanistic studies on the inactivation of the proteasome by lactacystin in cultured cells. J Biol Chem 272:182–188
Domenech J, Georget MT, Gihana E, Colombat P, Bremond JL, Chassaigne M, Lamagnere JP, Binet C (1992) Evaluation of doxorubicin in combination with mafosfamide for in vitro elimination of myeloid and lymphoid tumor cells from human bone marrow. Bone Marrow Transplant 9:101–106
Drexler HC (1997) Activation of the cell death program by inhibition of proteasome function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:855–860
Endl E, Gerdes J (2000) Posttranslational modifications of the KI-67 protein coincide with two major checkpoints during mitosis. J Cell Physiol 182:371–380
Fujisawa T, Watanabe J, Akaboshi M, Ohno E, Kuramoto H (2001) Immunohistochemical study on VEGF expression in endometrial carcinoma—comparison with p53 expression, angiogenesis, and tumor histologic grade. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 127:668–674
Fuse T, Tanikawa M, Nakanishi M, Ikeda K, Tada T, Inagaki H, Asai K, Kato T, Yamada K (2000) p27Kip1 expression by contact inhibition as a prognostic index of human glioma. J Neurochem 74:1393–1399
Gerdes J, Lemke H, Baisch H, Wacker HH, Schwab U, Stein H (1984) Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol 133:1710–1715
Ghielmini M, Colli E, Bosshard G, Pennella G, Geroni C, Torri V, D'Incalci M, Cavalli F, Sessa C (1998) Hematotoxicity on human bone marrow- and umbilical cord blood-derived progenitor cells and in vitro therapeutic index of methoxymorpholinyl-doxorubicin and its metabolites. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 42:235–240
Hideshima T, Richardson P, Chauhan D, Palombella VJ, Elliott PJ, Adams J, Anderson KC (2001) The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 inhibits growth, induces apoptosis, and overcomes drug resistance in human multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Res 61:3071–3076
Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Richardson P, Mitsiades C, Mitsiades N, Hayashi T, Munshi N, Dang L, Castro A, Palombella V, Adams J, Anderson KC (2002) NF-kappa B as a therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. J Biol Chem 277:16639–16647
King RW, Deshaies RJ, Peters JM, Kirschner MW (1996) How proteolysis drives the cell cycle. Science 274:1652–1659
Kitagawa H, Tani E, Ikemoto H, Ozaki I, NakanoA, Omura S (1999) Proteasome inhibitors induce mitochondria independent apoptosis in human glioma cells. FEBS Lett 443:181–186
Komuro H, Kaneko S, Kaneko M, Nakanishi Y (2001) Expression of angiogenic factors and tumor progression in human neuroblastoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 127:739–743
Kumeda SI, Deguchi A, Toi M, Omura S, Umezawa K (1999) Induction of G1 arrest and selective growth inhibition by lactacystin in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Anticancer Res 19:3961–3968
Li B, Dou QP (2000) Bax degradation by the ubiquitin/proteasome-dependent pathway: involvement in tumor survival and progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3850–3855
Machiels BM, Henfling ME, Gerards WL, Broers JL, Bloemendal H, Ramaekers FC, Schutte B (1997) Detailed analysis of cell cycle kinetics upon proteasome inhibition. Cytometry 28:243–252
Maehara Y, Anai H, Tamada R, Sugimachi K (1987) The ATP assay is more sensitive than the succinate dehydrogenase inhibition test for predicting cell viability. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 23:273–276
Maki CG, Huibregtse JM, Howley PM (1996) In vivo ubiquitination and proteasome mediated degradation of p53. Cancer Res 56:2649–2654
Mitsiades N, Mitsiades CS, Poulaki V, Chauhan D, Richardson PG, Hideshima T, Munshi N, Treon SP, Anderson KC (2002a) Biologic sequelae of nuclear factor-kappaB blockade in multiple myeloma: therapeutic applications. Blood 99:4079–4086
Mitsiades N, Mitsiades CS, Poulaki V, Chauhan D, Fanourakis G, Gu X, Bailey C, Joseph M, Libermann TA, Treon SP, Munshi NC, Richardson PG, Hideshima T, Anderson KC (2002b) Molecular sequelae of proteasome inhibition in human multiple myeloma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:14374–14379
Naujokat C, Sezer O, Zinke H, Leclere A, Hauptmann S, Possinger K (2000) Proteasome inhibitors induce caspase-dependent apoptosis and accumulation of p21 WAF1/Cip1 in human immature leukemic cells. Eur J Haematol 65:221–236
Naujokat C, Hoffmann S (2002) Role and function of the 26S proteasome in proliferation and apoptosis. Lab Invest 82:965–980
Nawrocki ST, Bruns CJ, Harbison MT, Bold RJ, Gotsch BS, Abbruzzese JL, Elliott P, Adams J, McConkey DJ (2002) Effects of the proteasome inhibitor PS-341 on apoptosis and angiogenesis in orthotopic human pancreatic tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther 1:1243–1253
Nicholson DW, Ali A, Thornberry NA, Vaillancourt JP, Ding CK, Gallant M, Gareau Y, Griffin PR, Labelle M, Lazebnik YA (1995) Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nature 376:37–43
Niemöller K, Jakob C, Heider U, Zavrski I, Eucker J, Kaufmannn O, Possinger K, Sezer O (2003) Bone marrow angiogenesis and its correlation with other disease characteristics in multiple myeloma in stage I versus stage II-III. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 129:234–238
Orlowski RZ (1999) The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 6:303–313
Orlowski M, Cardozzo C, Michaud C (1993) Evidence for the presence of five distinct proteolytic components in the pituitary multicatalytic proteinase complex. Properties of two components cleaving bonds on the carboxyl side of branched chain an small neutral amino acids. Biochemistry 32:1563–1572
Pagano M, Tam SW, Theodoras AM, Beer-Romero P, Del Sal G, Chau V, Yew PR, Draetta GF, Rolfe M (1995) Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in regulating abundance of the cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor p27. Science 269:682–685
Palombella VJ, Rando OJ, Goldberg AL, Maniatis T (1994) The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is required for processing the NF-κB1 precusor protein and the activation of NF-κB. Cell 78:773–785
San Miguel JF, Blade Creixenti J, Garcia-Sanz R (1999) Treatment of multiple myeloma. Haematologica 84:36–58
Schluter C, Duchrow M, Wohlenberg C, Becker MH, Key G, Flad HD, Gerdes J (1993) The cell proliferation-associated antigen of antibody Ki-67: a very large, ubiquitous nuclear protein with numerous repeated elements, representing a new kind of cell cycle-maintaining proteins. J Cell Biol 123:513–522
Schmid I, Cole SW, Korin YD, Zack JA, Giorgi JV (2000) Detection of cell cycle subcompartments by flow cytometric estimation of DNA-RNA content in combination with dual color immunofluorescence. Cytometry 39:108–116
Shaughnessy J, Tian E, Sawyer J, Bumm K, Landes R, Badros A, Morris C, Tricot G, Epstein J, Barlogie B (2000) High incidence of chromosome 13 deletion in multiple myeloma detected by multiprobe interphase FISH. Blood 96:1505–1511
Taniguchi T, Endo H, Chikatsu N, Uchimaru K, Asano S, Fujita T, Nakahata T, Motokura T (1999) Expression of p21(Cip1/Waf1/Sdi1) and p27(Kip1) cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors during human hematopoiesis. Blood 93:4167–4178
Traenckner EB, Wilk S, Baeuerle PA (1994) A proteasome inhibitor prevents activation of NF-κB and stabilizes a newly phosphorylated form of I κB-α that is still bound to NF-κB. EMBO 13:5433–5441
Tricot G, Sawyer JR, Jagannath S, Desikan KR, Siegel D, Naucke S, Mattox S, Bracy D, Munshi N, Barlogie B (1997) Unique role of cytogenetics in the prognosis of patients with myeloma receiving high-dose therapy and autotransplants. J Clin Oncol 15:2659–2666
Tsurusawa M, Fujimoto T (1995) Cell cycle progression and phenotypic modification of Ki-67 antigen-negative G1- and G2-phase cells in phorbol ester-treated Molt-4 human leukemia cells. Cytometry 20:146–153
Wu Y, Luo H, Kanaan N, Wu J (2000) The proteasome controls the expression of a proliferation-associated nuclear antigen Ki-67. J Cell Biochem 76:596–604
Yamada Y, Sugahara K, Tsuruda K, Nohda K, Mori N, Hata T, Maeda T, Hayashibara T, Joh T, Honda M, Tawara M, Tomonaga M, Miyazaki Y, Kamihira S (2000) Lactacystin activates FLICE (caspase 8) protease and induces apoptosis in Fas-resistant adult T-cell leukemia cell lines. Eur J Haematol 64:315–322
Zojer N, Konigsberg R, Ackermann J, Fritz E, Dallinger S, Kromer E, Kaufmann H, Riedl L, Gisslinger H, Schreiber S, Heinz R, Ludwig H, Huber H, Drach J (2000) Deletion of 13q14 remains an independent adverse prognostic variable in multiple myeloma despite its frequent detection by interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization. Blood 95:1925–1930
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zavrski, I., Naujokat, C., Niemöller, K. et al. Proteasome inhibitors induce growth inhibition and apoptosis in myeloma cell lines and in human bone marrow myeloma cells irrespective of chromosome 13 deletion. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 129, 383–391 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-003-0454-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-003-0454-6