Abstract
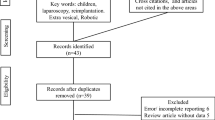
The purpose of this study is to determine the effectiveness and safety of endoscopic management compared to ureterovesical reimplantation in pediatric patients with high-grade vesicoureteral reflux in terms of urinary tract infection. We performed a network meta-analysis. We searched in MEDLINE, EMBASE, LILACS, and CENTRAL. We included clinical experiments, quasi-experiments, and cohorts studies. The population was men and women between 1 month and 15 years old. Patients had primary high-grade VUR diagnosed by voiding cystourethrography. The interventions were subureteric bulking agent endoscopic injection (polytetrafluoroethylene, hyaluronic acid, collagen, Dx/Ha, and PPC) vs vesicoureteral reimplantation (Cohen, Politano-Leadbetter, Glenn-Anderson, and Lich-Gregoir), and the primary outcome was urinary infections. Nine studies accomplished the inclusion criteria (seven observational and two clinical experiments). A total of 1448 renal units underwent surgical treatments for the correction of high-grade VUR. Regarding the primary outcome, we compared Dx/Ha with Cohen, Lich-Gregoir, and PPC, finding an RD of −0.02 (95%CI −0.09 to 0.06), RD of −0.02 (95%CI −0.10 to 0.07), and an RD of −0.03 (− 0.13 to 0.07), respectively.
Conclusion: Our study showed that there were no differences in UTI episodes after VUR correction in patients undergoing endoscopic management compared with vesicoureteral reimplantation.
What is Known: • Primary vesicoureteral reflux is one of the most common congenital anomalies of the urinary tract. • The clinical practice guidelines recommend the surgical management of patients with high-grade VUR. | |
What is New: • There were no differences in UTI episodes after VUR correction in patients undergoing endoscopic management compared with vesicoureteral reimplantation. |




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All information is available.
Abbreviations
- VUR:
-
Primary vesicoureteral reflux
- UTI:
-
Urinary tract infection
- Dx/Ha:
-
Dextranomer/hyaluronic acid copolymer
- PPC:
-
Polyalcohol polyacrylate copolymer
- DeCS:
-
Descriptors in health sciences
- MINORS:
-
Methodological index for non-randomized studies
- RR:
-
Relative risk
- ALARA:
-
As low as reasonably achievable
- MIS:
-
Minimally invasive surgery
References
Hunziker M, Colhoun E, Puri P (2013) Prevalence and predictors of renal functional abnormalities of high grade vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol 190(4 SUPPL):1490–1494
Hoberman A, Charron M, Hickey R, Baskin M, Kearney DH, Wald ER (2003) Imaging studies after a first febrile urinary tract infection in young children. NEJM 348(3):195–202
Mohanan N, Colhoun E, Puri P (2008) Renal parenchymal damage in intermediate and high grade infantile vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol 180(4):1635–1638
Lebowitz RL, Olbing H, Parkkulainen KV (1985) International system of radiographic grading of vesicoureteric reflux. International Reflux Study in Children. Pediatr Radiol 15(2):105–106
Zaffanello M, Cataldi L, Brugnara M, Franchini M, Bruno C, Fanos V (2009) Hidden high-grade vesicoureteral reflux is the main risk factor for chronic renal damage in children under the age of two years with first urinary tract infection. Scand J Urol Nephrol (July):494–500
Swerkersson S, Jodal U, Sixt R, Stokland E, Hansson S (2007) Relationship among vesicoureteral reflux, urinary tract infection and renal damage in children. J Urol 178(2):647–651
Silva JM, Diniz JS, Lima E, Vergara R, Oliveira E (2006) Predictive factors of resolution of primary vesico-ureteric reflux: a multivariate analysis. BJU Int 97(5):981–988
Wheeler D, Vimalachandra D, Hodson E, Smith G, Craig J (2004) Interventions for primary vesicoureteric reflux. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 3:CD001532
Williams G, Craig J, Group C (2019) Kidney and transplant. Long-term antibiotics for preventing recurrent urinary tract infection in children ( review ). Cochrane Database Syst Rev 3:CD001534
Shapiro E, Snow B, Zaontz M (2003) Management of vesicoureteral reflux. Rev Urol 5(2):121–125
Kocaoglu C (2016) Endoscopic treatment of grades IV and V vesicoureteral reflux with two bulking substances: dextranomer hyaluronic acid copolymer versus polyacrylate polyalcohol copolymer in children. J Pediatr Surg 51(10):1711–1715
Kocherov S, Ulman I, Nikolaev S, Corbetta JP, Rudin Y, Slavkovic A, Dokumcu Z, Avanoglu A, Menovshchikova L, Kovarskiy S, Skliarova T, Weller S, Bortagaray JI, Lopez JC, Durán V, Burek C, Sager C, Dmitriy M, Garmanova T, Djamal A, Jovanovic Z, Vacic N, Abu Arafeh W, Chertin B (2014) Multicenter survey of endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux using polyacrylate-polyalcohol bulking copolymer (Vantris). Urology. 84(3):689–693
Hajiyev P, Burgu B, Catto J (2017) Contemporary management of vesicoureteral reflux. Eur Urol Focus 3(2–3):181–188
Hodson EM, Wheeler DM, Vimalchandra D, Smith GH, Craig JC (2007) Interventions for primary vesicoureteric reflux. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 3
Tekgül S, Dogan HS, Hoebeke P, Ko R, Stein R. Guidelines on Paediatric urology. 2015
R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing [Internet]. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2017. Available from: https://www.r-project.org/
Garcia-aparicio L, Rovira J, Blazquez-gomez E (2013) Randomized clinical trial comparing endoscopic treatment with dextranomer hyaluronic acid copolymer and Cohen’s ureteral reimplantation for vesicoureteral reflux: long-term results. J Pediatr Urol 9(4):483–487
Comploj E, Mian M, Koen M, Becker T, Berger C, Riccabona M (2010) Effectiveness and cost analysis of different methods of anti-refluxive operations in VUR grade 3 in a single institution. CEJU. 63(2):129–131
Kenneth LY, Sihoe J, Liu K, Yam F, Leung Y, Tam P et al (2017) Surgical outcome analysis of pneumovesicoscopic ureteral reimplantation and endoscopic dextranomer/hyaluronic acid injection for primary vesicoureteral reflux in children: a multicenter 12-year review. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 28(3):1–6
Esposito C, Lopez M, Caprio MG, Settimi A (2016) Surgical management of pediatric vesicoureteral reflux: a comparative study between endoscopic, laparoscopic and open surgery. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 26(7):574–580
Oberson C, Boubaker A, Ramseyer P, Bj M, Frey P (2007) Endoscopic and surgical treatment of vesico-ureteral reflux in children. Swiss Med Wkly 137(33–34):471–476
García-Aparicio L, Blázquez-Gomez E, Martin O, Perez-Bertolez S, Arboleda J, Soria A et al (2018) Randomized clinical trial between polyacrylate - polyalcohol copolymer (PPC) and dextranomer - hyaluronic acid copolymer (Dx/HA) as bulking agents for endoscopic treatment of primary vesicoureteral reflux. World J Urol 36(10):1651–1656
Cuneyt S, Rana İ, Demircioglu B, Akçaer V, Ceylan H, Hayri B (2016) The comparison of dextranomer/hyaluronic acid and polyacrylate-polyalcohol copolymers in endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral re fl ux. J Pediatr Urol 51(9):1496–1500
Avlan D, Bahadir GB, Nayci A (2016) The outcomes of two different bulking agents (dextranomer hyaluronic acid copolymer and polyacrylate-polyalcohol copolymer) in the treatment of primary vesico-ureteral reflux. Int Braz J Urol 42(3):514–520
Fernandez N, Puerto A, Azuero A, Hannick M, Rickard M (2018) Historical bibliometric analysis of the top cited articles on vesicoureteral reflux 1950–2016, and incorporation of an impact index. J Pediatr Urol 14:446.e1–446.e9
Tekgul S, Stein R, Bogaert G, Undre S, Nijman RJM, Quaedackers J, ‘t Hoen L, Kocvara R, Silay MS, Radmayr C, Dogan HS (2020) EAU-ESPU guidelines recommendations for daytime lower urinary tract conditions in children. Eur J Pediatr 179(7):1069–1077
Deng T, Liu B, Luo L, Duan X, Cai C, Zhao Z, Zhu W, Wu W, Zeng G (2018) Robot-assisted laparoscopic versus open ureteral reimplantation for pediatric vesicoureteral reflux: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Urol 36(5):819–828
Williams G, Hodson E, Craig J (2019) Interventions for primary vesicoureteric reflux. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2:CD001532
Estrada CR, Passerotti CC, Graham DA, Peters CA, Bauer SB, Diamond DA et al (2009) Nomograms for predicting annual resolution rate of primary vesicoureteral reflux: results from 2, 462 Children. JURO 182(4):1535–1541
Elder JS, Peters CA, Arant BS, Ewalt DH, Hawrey CE, Hurwitz RS et al (1997) Pediatric vesicoureteral reflux guidelines panel summary report on the management of primary vesicoureteral reflux in children. J Urol 157(5):1846–1851
Duckett JW, Walker RD, Weiss R (1992) Surgical results: international reflux study in children-United States branch. J Urol 148(5):1674–1675
Code availability
NA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All three authors (SM, HAG, NF) participated in all steps of this research: idea/concept, protocol, running the strategies, extracting data, statistical analysis, discussing the results, writing the manuscript draft, and approval of the final manuscript.
SM participated in all steps of this research: idea/concept, protocol, running the strategies, extracting data, statistical analysis, discussing the results, writing the manuscript draft, and approval of the final manuscript.
NF participated in all steps of this research: idea/concept, protocol, running the strategies, extracting data, statistical analysis, discussing the results, writing the manuscript draft, and approval of the final manuscript.
HAGP participated in all steps of this research: idea/concept, protocol, running the strategies, extracting data, statistical analysis, discussing the results, writing the manuscript draft, and approval of the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This research accomplishes with all the international requirements for ethics in research. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
NA
Consent for publication
We consent the publication of this manuscript.
Additional information
Communicated by Gregorio Paolo Milani
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix. Search strategy
Appendix. Search strategy
MEDLINE (OVID)
(Exp Vesico Ureteral Reflux or (Vesico*ureteral adj2 Reflux).mp or VUR.mp or (Vesico*ureteric reflux).mp) AND (Reimplantation*.mp or (subureteric adj2 implantation).mp or (subureteric adj2 injection).mp or vantris.mp or polytetrafluoroethylene.mp or hyaluronic adj2 acid or collagen.mp or deflux.mp) or (politano*leadbetter).mp or (Glenn*anderson).mp or cohen.mp or (lich*gregoir).mp) AND (randomized controlled trial.pt or controlled clinical trial.pt or randomized.ab or placebo.ab or randomly.ab or trial.ab or (clinical adj2 trial).mp or (randomi*ed adj2 controlled adj2 trial).mp or exp double-blind method or clinical trial.pt or exp Non-Randomized Controlled Trials or (quasi adj2 experiment*).mp or exp cohort studies or cohort*.mp)
EMBASE (Scopus)
TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Vesico Ureteral Reflux” or VUR or “Vesico*ureteric reflux”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(“Reimplantation*” or “subureteric implantation” or “subureteric injection” or vantris or polytetrafluoroethylene or “hyaluronic acid” or collagen or deflux or “politano*leadbetter” or “Glenn*anderson” or cohen or “lich*gregoir”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(“randomized controlled trial” or “controlled clinical trial” or randomized or placebo or randomly or trial or “clinical trial” or “double-blind method” or “Non-Randomized Controlled Trials” or “quasi experiment*” or “cohort stud*” or “cohort*”)
CENTRAL
(Exp Vesico Ureteral Reflux or (Vesico*ureteral adj2 Reflux).mp or VUR.mp or (Vesico*ureteric reflux).mp) AND (Reimplantation*.mp or (subureteric adj2 implantation).mp or (subureteric adj2 injection).mp or vantris.mp or polytetrafluoroethylene.mp or hyaluronic adj2 acid or collagen.mp or deflux.mp) or (politano*leadbetter).mp or (Glenn*anderson).mp or cohen.mp or (lich*gregoir).mp)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mina-Riascos, S.H., Fernández, N. & García-Perdomo, H.A. Effectiveness and risks of endoscopic management compared to vesicoureteral reimplantation in patients with high-grade vesicoureteral reflux: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Eur J Pediatr 180, 1383–1391 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-021-03948-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-021-03948-w