Abstract
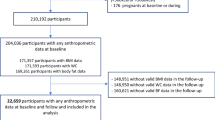
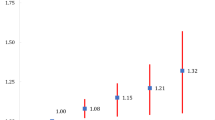
The purpose of this study was to determine breakfast habits, dairy product consumption, and physical activity and their relations with body mass index (BMI) in schoolchildren and adolescents. This cross-sectional, school-based study was performed with children aged 6–18 years. Height and weight were measured, and a BMI z-score was calculated for each child. Breakfast consumption frequency, intake of milk and other dairy products, physical activity habits, and mothers’ employment status were assessed via a self-report questionnaire. Multiple linear regression analysis was used to estimate the association between these habits and BMI z-scores. Seven thousand one hundred sixteen children were included, 3445 (48.4%) female, with a mean age of 11.7 ± 2.7 years (5.8–18.9). Of these, 62.6% had breakfast every day. Boys ate breakfast daily significantly more often than girls (64.5 and 60.7%, respectively; p < 0.001). The percentage of children eating breakfast daily decreased with age (79.1% at 6–11 vs. 52.1% at 12–18 years, p < 0.001). Sixty-four (0.9%) children consumed no dairy products. Milk intake was negatively and significantly associated with BMI z-score (β = − 0.103, p < 0.001). Cheese consumption and the mother being employed were positively and significantly associated with BMI z-score (β = 0.517, p < 0.001, and β = 0.172, p < 0.001, respectively). Children engaging in physical activity had higher BMI z-score values than others (0.22 ± 0.01 vs. 0.12 ± 0.02, p < 0.001). Prevalence of overweight/obese was higher among children of working mothers compared to those of unemployed mothers (respectively, 29.3, 23.3%, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Skipping breakfast was associated with overweight/obesity in schoolchildren and adolescents, while milk consumption exhibited a protective effect.
What is known? • Dietary interventions should be incorporated into a multidisciplinary strategy for obesity prevention. • Most studies of habitual physical activity in children suggest that the overweight and obese children are less active. |
What is new? • Milk consumption seems to have a protective effect against overweight/obesity, irrespective of yogurt or cheese consumption. • Children engaging in greater physical activity had higher body mass index values than others. |

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
body mass index
- FFQ:
-
food frequency questionnaire
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Abreu S, Santos R, Moreira C, Santos PC, Vale S, Soares-Miranda L, Mota J, Moreira P (2012) Milk intake is inversely related to body mass index and body fat in girls. Eur J Pediatr 171:1467–1474
Alberdi G, McNamara A, Lindsay K, Scully H, Horan M, Gibney E, McAuliffe F (2016) The association between childcare and risk of childhood overweight and obesity in children aged 5 years and under: a systematic review. Eur J Pediatr 175:1277–1294
Ascenso A, Palmeira A, Pedro LM, Martins S, Fonseca H (2016) Physical activity and cardiorespiratory fitness, but not sedentary behavior, are associated with carotid intima-media thickness in obese adolescents. Eur J Pediatr 175:391–398
Baldinger N, Krebs A, Müller R, Aeberli I (2012) Swiss children consuming breakfast regularly have better motor functional skills and are less overweight than breakfast skippers. J Am Coll Nutr 31:87–93
Beydoun MA, Gary TL, Caballero BH, Lawrence RS, Cheskin LJ, Wang Y (2008) Ethnic differences in dairy and related nutrient consumption among US adults and their association with obesity, central obesity, and the metabolic syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr 87:1914–1925
Biro F, Wien M (2010) Childhood obesity and adult morbidities. Am J Clin Nutr 91:1499–1505
Corder K, van Sluijs EM, Ekelund U, Jones AP, Griffin SJ (2010) Changes in children’s physical activity over 12 months: longitudinal results from the SPEEDY study. Pediatrics 126:926–935
Dundar C, Oz H (2012) Obesity-related factors in Turkish school children. Sci World J 2012:353485
Eaton DK, Kann L, Kinchen S, Shanklin S, Ross J, Hawkins J, Harris WA, Lowry R, McManus T, Chyen D, Lim C, Whittle L, Brener ND, Wechsler H, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2009) Youth risk behavior surveillance—United States, 2009. MMWR Surveill Summ 59:1–142
Groholt EK, Stigum H, Nordhagen R (2008) Overweight and obesity among adolescents in Norway: cultural and socio-economic differences. J Public Health (Oxf) 30:258–265
Hawkins SS, Cole TJ, Law C (2009) Examining the relationship between maternal behaviours in 5-years-old British children. J Epidemiol Commun Health 63:999–1004
Hearst MO, Harnack LJ, Bauer KW, Earnest AA, French SA, Michael Oakes J (2013) Nutritional quality at eight U.S. fast-food chains: 14-year trends. Am J Prev Med 44:589–594
Hubbard K, Economos CD, Bakun P, Boulos R, Chui K, Mueller MP, Smith K, Sacheck J (2016) Disparities in moderate-to-vigorous physical activity among girls and overweight and obese schoolchildren during school- and out-of-school time. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 13:39
Huybrechts I, De Bacquer D, Matthys C, De Backer G, De Henauw S (2006) Validity and reproducibility of a semi-quantitative food-frequency questionnaire for estimating calcium intake in Belgian preschool children. Br J Nutr 95:802–816
Marlatt KL, Farbakhsh K, Dengel DR, Lytle LA (2016) Breakfast and fast food consumption are associated with selected biomarkers in adolescents. Prev Med Rep 3:49–52
Mindru DE, Moraru E (2013) Risk factors and their implications in the epidemiology of pediatric obesity. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi 116:739–745
Moore LL, Singer MR, Qureshi MM, Bradlee ML (2008) Dairy intake and anthropometric measures of body fat among children and adolescents in NHANES. J Am Coll Nutr 27:702–710
Nyberg GA, Nordenfelt AM, Ekelund U, Marcus C (2009) Physical activity patterns measured by accelerometry in 6- to 10-year-old children. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41:1842–1848
Rampersaud GC, Pereira MA, Girard BL, Adams J, Metzl JD (2005) Breakfast habits, nutritional status, body weight, and academic performance in children and adolescents. J Am Diet Assoc 105:743–760
Scully H, Alberdi G, Segurado R, McNamara A, Lindsay K, Horan M, Hennessy E, Gibney E, McAuliffe F (2017) Childcare exposure influences childhood adiposity at 2 years: analysis from the ROLO Study. Child Obes 13:93–101
Smetanina N, Albaviciute E, Babinska V, Karinauskiene L, Albertsson-Wikland K, Petrauskiene A, Verkauskiene R (2015) Prevalence of overweight/obesity in relation to dietary habits and lifestyle among 7–17 years old children and adolescents in Lithuania. BMC Public Health 15:1001
Wijnhoven TM, van Raaij JM, Spinelli A, Rito AI, Hovengen R, Kunesova M, Starc G, Rutter H, Sjöberg A, Petrauskiene A, O’Dwyer U, Petrova S, Farrugia Sant’angelo V, Wauters M, Yngve A, Rubana IM, Breda J (2015) WHO European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative: health-risk behaviours on nutrition and physical activity in 6–9-year-old schoolchildren. Public Health Nutr 18:3108–3124
Wiley AS (2010) Dairy and milk consumption and child growth: is BMI involved? An analysis of NHANES 1999–2004. Am J Hum Biol 22:517–525
Wüenstel JW, Kowalkowska J, Wądołowska L, Słowińska MA, Niedźwiedzka E, Kurp L (2015) Habitual eating of breakfast, consumption frequency of selected food and overweight prevalence in adolescents from various age groups. Dev Period Med 2:193–201
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tugba Koca conceived the study; collected, assembled and processed data; performed statistical analyses; performed literature search and wrote the manuscript. Mustafa Akcam conceived the study; provided expert professional opinion and input. Filiz Serdaroglu performed literature search and edited the report. Selim Dereci collected, assembled and processed data; edited the report.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Financial source
No funding was secured for this study.
Financial disclosure
The authors have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants (their parents, and children (if ≥ 12 years)) prior to their inclusion in the study.
Additional information
Communicated by Mario Bianchetti
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koca, T., Akcam, M., Serdaroglu, F. et al. Breakfast habits, dairy product consumption, physical activity, and their associations with body mass index in children aged 6–18. Eur J Pediatr 176, 1251–1257 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-017-2976-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-017-2976-y