Abstract
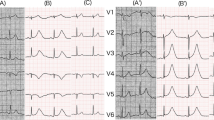
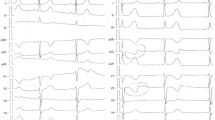
As a noncentral nerve-stimulating agent blocking reuptake of noradrenalin, atomoxetine is used for treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Because it has less potential for addiction and abuse and improves core symptoms of ADHD, it is commonly prescribed in many children and adolescents internationally. Its common side effects include headache, abdominal pain, decreased appetite, and weight loss. In addition, cardiac effects such as tachycardia and hypertension have also been reported. In this case report, an 11-year-old Japanese boy with a past medical history of ADHD on atomoxetine for more than 2 years presented with a loss of consciousness. Initial electrocardiogram (ECG) showed significant QT prolongation, and 9 h later, it worsened, along with bradycardia, inversed T waves, and multiple premature ventricle contractions (PVCs). Transthoracic echocardiography showed akinesis with dilation and systolic ballooning of the left ventricle's (LV) apical segment (Takotsubo cardiomyopathy). At that point, bisoprolol and transcutaneous pacing were started. After 5 days, transcutaneous pacing was discontinued due to improvement in his cardiac rhythm. He continued to remain asymptomatic for the next year, while his QT interval returned to normal. Conclusion: This case report suggests a serious side effect of atomoxetine, and to avoid life-threatening cardiovascular events for children and adolescents with ADHD on atomoxetine, prior screening for cardiovascular conditions by ECG with close monitoring is necessary.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bangs ME, Hazell P, Danckaerts M, Hoare P, Coghill DR, Wehmeier PM, Williams DW, Moore RJ, Levine L (2008) Atomoxetine for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and oppositional defiant disorder. Pediatrics 121:314–320
Cooper WO, Habel LA, Sox CM, Chan KA, Arbogast PG, Cheetham TC, Murray KT, Quinn VP, Stein CM, Callahan ST, Fireman BH, Fish FA, Kirshner HS, O'Duffy A, Connell FA, Ray WA (2011) ADHD drugs and serious cardiovascular events in children and young adults. N Engl J Med 365:1896–1904
Donnelly C, Bangs M, Trzepacz P, Jin L, Zhang S, Witte MM, Ball SG, Spencer TJ (2009) Safety and tolerability of atomoxetine over 3 to 4 years in children and adolescents with ADHD. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 48:176–185
Eli Lilly and Company (2013) Prescribing information on Strattera, pp 1–17. http://pi.lilly.com/us/strattera-pi.pdf
Eli Lilly and Company (2009) Press release information on Strattera. https://www.lilly.co.jp/pressrelease/2009/news_2009_013.aspx
Geller D, Donnelly C, Lopez F, Rubin R, Newcorn J, Sutton V, Bakken R, Paczkowski M, Kelsey D, Sumner C (2007) Atomoxetine treatment for pediatric patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder with comorbid anxiety disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 46:1119–1127
Kelsey DK, Sumner CR, Casat CD, Coury DL, Quintana H, Saylor KE, Sutton VK, Gonzales J, Malcolm SK, Schuh KJ, Allen AJ (2004) Once-daily atomoxetine treatment for children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, including an assessment of evening and morning behavior: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pediatrics 114:1–8
Martinez-Raga J, Knecht C, Szerman N, Martinez MI (2013) Risk of serious cardiovascular problems with medications for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. CNS Drugs 27(1):15–30
Michelson D, Allen AJ, Busner J, Casat C, Dunn D, Kratochvil C, Newcorn J, Sallee FR, Sangal RB, Saylor K, West S, Kelsey D, Wernicke J, Trapp NJ, Harder D (2002) Once-daily atomoxetine treatment for children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am J Psychiatry 159:1896–1901
Ring BJ, Gillespie JS, Eckstein JA, Wrighton SA (2002) Identification of the human cytochromes P450 responsible for atomoxetine metabolism. Drug Metab Dispos 30(3):319–323
Sawant S, Daviss SR (2004) Seizures and prolonged QTc with atomoxetine overdose. Am J Psychiatry 161(4):757
Schelleman H, Bilker WB, Strom BL, Kimmel SE, Newcomb C, Guevara JP, Daniel GW, Cziraky MJ, Hennessy S (2011) Cardiovascular events and death in children exposed and unexposed to ADHD agents. Pediatrics 127:1102–1110
Scherer D, Hassel D, Bloehs R, Zitron E, von Löwenstern K, Seyler C, Thomas D, Konrad F, Bürgers HF, Seemann G, Rottbauer W, Katus HA, Karle CA, Scholz EP (2009) Selective noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor atomoxetine directly blocks hERG currents. Br J Pharmacol 156:226–236
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Christine Kwan for editing and revising this case report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamaguchi, H., Nagumo, K., Nakashima, T. et al. Life-threatening QT prolongation in a boy with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder on atomoxetine. Eur J Pediatr 173, 1631–1634 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-013-2206-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-013-2206-1