Abstract
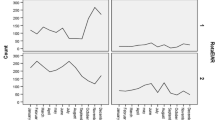
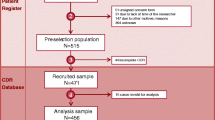
Rotavirus (RV) is a frequent cause of severe gastroenteritis (GE) in children. With the licensure of new RV vaccines, data on the burden of disease are important regarding immunization strategies. We reviewed the medical records of children hospitalized with RV infection in our institution between July 2002 and March 2006. Relevant data were extracted in a standardized fashion from records of hospitalized children with a positive RV antigen test in a stool sample. Severity of disease was graded by the 20-point Vesikari score. Population data were obtained from the Federal Office of Statistics. Six hundred eighty-six RVGE were identified and records of 608 hospitalizations (in 607 children) were available. In 539 (89%) cases, RVGE was the primary reason for hospitalization and 69 (11%) were nosocomial infections; yearly peaks occurred between February and May. Cumulative incidence of RVGE was 26.7/1,000 children <3 years of age. Median age of 539 children (55.6% male) with primary RVGE was 1.4 years and median stay in the hospital for both community acquired and nosocomial RVGE was 4 days (interquartile range 3–5). Thirtypercent and 94% of RV hospitalizations were in children <1 and <3 years of age, respectively. Mean Vesikari score was 15 (range 6–20; 96% >11). Intravenous fluids were administered in 378 (70%) patients, 130 (24%) patients were rehydrated via nasogastral tube, and 31 (5.7%) received rehydration by mouth. RVGE causes a substantial burden in children with an estimated risk for hospitalization due to RVGE of one in 37 children <3 years of age.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albano F, Bruzzese E, Bella A et al (2007) Rotavirus and not age determines gastroenteritis in children: a hospital-based study. Eur J Pediatr 166:241–247. doi:10.1007/s00431-006-0237-6
Alcalde FJ, Bouza JM, Rubio AP et al (2008) Gastroenteritis by rotavirus in Spanish children. Analysis of the disease burden. Eur J Pediatr 167:549–555. doi:10.1007/s00431-007-0550-8
Berner R, Schuhmacher RF, Hameister S et al (1999) Occurrence and impact of community acquired and nosocomial rotavirus infections: a hospital-based study over 10 years. Acta Paediatr Suppl 426:48–52. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.1999.tb14326.x
Bernstein DI, Sack DA, Reisinger K et al (1999) Efficacy of a live attenuated human rotavirus vaccine 89-12 in infants: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 354:287–290. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(98)12106-2
Bevölkerung In: Bundesamt für Statistik (BFS), Herausgeber. Statistisches Jahrbuch der Schweiz, 2001–2004
Bucher B, Aebi C (2006) Population-based epidemiology of rotavirus hospitalisations in Switzerland. Swiss Med Wkly 136:726–731
Centers for disease control and prevention (1999) Intussusception among recipients for rotavirus vaccine: United States, 1998–1999. MMWR 48:577–581
Chang HG, Glass RI, Smith PF et al (2003) Disease burden and risk factors for hospitalizations associated with rotavirus infection among children in New York State, 1989 through 2000. Pediatr Infect Dis J 22:808–814. doi:10.1097/01.inf.0000086404.31634.04
Diez-Domingo J, Martin IO, Sanz AB et al (2006) Rotavirus gastroentritis among children under five years of age in Valencia, Spain. Pediatr Infect Dis J 25:455–457. doi:10.1097/01.inf.0000217378.30444.21
Ehlken B, Laubereau B, Karmaus W et al (2002) Prospective population-based study on rotavirus disease in Germany. Acta Paediatr 91:769–775. doi:10.1080/08035250213227
Floret D, Lina B, Pinchinat S et al (2006) Epidemiology and burden of rotavirus diarrhea in day care centers in Lyon, France. Eur J Pediatr 165:905–906. doi:10.1007/s00431-006-0187-z
Frühwirth M, Heininger U, Ehlken B et al (2001) International variation in disease burden of rotavirus gastroenteritis in children with community- and nosocomially acquired infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J 20:784–791. doi:10.1097/00006454-200108000-00013
Glass RI, Kilgore PE, Holman RC et al (1996) The epidemiology of rotavirus diarrhea in the United States: surveillance and estimates of disease burden. J Infect Dis 174(Suppl):S5–S11
Huppertz HI, Forster J, Heininger U et al (2008) The parental appraisal of the morbidity of diarrhea in infants and toddlers (PAMODI) survey. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 47:363–371. doi:10.1177/0009922807310933
Joensuu J, Koskenniemi E, Pang XL et al (1997) A randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial of rhesus-human reassortant rotavirus vaccine for prevention of severe rotavirus gastroenteritis. Lancet 350:1205–1209. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(97)05118-0
Johansen K, Bennet R, Bondesson K et al (1999) Incidence and estimates of disease burden of rotavirus in Sweden. Acta Paediatr Suppl 88:20–23. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.1999.tb14321.x
Kapikian AZ (1996) Overview of viral gastroenteritis. Arch Virol Suppl 12:7–19
Koopmans M, Van Asperen I (1999) Epidemiology of rotavirus infections in the Netherlands. Acta Paediatr Suppl 88:31–37. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.1999.tb14323.x
Laubereau B, Gateau S, Ehlken B et al (1999) Rotavirus-Gastroenteritis im Säuglings- und Kleinkindesalter. Ergebnisse einer prospektiven Erfassung in den Regionen Genf und Basel 1997/1998 (RoMoS). Schweiz Med Wochenschr 129:1822–1830
Lynch M, O'Halloran F, Whyte D et al (2001) Rotavirus in Ireland: national estimates of disease burden, 1997 to 1998. Pediatr Infect Dis J 20:693–698. doi:10.1097/00006454-200107000-00010
Matson DO, Estes MK (1990) Impact of rotavirus infection at a large pediatric hospital. J Infect Dis 162:598–604
Mrukowicz JZ, Krobicka B, Duplaga M et al (1999) Epidemiology and impact of rotavius diarrhea in Poland. Acta Paediatr Suppl 88:53–60. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.1999.tb14327.x
Parashar UD, Hummelmann EG, Bresee JS et al (2003) Global illness and deaths caused by rotavirus disease in children. Emerg Infect Dis 9:565–572
Raes M, Aerssens Alliet P et al (2008) Rotavirus gastroenteritis: epidemiological data from a regional hospital in Belgium. Eur J Pediatr 167:71–73. doi:10.1007/s00431-007-0428-9
Rennels MB, Glass RI, Dennehy PH et al (1996) Safety and efficacy of high-dose rhesus-human reassortant rotavirus vaccines: report of the national multicenter trial. Pediatrics 97:7–13
Ruggeri FM, Declich S (1999) Rotavirus infection among children with diarrhea in Italy. Acta Paediatr Suppl 426:66–71. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.1999.tb14329.x
Ruuska T, Vesikari T (1990) Rotavirus disease in Finnish children: use of numerical scores for clinical severity of diarrheael episodes. Scand J Infect Dis 22:259–267. doi:10.3109/00365549009027046
Ryan MJ, Ramsay M, Brown D et al (1996) Hospital admissions attributable to Rotavirus infection in England and Wales. J Infect Dis 174(Suppl 1):S12–S18
Tucker AW, Haddix AC, Bresee JS et al (1998) Cost-effectiveness analysis of rotavirus immunization programmed for the United States. JAMA 279:1371–1376. doi:10.1001/jama.279.17.1371
Velazquez FR, Matson DO, Guerrero ML et al (2000) Serum antibody as a marker of protection against natural rotavirus infection and disease. J Infect Dis 182:1602–1609. doi:10.1086/317619
Vesikari T, Clark HF, Offit PA et al (1996) The development of a multivalent bovine rotavirus (strain WC3) reassortant vaccine for infants. J Infect Dis 174(Suppl 1):S73–S80
Vesikari T, Matson DO, Dennehy P et al (2006) Safety and efficacy of a pentavalent human-bovine (WC3) reassortant rotavirus vaccine. N Engl J Med 354:23–33. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa052664
Vesikari T, Rautanen T, Von Bonsdorff CH (1999) Rotavirus gastroenteritis in Finland: burden of disease and epidemiologic features. Acta Paediatr Suppl 426:24–30. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.1999.tb14322.x
Vesikari T, Van Damme P, Giaquinto C et al (2008) European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases/European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition evidence-based recommendations for rotavirus vaccination in Europe: executive summary. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 46:615–618. doi:10.1097/01.mpg.0000319063.86281.40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wildi-Runge, S., Allemann, S., Schaad, U.B. et al. A 4-year study on clinical characteristics of children hospitalized with rotavirus gastroenteritis. Eur J Pediatr 168, 1343–1348 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-009-0934-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-009-0934-z