Abstract
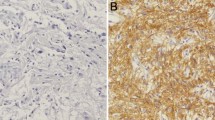
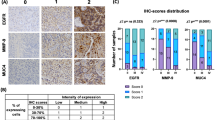
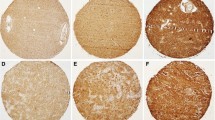
Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN), a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, is present on the surface of tumor cells where it stimulates adjacent fibroblasts to produce matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). We have analyzed the clinicopathological characteristics of EMMPRIN and MMP2 expression in normal brain tissue and pediatric gliomas and evaluated their prognostic value in diagnosing the latter. Immunochemistry analysis revealed EMMPRIN and MMP2 expression in cryo-sections of pediatric gliomas (45 samples) and normal brain tissue (20 samples). Both EMMPRIN and MMP2 were expressed in normal brain and glioma tissues with different levels of malignancy. The intensively positive expression rates of EMMPRIN (22/27) and MMP2 (21/27) in anaplastic astrocytoma and glioblastoma tissues were significantly higher than those in normal brain and low-grade astrocytoma tissues (2/28 and ½8, respectively). Spearman analysis indicated that the expression level of EMMPRIN was significantly positively correlated with that of MMP2 (r = 0.86, p < 0.01). The positive expression of EMMPRIN and MMP2 was associated with higher grade gliomas. Patients with EMMPRIN+/MMP2+ expression had the lowest survival rate (p < 0.01). Based on these results, we conclude that EMMPRIN and MMP2 are expressed differently in normal brain and pediatric gliomas. The detection of their co-expression may facilitate the prediction of pediatric gliomas prognosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- EMMPRIN:
-
Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer
- MMPs:
-
Matrix metalloproteinases
References
Brat DJ, Shehata BM, Castellano-Sanchez AA et al (2007) Congenital glioblastoma: a clinicopathologic and genetic analysis. Brain Pathol 17:276–281
Marieb EA, Zoltan-Jones A (2004) Emmprin promotes anchorage-independent growth in human mammary carcinoma cells by stimulating hyaluronan production. Cancer Res 64:1229–1232
Gabison EE, Mourah S, Steinfels E (2005) Differential expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (CD147) in normal and ulcerated corneas: role in epithelio- stromal interactions and matrix metalloproteinase induction. Am J Pathol 166:209–219
Heppner KJ, Matrisian LM, Jensen RA et al (1996) Expression of most matrix metalloproteinase family members in breast cancer represents a tumor-induced host response. Am J Pathol 149:273–282
Sun J, Hemle ME (2001) Regulation of MMP-1 and MMP-2 production through CD147/extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer interactions. Cancer Res 61:2276–2281
Kleihues P, Burger PC, Scheithauer BW (1993) The new WHO classification of brain tumours. Brain Pathol 3:255–268
Kossakowska AE, Huchcroft SA, Urbanski SJ et al (1996) Comparative analysis of the expression patterns of metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in breast neoplasia, sporadic colorectal neoplasia, pulmonary carcinomas and malignant non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas in humans. Br J Cancer 73:1401–1408
London CA, Sekhon HS, Arora V et al (2003) A novel antisense inhibitor of MMP-9 attenuates angiogenesis, human prostate cancer cell invasion and tumorigenicity. Cancer Gene Ther 10:823–832
Madigan MC, Kingsley EA, Cozzi PJ et al (2008) The role of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer protein in prostate cancer progression. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57:1367–1379
Lanyi M, Antonescu CR (2002) The precrystalline cytoplasmic granules of alveolar soft part sarcoma contain monocarboxylate transporter 1 and CD147. Am J Pathol 160:1215–1221
Mi Z, Oliver T, Guo H et al (2007) Thrombin-cleaved COOH (-) terminal osteopontin peptide binds with cyclophilin C to CD147 in murine breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 67:4088–4097
Nabeshima K, Iwasaki H, Koga K et al (2006) Emmprin (basigin/CD147): matrix metalloproteinase modulator and multifunctional cell recognition molecule that plays a critical role in cancer progression. Pathol Int 56:359–367
Nakada M, Nakamura H, Ikeda E et al (1999) Expression and tissue localization of membrane-types 1, 2 and 3 matrix metalloproteinases in human astrocytic tumors. Am J Pathol 154:417–428
Pulukuri SM, Patibandla S, Patel J et al (2007) Epigenetic inactivation of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2) gene in human prostate tumors. Oncogene 26:5229–5237
Rainov NG, Söling A (2006) Clinical studies with targeted toxins in malignant glioma. Rev Recent Clin Trials 1:119–131
Ranuncolo SM, Armanasco E, Cresta C (2003) Plasma MMP-9 (92 kDa-MMP) activity is useful in the follow-up and in the assessment of prognosis in breast cancer patients. Int J Cancer 106:745–751
Riethdorf S, Reimers N, Assmann V (2006) High incidence of EMMPRIN expression in human tumors. Int J Cancer 119:1800–1810
Sienel W, Hellers J, Morresi-Hauf A (2003) Prognostic impact of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in operable non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer 103:647–651
Zucker S, Hymowitz M, Rollo EE (2001) Tumorigenic potential of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer. Am J Pathol 158:1921–1928
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Vihinen P, Kahari VM (2002) Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer: prognostic markers and therapeutic targets. Int J Cancer 99:157–166
Wykosky J, Gibo DM, Stanton C et al (2005) EphA2 as a novel molecular marker and target in glioblastoma multiform. Mol Cancer Res 3:541–551
Tang Y, Nakada MT (2005) Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer stimulates tumor angiogenesis by elevating ascular endothelial cell growth factor and matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Res 65:3193–3199
Ishibashi Y, Matsumoto T, Niwa M (2004) CD147 and matrix metalloproteinase-2 protein expression as significant prognostic factors in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 101:1994–2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, J., Zhang, C., Chen, R. et al. Clinical implications and prognostic value of EMMPRIN/CD147 and MMP2 expression in pediatric gliomas. Eur J Pediatr 168, 705–710 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-008-0828-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-008-0828-5