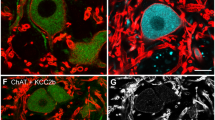
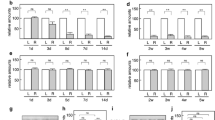
Abstract
Motoneurons of the oculomotor system show lesser vulnerability to neurodegeneration compared to other cranial motoneurons, as seen in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is involved in motoneuronal protection. As previously shown, motoneurons innervating extraocular muscles present a higher amount of VEGF and its receptor Flk-1 compared to facial or hypoglossal motoneurons. Therefore, we aimed to study the possible sources of VEGF to brainstem motoneurons, such as glial cells and target muscles. We also studied the regulation of VEGF in response to axotomy in ocular, facial, and hypoglossal motor nuclei. Basal VEGF expression in astrocytes and microglial cells of the cranial motor nuclei was low. Although the presence of VEGF in the different target muscles for brainstem motoneurons was similar, the presynaptic element of the ocular neuromuscular junction showed higher amounts of Flk-1, which could result in greater efficiency in the capture of the factor by oculomotor neurons. Seven days after axotomy, a clear glial reaction was observed in all the brainstem nuclei, but the levels of the neurotrophic factor remained low in glial cells. Only the injured motoneurons of the oculomotor system showed an increase in VEGF and Flk-1, but such an increase was not detected in axotomized facial or hypoglossal motoneurons. Taken together, our findings suggest that the ocular motoneurons themselves upregulate VEGF expression in response to lesion. In conclusion, the low VEGF expression observed in glial cells suggests that these cells are not the main source of VEGF for brainstem motoneurons. Therefore, the higher VEGF expression observed in motoneurons innervating extraocular muscles is likely due either to the fact that this factor is more avidly taken up from the target muscles, in basal conditions, or is produced by these motoneurons themselves, and acts in an autocrine manner after axotomy.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta L, Morcuende S, Silva-Hucha S, Pastor AM, de la Cruz RR (2018) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) prevents the downregulation of the cholinergic phenotype in axotomized motoneurons of the adult rat. Front Mol Neurosci 11:241
Alexianu ME, Ho B-KB-KK, Mohamed AH, La Bella V, Smith RG, Appel SH (1994) The role of calcium-binding proteins in selective motoneuron vulnerability in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 36:846–858
Arcondéguy T, Lacazette E, Millevoi S, Prats H, Touriol C (2013) VEGF-A mRNA processing, stability and translation: a paradigm for intricate regulation of gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. Nucleic Acids Res 41:7997–8010
Argaw AT, Asp L, Zhang J, Navrazhina K, Pham T, Mariani JN, Mahase S, Dutta DJ, Seto J, Kramer EG, Ferrara N, Sofroniew MV, John GR (2012) Astrocyte-derived VEGF-A drives blood-brain barrier disruption in CNS inflammatory disease. J Clin Invest 122:2454–2468
Azzouz M, Hottinger A, Paterna JC, Zurn AD, Aebischer P, Büeler H (2000) Increased motoneuron survival and improved neuromuscular function in transgenic ALS mice after intraspinal injection of an adeno-associated virus encoding Bcl-2. Hum Mol Genet 9:803–811
Azzouz M, Ralph GS, Storkebaum E, Walmsley LE, Mitrophanous KA, Kingsman SM, Carmeliet P, Mazarakis ND (2004) VEGF delivery with retrogradely transported lentivector prolongs survival in a mouse ALS model. Nature 429:413–417
Bartholdi D, Rubin BP, Schwab ME (1997) VEGF mRNA induction correlates with changes in the vascular architecture upon spinal cord damage in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 9:2549–2560
Benítez-Temiño B, Davis-López de Carrizosa MA, Morcuende S, Matarredona ER, de la Cruz RR, Pastor AM (2016) Functional diversity of neurotrophin actions on the oculomotor system. Int J Mol Sci 17:2016
Bogaert E, Van Damme P, Poesen K, Dhondt J, Hersmus N, Kiraly D, Scheveneels W, Robberecht W, Van Den Bosch L (2010) VEGF protects motor neurons against excitotoxicity by upregulation of GluR2. Neurobiol Aging 31:2185–2191
Bogaert E, Van Damme P, Van Den Bosch L, Robberecht W (2006) Vascular endothelial growth factor in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other neurodegenerative diseases. Muscle Nerve 34:391–405
Brockington A, Ning K, Heath PR, Wood E, Kirby J, Fusi N, Lawrence N, Wharton SB, Ince PG, Shaw PJ (2013) Unravelling the enigma of selective vulnerability in neurodegeneration: motor neurons resistant to degeneration in ALS show distinct gene expression characteristics and decreased susceptibility to excitotoxicity. Acta Neuropathol 125:95–109
Büttner U, Büttner-Ennever JA (2006) Present concepts of oculomotor organization. Prog Brain Res 151:1–42
Calvo PM, de la Cruz RR, Pastor AM (2018a) Synaptic loss and firing alterations in Axotomized Motoneurons are restored by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and VEGF-B. Exp Neurol 304:67–81
Calvo PM, Pastor AM, de la Cruz RR (2018b) Vascular endothelial growth factor: an essential neurotrophic factor for motoneurons? Neural Regen Res 13:1181–1182
Cárdenas-Rivera A, Campero-Romero AN, Heras-Romero Y, Penagos-Puig A, Rincón-Heredia R, Tovar-y-Romo LB (2019) Early post-stroke activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 hinders the receptor 1-dependent neuroprotection afforded by the endogenous ligand. Front Cell Neurosci 13:270
Castañeda-Cabral JL, Beas-Zarate C, Gudiño-Cabrera G, Ureña-Guerrero ME (2017) Glutamate neonatal excitotoxicity modifies VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 protein expression profiles during postnatal development of the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of male rats. J Mol Neurosci 63:17–27
Croll SD, Goodman JH, Scharfman HE (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in seizures: a double-edged sword. Adv Exp Med Biol 548:57–68
Davis-López de Carrizosa MA, Morado-Díaz CJ, Morcuende S, de la Cruz RR, Pastor AM (2010) Nerve growth factor regulates the firing patterns and synaptic composition of motoneurons. J Neurosci 30:8308–8319
Davis-López de Carrizosa MA, Morado-Díaz CJ, Tena JJ, Benítez-Temiño B, Pecero ML, Morcuende S, de la Cruz RR, Pastor AM (2009) Complementary actions of BDNF and neurotrophin-3 on the firing patterns and synaptic composition of motoneurons. J Neurosci 29:575–587
Devos D, Moreau C, Lassalle P, Perez T, De Seze J, Brunaud-Danel V, Destée A, Tonnel AB, Just N (2004) Low levels of the vascular endothelial growth factor in CSF from early ALS patients. Neurology 62:2127–2129
Gould TW, Oppenheim RW (2011) Motor neuron trophic factors: therapeutic use in ALS? Brain Res Rev 67:1–39
Guy R, Grynspan F, Ben-Zur T, Panski A, Lamdan R, Danon U, Yaffe D (2019) Human muscle progenitor cells overexpressing neurotrophic factors improve neuronal regeneration in a sciatic nerve injury mouse model. Front Neurosci 13:151
Haenggeli C, Kato AC (2002) Differential vulnerability of cranial motoneurons in mouse models with motor neuron degeneration. Neurosci Lett 335:39–43
Harandi VM, Gaied ARN, Brännström T, Pedrosa Domellöf F, Liu J-X (2016) Unchanged neurotrophic factors and their receptors correlate with sparing in extraocular muscles in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 57:6831–6842
Hoier B, Hellsten Y (2014) Exercise-induced capillary growth in human skeletal muscle and the dynamics of VEGF. Microcirculation 21:301–314
Ijichi A, Sakuma S, Tofilon PJ (1995) Hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression in normal rat astrocyte cultures. Glia 14:87–93
Kobayashi NR, Bedard AM, Hincke MT, Tetzlaff W (1996) Increased expression of BDNF and trkB mRNA in rat facial motoneurons after axotomy. Eur J Neurosci 8:1018–1029
Koliatsos VE, Crawford TO, Price DL (1991) Axotomy induces nerve growth factor receptor immunoreactivity in spinal motor neurons. Brain Res 549:297–304
Krakora D, Mulcrone P, Meyer M, Lewis C, Bernau K, Gowing G, Zimprich C, Aebischer P, Svendsen CN, Suzuki M (2013) Synergistic effects of GDNF and VEGF on lifespan and disease progression in a familial ALS rat model. Mol Ther 21:1602–1610
Krum JM, Rosenstein JM (1998) VEGF mRNA and its receptor flt-1 are expressed in reactive astrocytes following neural grafting and tumor cell implantation in the adult CNS. Exp Neurol 154:57–65
Lambrechts D et al (2003) VEGF is a modifier of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in mice and humans and protects motoneurons against ischemic death. Nat Genet 34:383–394
Lange C, Storkebaum E, Ruiz De Almodóvar C, Dewerchin M, Carmeliet P (2016) Vascular endothelial growth factor: a neurovascular target in neurological diseases. Nat Rev Neurol 12:439–454
Lennmyr F, Ata KA, Funa K, Olsoon Y, Terént A (1998) Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and its receptors (Flt-1 and Flk-1) following permanent and transient occlusion of the middle cerebral artery in the rat. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 57:874–882
Li B, Xu W, Luo C, Gozal D, Liu R (2003) VEGF-induced activation of the PI3-K/Akt pathway reduces mutant SOD1-mediated motor neuron cell death. Mol Brain Res 111:155–164
Li YN, Pan R, Qin XJ, Yang WL, Qi Z, Liu W, Liu KJ (2014) Ischemic neurons activate astrocytes to disrupt endothelial barrier via increasing VEGF expression. J Neurochem 129:120–129
Lladó J, Tolosa L, Olmos G (2013) Cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the neuroprotective effects of VEGF on motoneurons. Front Cell Neurosci 7:181
Lunn JS, Sakowski SA, Kim B, Rosenberg AA, Feldman EL (2009) Vascular endothelial growth factor prevents G93A-SOD1-induced motor neuron degeneration. Dev Neurobiol 69:871–884
McCloskey DP, Hintz TM, Scharfman HE (2008) Modulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in motor neurons and its electrophysiological effects. Brain Res Bull 76:36–44
Medina L, Figueredo-Cardenas G, Rothstein JD, Reiner A (1996) Differential abundance of glutamate transporter subtypes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)-vulnerable versus ALS-resistant brain stem motor cell groups. Exp Neurol 142:287–295
Morcuende S, Benítez-Temiño B, Pecero ML, Pastor AM, de la Cruz RR (2005) Abducens internuclear neurons depend on their target motoneurons for survival during early postnatal development. Exp Neurol 195:244–256
Morcuende S, Matarredona ER, Benítez-Temiño B, Muñoz-Hernández R, Pastor AM, De la Cruz RR, Pastor ÁM, De la Cruz RR (2011) Differential regulation of the expression of neurotrophin receptors in rat extraocular motoneurons after lesion. J Comp Neurol 519:2335–2352
Morcuende S, Muñoz-Hernández R, Benítez-Temiño B, Pastor AM, de la Cruz RR (2013) Neuroprotective effects of NGF, BDNF, NT-3 and GDNF on axotomized extraocular motoneurons in neonatal rats. Neuroscience 250:31–48
Murakami T, Ilieva H, Shiote M, Nagata T, Nagano I, Shoji M, Abe K (2003) Hypoxic induction of vascular endothelial growth factor is selectively impaired in mice carrying the mutant SOD1 gene. Brain Res 989:231–237
Navarro X, Vivó M, Valero-Cabré A (2007) Neural plasticity after peripheral nerve injury and regeneration. Prog Neurobiol 82:163–201
Nicoletti JN, Shah SK, McCloskey DP, Goodman JH, Elkady A, Atassi H, Hylton D, Rudge JS, Scharfman HE, Croll SD (2008) Vascular endothelial growth factor is up-regulated after status epilepticus and protects against seizure-induced neuronal loss in hippocampus. Neuroscience 151:232–241
Nimchinsky EA, Young WG, Yeung G, Shah RA, Gordon JW, Bloom FE, Morrison JH, Hof PR (2000) Differential vulnerability of oculomotor, facial, and hypoglossal nuclei in G86R superoxide dismutase transgenic mice. J Comp Neurol 416:112–125
Nordal RA, Nagy A, Pintilie M, Wong CS (2004) Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 target genes in central nervous system radiation injury: a role for vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Cancer Res 10:3342–3353
Ogunshola OO, Antic A, Donoghue MJ, Fan SY, Kim H, Stewart WB, Madri JA, Ment LR (2002) Paracrine and autocrine functions of neuronal vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the central nervous system. J Biol Chem 277:11410–11415
Olmstead DN, Mesnard-hoaglin NA, Batka RJ, Haulcomb MM, Miller WM, Jones KJ (2015) Facial nerve axotomy in mice : a model to study motoneuron response to injury. J Vis Exp 96:1–7
Oosthuyse B et al (2001) Deletion of the hypoxia-response element in the vascular endothelial growth factor promoter causes motor neuron degeneration. Nat Genet 28:131–138
Papavassiliou E, Gogate N, Proescholdt M, Heiss JD, Walbridge S, Edwards NA, Oldfield EH, Merrill MJ (1997) Vascular endothelial growth factor (vascular permeability factor) expression in injured rat brain. J Neurosci Res 49:451–460
Plate KH, Beck H, Danner S, Allegrini PR, Wiessner C (1999) Cell type specific upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in an MCA-occlusion model of cerebral infarct. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58:654–666
Pronto-Laborinho AC, Pinto S, de Carvalho M (2014) Roles of vascular endothelial growth factor in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biomed Res Int 947513:1–24
Purves D (1990) Body and brain: a trophic theory of neural connections. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Reiner A, Medina L, Figueredo-Cardenas G, Anfinson S (1995) Brainstem motoneuron pools that are selectively resistant in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are preferentially enriched in parvalbumin: evidence from monkey brainstem for a calcium-mediated mechanism in sporadic ALS. Exp Neurol 131:239–250
Ruiz de Almodovar C, Lambrechts D, Mazzone M, Carmeliet P, Almodovar CRDE, Lambrechts D, Mazzone M (2009) Role and therapeutic potential of VEGF in the nervous system. Physiol Rev 89:607–648
Sathasivam S (2008) VEGF and ALS. Neurosci Res 62:71–77
Senger D, Galli S, Dvorak A, Perruzzi C, Harvey V, Dvorak H (1983) Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science 219:983–985
Silva-Hucha S, Hernández RG, Benítez-Temiño B, Pastor AM, de la Cruz RR, Morcuende S (2017) Extraocular motoneurons of the adult rat show higher levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor Flk-1 than other cranial motoneurons. PLoS ONE 12:e0178616
Sköld M, Cullheim S, Hammarberg H, Piehl F, Suneson A, Lake S, Sjögren A, Walum E, Risling M (2000) Induction of VEGF and VEGF receptors in the spinal cord after mechanical spinal injury and prostaglandin administration. Eur J Neurosci 12:3675–3686
Sköld MK, von Gertten C, Sandberg-Nordqvist A-C, Mathiesen T, Holmin S (2005) VEGF and VEGF receptor expression after experimental brain contusion in rat. J Neurotrauma 22:353–367
Sondell M, Sundler F, Kanje M (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor is a neurotrophic factor which stimulates axonal outgrowth through the flk-1 receptor. Eur J Neurosci 12:4243–4254
Storkebaum E et al (2005) Treatment of motoneuron degeneration by intracerebroventricular delivery of VEGF in a rat model of ALS. Nat Neurosci 8:85–92
Storkebaum E, Lambrechts D, Carmeliet P (2004) VEGF: once regarded as a specific angiogenic factor, now implicated in neuroprotection. BioEssays 26:943–954
Sun Y, Jin K, Xie L, Childs J, Mao XO, Logvinova A, Greenberg DA (2003) VEGF-induced neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J Clin Invest 111:1843–1851
Tolosa L, Mir M, Olmos G, Lladó J (2009) Vascular endothelial growth factor protects motoneurons from serum deprivation-induced cell death through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-mediated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibition. Neuroscience 158:1348–1355
Tonchev AB, Yamashima T, Guo J, Chaldakov GN, Takakura N (2007) Expression of angiogenic and neurotrophic factors in the progenitor cell niche of adult monkey subventricular zone. Neuroscience 144:1425–1435
Tovar-y-Romo LB, Tapia R (2012) Delayed administration of VEGF rescues spinal motor neurons from death with a short effective time frame in excitotoxic experimental models in vivo. ASN Neuro 4:121–129
Van Den Bosch L, Vandenberghe W, Klaassen H, Van Houtte E, Robberecht W (2000) Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors and selective vulnerability of motor neurons. J Neurol Sci 180:29–34
Vanselow BK, Keller BU (2000) Calcium dynamics and buffering in oculomotor neurones from mouse that are particularly resistant during amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)-related motoneurone disease. J Physiol 525(Pt 2):433–445
Vlasova-St. Louis I, Bohjanen PR (2017) Post-transcriptional regulation of cytokine and growth factor signaling in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 33:83–93
von Lewinski F, Keller BU (2005) Ca2+, mitochondria and selective motoneuron vulnerability: implications for ALS. Trends Neurosci 28:494–500
Wang Y, Mao XO, Xie L, Banwait S, Marti HH, Greenberg DA, Jin K (2007) Vascular endothelial growth factor overexpression delays neurodegeneration and prolongs survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mice. J Neurosci 27:304–307
Zheng C, Nennesmo I, Fadeel B, Henter JI (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor prolongs survival in a transgenic mouse model of ALS. Ann Neurol 56:564–567
Zhou D, Huang X, Xie Y, Deng Z, Guo J, Huang H (2019) Astrocytes-derived VEGF exacerbates the microvascular damage of late delayed RBI. Neuroscience 408:14–21
Acknowledgements
Confocal microscopy imaging was performed in the central research services of the Universidad de Sevilla (CITIUS). This work was supported by the Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (Grant reference: BFU2015-64515-P and PGC2018-094654-B-100) and Consejería de Economía, Innovación, Ciencia y Empleo, Junta de Andalucía, BIO-297, in Spain. Confocal images were performed in the Central Research Services of University of Sevilla (CITIUS). We acknowledge Dr. Paul J May from UMMC for helpful comments and editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SM, SSH, AMP, MADLC, and BBT designed the experiments. SM, SSH, BBT, GCR, MEFS, and AMP performed the experiments. SM, SSH, and BBT analyzed and processed the data. SM wrote the manuscript. SM, AMP, MADLC, and BBT proofread and edited the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was carried out in accordance with the recommendations of the University of Seville ethics committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva-Hucha, S., Carrero-Rojas, G., Fernández de Sevilla, M.E. et al. Sources and lesion-induced changes of VEGF expression in brainstem motoneurons. Brain Struct Funct 225, 1033–1053 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-020-02057-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-020-02057-y