Abstract
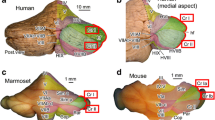
Comparative neuroanatomy provides insights into the evolutionary functional adaptation of specific mammalian cerebellar lobules, in which the lobulation pattern and functional localization are conserved. However, accurate identification of homologous lobules among mammalian species is challenging. In this review, we discuss the inter-species homology of crus I and II lobules which occupy a large volume in the posterior cerebellar hemisphere, particularly in humans. Both crus I/II in humans are homologous to crus I/II in non-human primates, according to Paxinos and colleagues; however, this area has been defined as crus I alone in non-human primates, according to Larsell and Brodal. Our neuroanatomical analyses in humans, macaques, marmosets, rats, and mice demonstrate that both crus I/II in humans are homologous to crus I/II or crus I alone in non-human primates, depending on previous definitions, and to crus I alone in rodents. Here, we refer to the region homologous to human crus I/II lobules as “ansiform area (AA)” across animals. Our results show that the AA’s olivocerebellar climbing fiber and Purkinje cell projections as well as aldolase C gene expression patterns are both distinct and conserved in marmosets and rodents. The relative size of the AA, as represented by the AA volume fraction in the whole cerebellum was 0.34 in human, 0.19 in macaque, and approximately 0.1 in marmoset and rodents. These results indicate that the AA reflects an evolutionarily conserved structure in the mammalian cerebellum, which is characterized by distinct connectivity from neighboring lobules and a massive expansion in skillful primates.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki S, Sato Y, Yanagihara D (2013) Lesion in the lateral cerebellum specifically produces overshooting of the toe trajectory in leading forelimb during obstacle avoidance in the rat. J Neurophysiol 110:1511–1524. doi:10.1152/jn.01048.2012
Balsters JH, Cussans E, Diedrichsen J, Phillips KA, Preuss TM, Rilling JK, Ramnani N (2010) Evolution of the cerebellar cortex: the selective expansion of prefrontal-projecting cerebellar lobules. Neuroimage 49:2045–2052. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.10.045
Barmack NH, Baughman RW, Eckenstein FP, Shojaku H (1992) Secondary vestibular cholinergic projection to the cerebellum of rabbit and rat as revealed by choline acetyltransferase immunohistochemistry, retrograde and orthograde tracers. J Comp Neurol 317:250–270
Batson MA, Petridou N, Klomp DWJ, Frens MA, Neggers SFW (2015) Single session imaging of cerebellum at 7 tesla: obtaining structure and function of multiple motor subsystems in individual subjects. PLoS One 10:e0134933. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0134933
Bauer CA, Kurt W, Sybert LT, Brozoski TJ (2013) The cerebellum as a novel tinnitus generator. Hear Res 295:130–139
Bolk L (1906) Das Cerebellum der Saugetiere, Eine Vergleichend Anatomische Untersuchung. Verlag von Gustav Fischer, Jena
Brodal P (1979) The pontocerebellar projection in the rhesus monkey: an experimental study with retrograde axonal transport of horseradish peroxidase. Neuroscience 4:193–208
Brodal A (1981) Neurological anatomy in relation to clinical medicine, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Brodal P, Bjaalie JG (1992) Organization of the pontine nuclei. Neurosci Res 13:83–118
Buckner RL, Krienen FM, Castellanos A, Diaz JC, Yeo BTT (2011) The organization of the human cerebellum estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity. J Neurophysiol 106:2322–2345. doi:10.1152/jn.00339.2011
Buisseret-Delmas C (1988) Sagittal organization of the olivocerebellonuclear pathway in the rat.II. Connections with the nucleus interpositus. Neurosci Res 5:494–512
Buisseret-Delmas C, Angaut P (1989) Sagittal organisation of the olivocerebellonuclear pathway in the rat. III. Connections with the nucleus dentatus. Neurosci Res 7:131–143
Burne RA, Eriksson MA, Saint-Cyr JA, Woodward DJ (1978) The organization of the pontine projection to lateral cerebellar areas in the rat: dual zones in the pons. Brain Res 139:340–347
Catz N, Thier P (2007) Neural control of saccadic eye movements. Dev Ophthalmol 40:52–75
Coffman KA, Dum RP, Strick PL (2011) Cerebellar vermis is a target of projections from the motor areas in the cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:16068–16073. doi:10.1073/pnas.1107904108
D’Mello AM, Stoodley CJ (2015) Cerebro-cerebellar circuits in autism spectrum disorder. Front Neurosci 9:408. doi:10.3389/fnins.2015.00408
Emmers R, Akert K (1963) A stereotaxic Atlas of the Brain of the Squirrel Monkey (Saimiri sciureus). The University of Wisconsin Press, Madison
Fujita H, Sugihara I (2013) Branching patterns of olivocerebellar axons in relation to the compartmental organization of the cerebellum. Front Neural Circuits 7:3. doi:10.3389/fncir.2013.00003
Fujita H, Oh-Nishi A, Obayashi S, Sugihara I (2010) Organization of the marmoset cerebellum in three-dimensional space: lobulation, aldolase C compartmentalization and axonal projection. J Comp Neurol 518:1764–1791. doi:10.1002/cne.22301
Fujita H, Morita N, Furuichi T, Sugihara I (2012) Clustered fine compartmentalization of the mouse embryonic cerebellar cortex and its rearrangement into the postnatal striped configuration. J Neurosci 32:15688–15703. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1710-12.2012
Fujita H, Aoki H, Ajioka I, Yamazaki M, Abe M, Oh-Nishi A, Sakimura K, Sugihara I (2014) Detailed expression pattern of aldolase C (Aldoc) in the cerebellum, retina and other areas of the CNS studied in Aldoc-Venus knock-in mice. PLoS One 9:e86679. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0086679
Glickstein M, May JG 3rd, Mercier BE (1985) Corticopontine projection in the macaque: the distribution of labelled cortical cells after large injections of horseradish peroxidase in the pontine nuclei. J Comp Neurol 235:343–359
Glickstein M, Sultan F, Voogd J (2011) Functional localization in the cerebellum. Cortex 47:59–80. doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2009.09.001
Graybiel AM (1974) Visuo-cerebellar and cerebello-visual connections involving the ventral lateral geniculate nucleus. Exp Brain Res 20:303–306
Groenewegen HJ, Voogd J, Freedman SL (1979) The parasagittal zonation within the olivocerebellar projection. II. Climbing fiber distribution in the intermediate and hemispheric parts of cat cerebellum. J Comp Neurol 183:551–601
Hanson CL, Chen G, Ebner TJ (2000) Role of climbing fibers in determining the spatial patterns of activation in the cerebellar cortex to peripheral stimulation: an optical imaging study. Neuroscience 96:317–331
Hartmann MJ, Bower JM (2001) Tactile responses in the granule cell layer of cerebellar folium crus IIa of freely behaving rats. J Neurosci 21:3549–3563
Hawkes R, Leclerc N (1987) Antigenic map of the rat cerebellar cortex: the distribution of parasagittal bands as revealed by monoclonal anti-Purkinje cell antibody mobQ113. J Comp Neurol 256:29–41
Huerta MF, Krubitzer LA, Kaas JH (1986) Frontal eye field as defined by intracortical microstimulation in squirrel monkeys, owl monkeys, and macaque monkeys: I. Subcortical connections. J Comp Neurol 253:415–439
Ito M, Nisimaru N, Yamamoto M (1977) Specific patterns of neuronal connexions involved in the control of the rabbit’s vestibulo-ocular reflexes by the cerebellar flocculus. J Physiol 265:833–854
Jahn K, Deutschländer A, Stephan T, Kalla R, Wiesmann M, Strupp M, Brandt T (2008) Imaging human supraspinal locomotor centers in brainstem and cerebellum. Neuroimage 39:786–792
Joyner AL, Herrup K, Auerbach BA, Davis CA, Rossant J (1991) Subtle cerebellar phenotype in mice homozygous for a targeted deletion of the En-2 homeobox. Science 251:1239–1243. doi:10.1126/science.1672471
Kelly RM, Strick PL (2003) Cerebellar loops with motor cortex and prefrontal cortex of a nonhuman primate. J Neurosci 23:8432–8444
Kim CH, Oh SH, Lee JH, Chang SO, Kim J, Kim SJ (2012) Lobule-specific membrane excitability of cerebellar Purkinje cells. J Physiol 590:273–288. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2011.221846
Koekkoek SK, v Alphen AM, vd Burg J, Grosveld F, Galjart N, De Zeeuw CI (1997) Gain adaptation and phase dynamics of compensatory eye movements in mice. Genes Funct 1:175–190
Larsell O (1937) The cerebellum. A review and interpretation. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 38:580–607
Larsell O (1952) The morphogenesis and adult pattern of the lobules and fissures of the cerebellum of the white rat. J Comp Neurol 97:281–356
Larsell O (1953) The cerebellum of the cat and the monkey. J Comp Neurol 99:135–199
Larsell O (1970) The comparative anatomy and histology of the cerebellum from monotremes through apes. The University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis
Larsell O, Jansen J (1972) The comparative anatomy and histology of the cerebellum, the human cerebellum, cerebellar connections and cerebellar cortex. The University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis
Lisberger SG, Fuchs AF (1978) Role of primate flocculus during rapid behavioral modification of vestibuloocular reflex. I. Purkinje cell activity during visually guided horizontal smooth-pursuit eye movements and passive head rotation. J Neurophysiol 41:733–763
Llinás R, Sasaki K (1989) The functional organization of the olivo-cerebellar system as examined by multiple Purkinje cell recordings. Eur J Neurosci 1:587–602
Lou JS, Bloedel JR (1992) Responses of sagittally aligned Purkinje cells during perturbed locomotion: synchronous activation of climbing fiber inputs. J Neurophysiol 68:570–580
MacKay WA, Murphy JT (1979) Cerebellar modulation of reflex gain. Prog Neurobiol 13:361–417
Madigan JC, Carpenter MB (1971) Cerebellum of the Rhesus Monkey, Atlas of Lobules, Laminae, and Folia, in Sections. University Park Press, Baltimore
Marani E, Voogd J (1979) The morphology of the mouse cerebellum. Acta Morphol Neerl Scand 17:33–52
Martinez S, Andreu A, Mecklenburg N, Echevarria D (2013) Cellular and molecular basis of cerebellar development. Front Neuroanat 7:18. doi:10.3389/fnana.2013.00018
Marzban H, Hawkes R (2011) On the architecture of the posterior zone of the cerebellum. Cerebellum 10:422–434. doi:10.1007/s12311-010-0208-3
Mihailoff GA, Burne RA, Azizi SA, Norell G, Woodward DJ (1981) The pontocerebellar system in the rat: an HRP study. II. Hemispheral components. J Comp Neurol 197:559–577
Nieuwenhuys R, Voogd J, Van Huijzen C (2008) The human central nervous system, 4th edn. Springer, Berlin
Ozden I, Dombeck DA, Hoogland TM, Tank DW, Wang SS (2012) Widespread state-dependent shifts in cerebellar activity in locomoting mice. PLoS One 7:e42650. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0042650
Ozol K, Hayden JM, Oberdick J, Hawkes R (1999) Transverse zones in the vermis of the mouse cerebellum. J Comp Neurol 412:95–111
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 6th edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Paxinos G, Huang X-F, Toga AW (2000) The rhesus monkey brain, in steriotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, San Diego
Paxinos G, Huang XF, Petrides M, Toga AW (2009) The rhesus monkey brain, in steriotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic-Elsevier, Amsterdam
Paxinos G, Watson C, Petrides M, Rosa M, Tokuno H (2011) The marmoset brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, San Diego
Pijpers A, Apps R, Pardoe J, Voogd J, Ruigrok TJH (2006) Precise spatial relationships between mossy fibers and climbing fibers in rat cerebellar cortical zones. J Neurosci 26:12067–12080
Quy PN, Fujita H, Sakamoto Y, Na J, Sugihara I (2011) Projection patterns of single mossy fiber axons originating from the dorsal column nuclei mapped on the compartments in the rat cerebellar cortex. J Comp Neurol 519:874–899. doi:10.1002/cne.22555
Sarna JR, Marzban H, Watanabe M, Hawkes R (2006) Complementary stripes of phospholipase Cbeta3 and Cbeta4 expression by Purkinje cell subsets in the mouse cerebellum. J Comp Neurol 496:303–313
Sato Y, Kawasaki T (1984) Functional localization in the three floccular zones related to eye movement control in the cat. Brain Res 290:25–31
Schmahmann JD, Pandya DN (1997) Anatomic organization of the basilar pontine projections from prefrontal cortices in rhesus monkey. J Neurosci 17:438–458
Schmahmann JD, Doyon J, McDonald D, Holmes C, Lavoie K, Hurwitz AS, Kabani N, Toga A, Evans A, Petrides M (1999) Three-dimensional MRI atlas of the human cerebellum in proportional stereotaxic space. Neuroimage 10:233–260
Serapide MF, Panto MR, Parenti R, Zappala A, Cicirata F (2001) Multiple zonal projections of the basilar pontine nuclei to the cerebellar cortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol 430:471–484
Sgaier SK, Lao Z, Villanueva MP, Berenshteyn F, Stephen D, Turnbull RK, Joyner AL (2007) Genetic subdivision of the tectum and cerebellum into functionally related regions based on differential sensitivity to engrailed proteins. Development 134:2325–2335
Shambes GM, Gibson JM, Welker W (1978) Fractured somatotopy in granule cell tactile areas of rat cerebellar hemispheres revealed by micromapping. Brain Behav Evol 15:94–140
Shidara M, Kawano K (1993) Role of Purkinje cells in the ventral paraflocculus in short-latency ocular following responses. Exp Brain Res 93:185–195
Shook BL, Schlag-Rey M, Schlag J (1990) The primate supplementary eye field. I. Comparative aspects of mesencephalic and pontine connections. J Comp Neurol 301:618–642
Sillitoe RV, Marzban H, Larouche M, Zahedi S, Affanni J, Hawkes R (2005) Conservation of the architecture of the anterior lobe vermis of the cerebellum across mammalian species. Prog Brain Res 148:283–297
Smaers JB (2014) Modeling the evolution of the cerebellum: from macroevolution to function. Prog Brain Res 210:193–216. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-63356-9.00008-X
Smith GE (1902) The primary subdivision of the mammalian cerebellum. J Anat Physiol 36:381–385
Springer MS, Stanhope MJ, Madsen O, de Jong WW (2004) Molecules consolidate the placental mammal tree. Trends Ecol Evol 19:430–438
Steele CJ, Anwander A, Bazini PL, Trampel R, Schaefer A, Turner R, Ramnani N, Villringer A (2016) Human cerebellar sub-millimeter diffusion imaging reveals the motor and non-motor topography of the dentate nucleus. Cereb Cortex. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhw258 (Epub)
Stoodley CJ, Schmahmann JD (2009) Functional topography in the human cerebellum: a meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Neuroimage 44:489–501
Strick PL, Dum RP, Fiez JA (2009) Cerebellum and nonmotor function. Annu Rev Neurosci 32:413–434. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125606
Sudarov A, Joyner AL (2007) Cerebellum morphogenesis: the foliation pattern is orchestrated by multi-cellular anchoring centers. Neural Dev 2:26
Sugihara I, Quy PN (2007) Identification of aldolase C compartments in the mouse cerebellar cortex by olivocerebellar labeling. J Comp Neurol 500:1076–1092
Sugihara I, Shinoda Y (2004) Molecular, topographic and functional organization of the cerebellar cortex: a study with combined aldolase C and olivocerebellar labeling. J Neurosci 24:8771–8785
Sugihara I, Shinoda Y (2007) Molecular, topographic and functional organization of the cerebellar nuclei: analysis by three-dimensional mapping of the olivonuclear projection and aldolase C labeling. J Neurosci 27:9696–9710
Sugihara I, Wu HS, Shinoda Y (2001) The entire trajectories of single olivocerebellar axons in the cerebellar cortex and their contribution to cerebellar compartmentalization. J Neurosci 21:7715–7723
Sugihara I, Ebata S, Shinoda Y (2004) Functional compartmentalization in the flocculus and the ventral dentate and dorsal group y nuclei: an analysis of single olivocerebellar axonal morphology. J Comp Neurol 470:113–133
Sugihara I, Fujita H, Na J, Quy PN, Li BY, Ikeda D (2009) Projection of reconstructed single Purkinje cell axons in relation to the cortical and nuclear aldolase C compartments of the rat cerebellum. J Comp Neurol 512:282–304. doi:10.1002/cne.21889
Sultan F, Augath M, Hamodeh S, Murayama Y, Oeltermann A, Rauch A, Thier P (2012) Unravelling cerebellar pathways with high temporal precision targeting motor and extensive sensory and parietal networks. Nat Commun 3:924. doi:10.1038/ncomms1912
Suzuki L, Coulon P, Sabel-Goedknegt EH, Ruigrok TJ (2012) Organization of cerebral projections to identified cerebellar zones in the posterior cerebellum of the rat. J Neurosci 32:10854–10869. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0857-12.2012
Swanson LW (1998) Brain maps: structure of the rat brain, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Voogd J (2004) Cerebellum. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system, 3rd edn. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 205–242
Voogd J, Barmack NH (2006) Oculomotor cerebellum. Prog Brain Res 151:231–268
Voogd J, Pardoe J, Ruigrok TJH, Apps R (2003) The distribution of climbing and mossy fiber collateral branches from the copula pyramidis and the paramedian lobule: congruence of climbing fiber cortical zones and the pattern of zebrin banding within the rat cerebellum. J Neurosci 23:4645–4656
Wadiche JI, Jahr CE (2005) Patterned expression of Purkinje cell glutamate transporters controls synaptic plasticity. Nat Neurosci 8:1329–1334
Watson TC, Becker N, Apps R, Jones MW (2014) Back to front: cerebellar connections and interactions with the prefrontal cortex. Front Syst Neurosci 8:4. doi:10.3389/fnsys.2014.00004
Welker W (1987) Spatial organization of somatosensory projections to granule cell cerebellar cortex: functional and connectional implications of fractured somatotopy (summary of Wisconsin studies). In: King JS (ed) New concepts in cerebellar neurobiology. Liss, New York, pp 239–280
Welsh JP, Lang EJ, Suglhara I, Llinás R (1995) Dynamic organization of motor control within the olivocerebellar system. Nature 374:453–457
Wu HS, Sugihara I, Shinoda Y (1999) Projection patterns of single mossy fibers originating from the lateral reticular nucleus in the rat cerebellar cortex and nuclei. J Comp Neurol 411:97–118
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Jan Voogd for his valuable comments to the manuscript, as well as, Dr. Enrico Marani for sending us a critical reference on mouse cerebellar morphology, Drs. Takafumi Minamimoto (NIRS) and Arata Oh-Nishi (NIRS) for providing the macaque (Japanese monkey) specimen, Dr. A. O.-N. for discussion, Nobuhiro Nitta (NIRS) for technical assistance in the MR imaging experiments, Prof. Emi Schinzinger for interpreting German literature, Gideon Anokye Sarpong for reading the manuscript, and Mr. Minoru Takada for technical assistance. This study was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (KAKENHI; to I.S., 16K070025, 26•04381; to H.F., 26430035; to I.A., 24300167) and COI STREAM Grant of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of Japan (to I.A.). Y.L. was a recipient of the TMDU self-financing international student special research grant and is a recipient of the MEXT scholarship. H.F. was supported by the JSPS postdoctoral fellowship for research abroad. M.S.B. is a recipient of the MEXT scholarship. S.Y. is a recipient of the JSPS invitation fellowship for Research in Japan (Short-Term). H.N. is a recipient of the JSPS Postdoctoral Fellowship for Overseas Researchers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors listed had full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Study concept and design: HF, IS. Acquisition of data: YL, IS (human, macaque, marmoset, rat, mouse), HF (marmoset, rat, mouse), MSB, SY (human), CS, MT, IA (human, macaque). Analysis and annotation of data: YL, HF, IS. Drafting of the manuscript: YL, HF, HN, SY, IS. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: HF, HN, IS. Statistical analysis: YL, IS. Obtained funding: HF, IA, IS. Administrative, technical, and material support: KA, TH, IA, IS. Study supervision: IS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Y., Fujita, H., Nedelescu, H. et al. Lobular homology in cerebellar hemispheres of humans, non-human primates and rodents: a structural, axonal tracing and molecular expression analysis. Brain Struct Funct 222, 2449–2472 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1436-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1436-9