Abstract
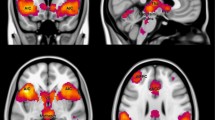
The neural circuits underlying fear learning have been intensively investigated in pavlovian fear conditioning paradigms across species. These studies established a predominant role for the amygdala in fear acquisition, while the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) has been shown to be important in the extinction of conditioned fear. However, studies on morphological correlates of fear learning could not consistently confirm an association with these structures. The objective of the present study was to investigate if interindividual differences in morphology of the amygdala and the vmPFC are related to differences in fear acquisition and extinction learning in humans. We performed structural magnetic resonance imaging in 68 healthy participants who underwent a differential cued fear conditioning paradigm. Volumes of subcortical structures as well as cortical thickness were computed by the semi-automated segmentation software Freesurfer. Stronger acquisition of fear as indexed by skin conductance responses was associated with larger right amygdala volume, while the degree of extinction learning was positively correlated with cortical thickness of the right vmPFC. Both findings could be conceptually replicated in an independent sample of 53 subjects. The data complement our understanding of the role of human brain morphology in the mechanisms of the acquisition and extinction of conditioned fear.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amano T, Unal CT, Pare D (2010) Synaptic correlates of fear extinction in the amygdala. Nat Neurosci 13:489–494
Anders S, Lotze M, Wildgruber D, Erb M, Grodd W, Birbaumer N (2005) Processing of a simple aversive conditioned stimulus in a divided visual field paradigm: an fMRI study. Exp Brain Res 162:213–219
Barnes J et al (2010) Head size, age and gender adjustment in MRI studies: a necessary nuisance? Neuroimage 53:1244–1255
Barrett J, Armony JL (2009) Influence of trait anxiety on brain activity during the acquisition and extinction of aversive conditioning. Psychol Med 39:255–265
Baur V, Hanggi J, Jancke L (2012) Volumetric associations between uncinate fasciculus, amygdala, and trait anxiety. BMC Neurosci 13:4
Benedek M, Kaernbach C (2010a) A continuous measure of phasic electrodermal activity. J Neurosci Methods 190:80–91
Benedek M, Kaernbach C (2010b) Decomposition of skin conductance data by means of non-negative deconvolution. Psychophysiology 47:647–658
Blackmon K et al (2011) Structural evidence for involvement of a left amygdala-orbitofrontal network in subclinical anxiety. Psychiatry Res 194:296–303
Boucsein W, Fowles DC, Grimnes S, Ben-Shakhar G, Roth WT, Dawson ME, Filion DL (2012) Publication recommendations for electrodermal measurements. Psychophysiology 49:1017–1034
Bradley MM, Lang PJ (1994) Measuring emotion: the self-assessment manikin and the semantic differential. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry 25:49–59
Büchel C, Morris J, Dolan RJ, Friston KJ (1998) Brain systems mediating aversive conditioning: an event-related fMRI study. Neuron 20:947–957
Cacciaglia R et al (2013) A risk variant for alcoholism in the NMDA receptor affects amygdala activity during fear conditioning in humans. Biol Psychol 94:74–81
Cacciaglia R, Pohlack ST, Flor H, Nees F (2014) Dissociable roles for hippocampal and amygdalar volume in human fear conditioning. Brain Struct Funct. doi:10.1007/s00429-014-0807-8
Chang CH, Berke JD, Maren S (2010) Single-unit activity in the medial prefrontal cortex during immediate and delayed extinction of fear in rats. PLoS One 5:e11971
Cheng DT, Knight DC, Smith CN, Helmstetter FJ (2006) Human amygdala activity during the expression of fear responses. Behav Neurosci 120:1187–1195
Chung MK, Worsley KJ, Nacewicz BM, Dalton KM, Davidson RJ (2010) General multivariate linear modeling of surface shapes using SurfStat. Neuroimage 53:491–505
Ciocchi S et al (2010) Encoding of conditioned fear in central amygdala inhibitory circuits. Nature 468:277–282
Corcoran KA, Quirk GJ (2007) Activity in prelimbic cortex is necessary for the expression of learned, but not innate, fears. J Neurosci 27:840–844
Coupe P, Yger P, Barillot C (2006) Fast non local means denoising for 3D MR images. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 9:33–40
Dale AM, Fischl B, Sereno MI (1999) Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage 9:179–194
Derix J et al (2014) Visualization of the amygdalo-hippocampal border and its structural variability by 7T and 3T magnetic resonance imaging. Hum Brain Mapp 35:4316–4329
Fischl B, Dale AM (2000) Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11050–11055
Fischl B, Sereno MI, Dale AM (1999) Cortical surface-based analysis. II: inflation, flattening, and a surface-based coordinate system. Neuroimage 9:195–207
Garcia R, Chang CH, Maren S (2006) Electrolytic lesions of the medial prefrontal cortex do not interfere with long-term memory of extinction of conditioned fear. Learn Mem 13:14–17
Gazendam FJ, Kamphuis JH, Kindt M (2013) Deficient safety learning characterizes high trait anxious individuals. Biol Psychol 92:342–352
Gottfried JA, Dolan RJ (2004) Human orbitofrontal cortex mediates extinction learning while accessing conditioned representations of value. Nat Neurosci 7:1144–1152
Haaker J, Lonsdorf TB, Thanellou A, Kalisch R (2013) Multimodal assessment of long-term memory recall and reinstatement in a combined cue and context fear conditioning and extinction paradigm in humans. PLoS One 8:e76179. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0076179
Han X et al (2006) Reliability of MRI-derived measurements of human cerebral cortical thickness: the effects of field strength, scanner upgrade and manufacturer. Neuroimage 32:180–194
Hartley CA, Fischl B, Phelps EA (2011) Brain structure correlates of individual differences in the acquisition and inhibition of conditioned fear. Cereb Cortex 21:1954–1962
Jovanovic T et al (2012) Reduced neural activation during an inhibition task is associated with impaired fear inhibition in a traumatized civilian sample. Cortex 49:1884–1891
Kanai R, Rees G (2011) The structural basis of inter-individual differences in human behaviour and cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:231–242
Knight DC, Waters NS, Bandettini PA (2009) Neural substrates of explicit and implicit fear memory. Neuroimage 45:208–214
Konorsky J (1967) Integrative Activity of the Brain. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Kuperberg GR et al (2003) Regionally localized thinning of the cerebral cortex in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:878–888
LaBar KS, Gatenby JC, Gore JC, LeDoux JE, Phelps EA (1998) Human amygdala activation during conditioned fear acquisition and extinction: a mixed-trial fMRI study. Neuron 20:937–945
Laux L, Glanzmann P, Schaffner P, Spielberger CD (1981) Das State-Trait-Angstinventar (STAI). Beltz-Testgesellschaft, Weinheim, Germany
LeDoux JE (2000) Emotion circuits in the brain. Annu Rev Neurosci 23:155–184
LeDoux JE, Cicchetti P, Xagoraris A, Romanski LM (1990) The lateral amygdaloid nucleus: sensory interface of the amygdala in fear conditioning. J Neurosci 10:1062–1069
Lykken DT, Venables PH (1971) Direct measurement of skin conductance: a proposal for standardization. Psychophysiology 8:656–672
Maren S, Quirk GJ (2004) Neuronal signalling of fear memory. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:844–852
Meulders A, Meulders M, Vlaeyen JW (2014) Positive affect protects against deficient safety learning during extinction of fear of movement-related pain in healthy individuals scoring relatively high on trait anxiety. J Pain 15:632–644
Milad MR, Quirk GJ (2002) Neurons in medial prefrontal cortex signal memory for fear extinction. Nature 420:70–74
Milad MR, Quirk GJ (2012) Fear extinction as a model for translational neuroscience: ten years of progress. Annu Rev Psychol 63:129–151
Milad MR, Vidal-Gonzalez I, Quirk GJ (2004) Electrical stimulation of medial prefrontal cortex reduces conditioned fear in a temporally specific manner. Behav Neurosci 118:389–394
Milad MR, Quinn BT, Pitman RK, Orr SP, Fischl B, Rauch SL (2005) Thickness of ventromedial prefrontal cortex in humans is correlated with extinction memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:10706–10711
Milad MR, Quirk GJ, Pitman RK, Orr SP, Fischl B, Rauch SL (2007a) A role for the human dorsal anterior cingulate cortex in fear expression. Biol Psychiatry 62:1191–1194
Milad MR, Wright CI, Orr SP, Pitman RK, Quirk GJ, Rauch SL (2007b) Recall of fear extinction in humans activates the ventromedial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus in concert. Biol Psychiatry 62:446–454
Morgan MA, Romanski LM, LeDoux JE (1993) Extinction of emotional learning: contribution of medial prefrontal cortex. Neurosci Lett 163:109–113
Ongur D, Price JL (2000) The organization of networks within the orbital and medial prefrontal cortex of rats, monkeys and humans. Cereb Cortex 10:206–219
Pape HC, Pare D (2010) Plastic synaptic networks of the amygdala for the acquisition, expression, and extinction of conditioned fear. Physiol Rev 90:419–463
Pavlov IP (1927) Conditioned reflexes. Oxford University Press, London
Phelps EA, O’Connor KJ, Gatenby JC, Gore JC, Grillon C, Davis M (2001) Activation of the left amygdala to a cognitive representation of fear. Nat Neurosci 4:437–441
Pineles SL, Orr MR, Orr SP (2009) An alternative scoring method for skin conductance responding in a differential fear conditioning paradigm with a long-duration conditioned stimulus. Psychophysiology 46:984–995
Pohlack ST, Nees F, Ruttorf M, Witt SH, Nieratschker V, Rietschel M, Flor H (2011) Risk variant for schizophrenia in the neurogranin gene impacts on hippocampus activation during contextual fear conditioning. Mol Psychiatry 16:1072–1073
Quirk GJ, Mueller D (2008) Neural mechanisms of extinction learning and retrieval. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:56–72
Quirk GJ, Russo GK, Barron JL, Lebron K (2000) The role of ventromedial prefrontal cortex in the recovery of extinguished fear. J Neurosci 20:6225–6231
Ridder S et al (2012) Brain activation during fear conditioning in humans depends on genetic variations related to functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: first evidence from two independent subsamples. Psychol Med 42:2325–2335
Rosas HD, Hevelone ND, Zaleta AK, Greve DN, Salat DH, Fischl B (2005) Regional cortical thinning in preclinical Huntington disease and its relationship to cognition. Neurology 65:745–747
Sehlmeyer C, Schoning S, Zwitserlood P, Pfleiderer B, Kircher T, Arolt V, Konrad C (2009) Human fear conditioning and extinction in neuroimaging: a systematic review. PLoS One 4:e5865
Sierra-Mercado D, Padilla-Coreano N, Quirk GJ (2011) Dissociable roles of prelimbic and infralimbic cortices, ventral hippocampus, and basolateral amygdala in the expression and extinction of conditioned fear. Neuropsychopharmacology 36:529–538
Striedter GF (2005) Principles of brain evolution. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Torrents-Rodas D, Fullana MA, Bonillo A, Caseras X, Andion O, Torrubia R (2013) No effect of trait anxiety on differential fear conditioning or fear generalization. Biol Psychol 92:185–190
van Well S, Visser RM, Scholte HS, Kindt M (2012) Neural substrates of individual differences in human fear learning: evidence from concurrent fMRI, fear-potentiated startle, and US-expectancy data. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 12:499–512
Venables PH, Christie MJ (1980) Electrodermal activity. In: Martin I, Venables PH (eds) Techniques in psychophysiology. John Wiley, New York, pp 2–67
Wittchen HU, Wunderlich U, Gruschwitz S, Zaudig M (1997) SKID-I. Strukturiertes Klinisches Interview für DSM-IV. Hogrefe, Göttingen
Worsley KJ, Taylor JE, Carbonell F, Chung MK, Duerden E, Bernhardt B, Lyttelton O, Boucher M, Evans AC (2009) SurfStat: A Matlab toolbox for the statistical analysis of univariate and multivariate surface and volumetric data using linear mixed effects models and random field theory. In: Proceedings of the 15th annual meeting of the organization for human brain mapping, San Francisco, California, June 2009
Zeidan MA et al (2011) Estradiol modulates medial prefrontal cortex and amygdala activity during fear extinction in women and female rats. Biol Psychiatry 70:920–927
Acknowledgments
We thank Stephanie Ridder, Slawomira Diener, Claudia Liebscher, Birgül Sarun, Claudia Stief and Bettina Kirr for assistance in data acquisition. This work was supported by a grant of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft to H.F. (SFB 636/C01) and to L.R.S (SFB 636/Z03).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winkelmann, T., Grimm, O., Pohlack, S.T. et al. Brain morphology correlates of interindividual differences in conditioned fear acquisition and extinction learning. Brain Struct Funct 221, 1927–1937 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-015-1013-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-015-1013-z