Abstract
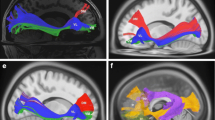
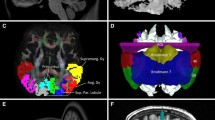
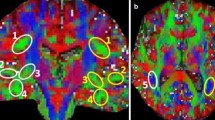
The major language pathways such as superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF) pathways have been outlined by experimental and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) studies. The SLF I and some of the superior parietal lobule connections of the SLF pathways have not been depicted by prior DTI studies due to the lack of imaging sensitivity and adequate spatial resolution. In the current study, the trajectory of the SLF fibers has been delineated on five healthy human subjects using diffusion tensor tractography on a 3.0-T scanner at high spatial resolution. We also demonstrate for the first time the trajectory and connectivity of the SLF fibers in relation to other language pathways as well as the superior parietal lobule connections of the language circuit using high spatial resolution DTI in the healthy adult human brain.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AF:
-
Arcuate fasciculus
- AG:
-
Angular gyrus
- BA:
-
Brodmann area
- Cing:
-
Cingulum
- DTI:
-
Diffusion tensor imaging
- DTT:
-
Diffusion tensor tractography
- DWI:
-
Diffusion-weighted imaging
- EmC:
-
Extreme capsule
- FA:
-
Fractional anisotropy
- FACT:
-
Fiber assignment by continuous tracking
- IFOF:
-
Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus
- ILF:
-
Inferior longitudinal fasciculus
- IPL:
-
Inferior parietal lobule
- MD:
-
Mean diffusivity
- MdLF:
-
Middle longitudinal fasciculus
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- SLF:
-
Superior longitudinal fasciculus
- SLF TP:
-
Temporoparietal portion of superior longitudinal fasciculus
- SMG:
-
Supramarginal gyrus
- SPL:
-
Superior parietal lobule
- UF:
-
Uncinate fasciculus
- WM:
-
White matter
References
Barrick TR, Clark CA (2004) Singularities in diffusion tensor fields and their relevance in white matter fiber tractography. Neuroimage 22:481–491
Ben-Shachar M, Dougherty RF, Wandell BA (2007) White matter pathways in reading. Curr Opin Neurobiol 17:258–270
Bernal B, Altman N (2010) The connectivity of the superior longitudinal fasciculus: a tractography DTI study. Magn Reson Imaging 28:217–225
Borra E, Belmalih A, Calzavara R, Gerbella M, Murata A, Rozzi S, Luppino G (2008) Cortical connections of the macaque anterior intraparietal (AIP) area. Cereb Cortex 18:1094–1111
Breier JI, Hasan KM, Zhang W, Men D, Papanicolaou AC (2008) Language dysfunction after stroke and damage to white matter tracts evaluated using diffusion tensor imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:483–487
Catani M, Ffytche DH (2005) The rises and falls of disconnection syndromes. Brain 128:2224–2239
Catani M, Mesulam M (2008) The arcuate fasciculus and the disconnection theme in language and aphasia: history and current state. Cortex 44:953–961
Catani M, Howard RJ, Pajevic S, Jones DK (2002) Virtual in vivo interactive dissection of white matter fasciculi in the human brain. Neuroimage 17:77–94
Catani M, Piccirilli M, Cherubini A, Tarducci R, Sciarma T, Gobbi G, Pelliccioli G, Petrillo SM, Senin U, Mecocci P (2003) Axonal injury within language network in primary progressive aphasia. Ann Neurol 53:242–247
Catani M, Jones DK, ffytche DH et al (2005) Perisylvian language networks of the human brain. Ann Neurol 57:8–16
Catani M, Allin MP, Husain M, Pugliese L, Mesulam MM, Murray RM, Jones DK (2007) Symmetries in human brain language pathways correlate with verbal recall. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:17163–17168
de Weijer AD, Mandl RC, Diederen KM, Neggers SF, Kahn RS, Hulshoff Pol HE, Sommer IE et al (2011) Microstructural alterations of the arcuate fasciculus in schizophrenia patients with frequent auditory verbal hallucinations. Schizophr Res 130:68–77
Dubois J, Hertz-Pannier L, Cachia A, Mangin JF, Le Bihan D, Dehaene-Lambertz G (2009) Structural asymmetries in the infant language and sensori-motor networks. Cereb Cortex 19:414–423
Fernández-Miranda JC, Rhoton AL Jr, Alvarez-Linera J, Kakizawa Y, Choi C, de Oliveira EP (2008) Three-dimensional microsurgical and tractographic anatomy of the white matter of the human brain. Neurosurgery 62:989–1026; discussion 1026–1028
Fletcher PT, Whitaker RT, Tao R, DuBray MB, Froehlich A, Ravichandran C, Alexander AL, Bigler ED, Lange N, Lainhart JE (2010) Microstructural connectivity of the arcuate fasciculus in adolescents with high-functioning autism. Neuroimage 51:1117–1125
Frey S, Campbell JS, Pike GB, Petrides M (2008) Dissociating the human language pathways with high angular resolution diffusion fiber tractography. J Neurosci 28:11435–11444
Frye RE, Hasan K, Malmberg B, Desouza L, Swank P, Smith K, Landry S (2010) Superior longitudinal fasciculus and cognitive dysfunction in adolescents born preterm and at term. Dev Med Child Neurol 52:760–766
Frye RE, Liederman J, Hasan KM, Lincoln A, Malmberg B, McLean J 3rd, Papanicolaou A (2011) Diffusion tensor quantification of the relations between microstructural and macrostructural indices of white matter and reading. Hum Brain Mapp 32:1220–1235
Galantucci S, Tartaglia MC, Wilson SM, Henry ML, Filippi M, Agosta F, Dronkers NF, Henry RG, Ogar JM, Miller BL, Gorno-Tempini ML (2011) White matter damage in primary progressive aphasias: a diffusion tensor tractography study. Brain 134:3011–3029
Glasser MF, Rilling JK (2008) DTI tractography of the human brain’s language pathways. Cereb Cortex 18:2471–2482
Hains DE (2007) Neuroanatomy. An atlas of structures, sections and systems 7th (edn) Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, New York
Hasan KM, Narayana PA (2003) Computation of the fractional anisotropy and mean diffusivity maps without tensor decoding and diagonalization: theoretical analysis and validation. Magn Reson Med 50:589–598
Hasan KM, Halphen C, Boska MD, Narayana PA (2008) Diffusion tensor metrics, T2 Relaxation and volumetry of the naturally aging human caudate nuclei in healthy young and middle-aged adults: possible implications to the neurobiology of human brain aging and disease. Magn Reson Med 59:7–13
Hasan KM, Kamali A, Kramer LA (2009) Mapping the human brain white matter tracts relative to cortical and deep gray matter using diffusion tensor imaging at high spatial resolution. Magn Reson Imaging 27:631–636
Jang SH, Hong JH (2012) The anatomical characteristics of superior longitudinal fasciculus I in human brain: diffusion tensor tractography study. Neurosci Lett 506:146–148
Jones DK (2008) Studying connections in the living human brain with diffusion MRI. Cortex 44:936–952
Kamali A, Kramer LA, Hasan KM (2010) Feasibility of prefronto-caudate pathway tractography using high resolution diffusion tensor tractography data at 3T. J Neurosci Methods 191:249–254
Koch G, Cercignani M, Pecchioli C, Versace V, Oliveri M, Caltagirone C, Rothwell J, Bozzali M (2010) In vivo definition of parieto-motor connections involved in planning of grasping movements. Neuroimage 51:300–312
Lebel C, Beaulieu C (2009) Lateralization of the arcuate fasciculus from childhood to adulthood and its relation to cognitive abilities in children. Hum Brain Mapp 30:3563–3573
Liu Y, Balériaux D, Kavec M, Metens T, Absil J, Denolin V, Pardou A, Avni F, Van Bogaert P, Aeby A (2010) Structural asymmetries in motor and language networks in a population of healthy preterm neonates at term equivalent age: a diffusion tensor imaging and probabilistic tractography study. Neuroimage 51:783–788
Luppino G, Murata A, Govoni P, Matelli M (1999) Largely segregated parietofrontal connections linking rostral intraparietal cortex (areas AIP and VIP) and the ventral premotor cortex (areas F5 and F4). Exp Brain Res 128:181–187
Makris N, Pandya DN (2009) The extreme capsule in humans and rethinking of the language circuitry. Brain Struct Funct 213:343–358
Makris N, Kennedy DN, McInerney S, Sorensen AG, Wang R, Caviness VS Jr, Pandya DN (2005) Segmentation of subcomponents within the superior longitudinal fascicle in humans: a quantitative, in vivo, DT-MRI study. Cereb Cortex 15:854–869
Makris N, Papadimitriou GM, Kaiser JR, Sorg S, Kennedy DN, Pandya DN (2009) Delineation of the middle longitudinal fascicle in humans: a quantitative, in vivo, DT-MRI study. Cereb Cortex 19:777–785
Mesulam MM (1998) From sensation to cognition. Brain 121:1013–1052
Mori S, van Zijl PC (2002) Fiber tracking: principles and strategies—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:468–480
Petrides M, Pandya DN (1984) Projections to the frontal cortex from the posterior parietal region in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 228:105–116
Petrides M, Pandya DN (2002) Comparative cytoarchitectonic analysis of the human and the macaque ventrolateral prefrontal cortex and corticocortical connection patterns in the monkey. Eur J Neurosci 16:291–310
Poustka L, Jennen-Steinmetz C, Henze R, Vomstein K, Haffner J, Sieltjes B (2012) Fronto-temporal disconnectivity and symptom severity in children with autism spectrum disorder. World J Biol Psychiatry 13:269–280
Rozzi S, Calzavara R, Belmalih A, Borra E, Gregoriou GG, Matelli M, Luppino G (2006) Cortical connections of the inferior parietal cortical convexity of the macaque monkey. Cereb Cortex 16:1389–1417
Schmahmann JD, Pandya DN, Wang R, Dai G, D’Arceuil HE, de Crespigny AJ, Wedeen VJ (2007) Association fibre pathways of the brain: parallel observations from diffusion spectrum imaging and autoradiography. Brain 130:630–653
Schmahmann JD, Smith EE, Eichler FS, Filley CM (2008) Cerebral white matter: neuroanatomy, clinical neurology, and neurobehavioral correlates. Ann NY Acad Sci 1142:266–309
Seltzer B, Pandya DN (1984) Further observations on parieto-temporal connections in the rhesus monkey. Exp Brain Res 55:301–312
Shinoura N, Onodera T, Kurokawa K, Tsukada M, Yamada R, Tabei Y, Koizumi T, Yagi K (2010) Damage to the upper portion of area 19 and the deep white matter in the left inferior parietal lobe, including the superior longitudinal fasciculus, results in alexia with agraphia. Eur Neurol 64:224–229
Turken AU, Dronkers NF (2011) The neural architecture of the language comprehension network: converging evidence from lesion and connectivity analyses. Front Syst Neurosci 5:1
Vandermosten M, Boets B, Poelmans H, Sunaert S, Wouters J, Ghesquière P (2012) A tractography study in dyslexia: neuroanatomic correlates of orthographic, phonological and speech processing. Brain 135(Pt 3):935–948
Wahl M, Li YO, Ng J, Lahue SC, Cooper SR, Sherr EH, Mukherjee P (2010) Microstructural correlations of white matter tracts in the human brain. Neuroimage 51:531–541
Wedeen VJ, Wang RP, Schmahmann JD, Benner T, Tseng WY, Dai G, Pandya DN, Hagmann P, D’Arceuil H, de Crespigny AJ (2008) Diffusion spectrum magnetic resonance imaging (DSI) tractography of crossing fibers. Neuroimage 41:1267–1277
Yeatman JD, Dougherty RF, Rykhlevskaia E, Sherbondy AJ, Deutsch GK, Wandell BA, Ben-Shachar M (2011) Anatomical properties of the arcuate fasciculus predict phonological and reading skills in children. J Cogn Neurosci 23:3304–3317
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Oishi K, Faria AV, Jiang H, Li X, Akhter K, Rosa-Neto P, Pike GB, Evans A, Toga AW, Woods R, Mazziotta JC, Miller MI, van Zijl PC, Mori S (2010) Atlas-guided tract reconstruction for automated and comprehensive examination of the white matter anatomy. Neuroimage 1(52):1289–1301
Acknowledgments
This work is funded by the American National Institutes of Health (NIH)-Institute for Neurological Diseases and Stroke (NIH-NINDS: R01-NS052505-04) and the Dunn Research Foundation. The purchase of the 3.0-T MRI clinical scanner was partially funded by NIH grant S10 RR19186 awarded to Dr. Ponnada A. Narayana. We wish to thank Vipul Kumar Patel for helping in data acquisition.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamali, A., Flanders, A.E., Brody, J. et al. Tracing superior longitudinal fasciculus connectivity in the human brain using high resolution diffusion tensor tractography. Brain Struct Funct 219, 269–281 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-012-0498-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-012-0498-y