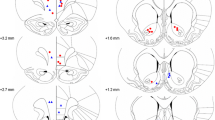
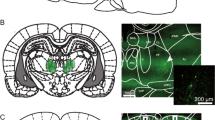
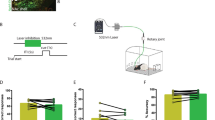
Abstract
On account of its strong efferent projections to the hippocampus, recent animal studies have emphasized an important role for the nucleus reuniens (NRe) of the midline thalamus in spatial memory. However, by virtue of its reciprocal connections with the orbital and ventromedial prefrontal cortex, the NRe may also be involved in aspects of executive inhibition. To date, there has been no systematic attempt to examine the role of the NRe in inhibitory mechanisms of response control. Accordingly, we compared rats with neurotoxic lesions of the NRe with sham surgery controls on performance of the 5-choice reaction time task, a test of visuospatial attention and inhibitory control. When tested post-operatively, rats with NRe lesions were unable to actively inhibit premature responses when the intertrial interval was varied. However, the same rats with NRe lesions showed normal inhibition of perseverative responses, and under some conditions were less perseverative than shams. The NRe lesion was also associated with a reduction in omissions and fast reward collection latencies, which persisted 2 months following surgery. The NRe lesion did not affect response accuracy or latency to respond correctly throughout the course of experimental testing. Together, these results signify the important role of the NRe in impulse inhibition, especially when slight changes are made to the temporal demands of the environment, and reveal the potential contribution of the NRe in motivational processes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggleton JP, Mishkin M (1983) Memory impairments following restricted medial thalamic lesions in monkeys. Exp Brain Res 52:199–209
Bertram EH, Zhang DX (1999) Thalamic excitation of hippocampal CA1 neurons: a comparison with the effects of CA3 stimulation. Neuroscience 92:15–26
Bissonette GB, Martins GJ, Franz TM, Harper ES, Schoenbaum G, Powell EM (2008) Double dissociation of the effects of medial and orbital prefrontal cortical lesions on attentional and affective shifts in mice. J Neurosci 28:11124–11130
Bogousslavsky J, Miklossy J, Deruaz JP, Regli F (1988a) Thalamic aphasia. Neurology 38:1662
Bogousslavsky J, Ferrazzini M, Regli F, Assal G, Tanabe H, Delaloye-Bischof A (1988b) Manic delirium and frontal-like syndrome with paramedian infarction of the right thalamus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:116–119
Bokor H, Csáki A, Kocsis K, Kiss J (2002) Cellular architecture of the nucleus reuniens thalami and its putative aspartatergic/glutamatergic projection to the hippocampus and medial septum in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 16:1227–1239
Burk JA, Mair RG (2001) Effects of intralaminar thalamic lesions on sensory attention and motor intention in the rat: a comparison with lesions involving frontal cortex and hippocampus. Behav Brain Res 123:49–63
Byatt G, Dalrymple-Alford JC (1996) Both anteromedial and anteroventral thalamic lesions impair radial-maze learning in rats. Behav Neurosci 110:1335–1348
Cardinal RN, Aitken MRF (2010) Whisker: a client-server high-performance multimedia research control system. Behav Res Methods 42:1059–1071
Christakou A, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2004) Prefrontal cortical-ventral striatal interactions involved in affective modulation of attentional performance: implications for corticostriatal circuit function. J Neurosci 24:773–780
Chudasama Y, Muir JL (2001) Visual attention in the rat: a role for the prelimbic cortex and thalamic nuclei? Behav Neurosci 115:417–428
Chudasama Y, Robbins TW (2003) Dissociable contributions of the orbitofrontal and infralimbic cortex to pavlovian autoshaping and discrimination reversal learning: further evidence for the functional heterogeneity of the rodent frontal cortex. J Neurosci 23:8771–8780
Chudasama Y, Bussey TJ, Muir JL (2001) Effects of selective thalamic and prelimbic cortex lesions on two types of visual discrimination and reversal learning. Eur J Neurosci 14:1009–1020
Chudasama Y, Passetti F, Rhodes SEV, Lopian D, Desai A, Robbins TW (2003) Dissociable aspects of performance on the 5-choice serial reaction time task following lesions of the dorsal anterior cingulate, infralimbic and orbitofrontal cortex in the rat: differential effects on selectivity, impulsivity and compulsivity. Behav Brain Res 146:105–119
Dalley JW, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (2011) Impulsivity, compulsivity, and top-down cognitive control. Neuron 69:680–694
Daum I, Ackermann H (1994) Frontal-type memory impairment associated with thalamic damage. Int J Neurosci 77:187–198
Davoodi FG, Motamedi F, Naghdi N, Akbari E (2009) Effect of reversible inactivation of the reuniens nucleus on spatial learning and memory in rats using Morris water maze task. Behav Brain Res 198:130–135
Dolleman-van der Weel MJ, da Silva FHL, Witter MP (1997) Nucleus reuniens thalami modulates activity in hippocampal field CA1 through excitatory and inhibitory mechanisms. J Neurosci 17:5640–5650
Dolleman-van der Weel MJ, Morris RGM, Witter MP (2009) Neurotoxic lesions of the thalamic reuniens or mediodorsal nucleus in rats affect non-mnemonic aspects of watermaze learning. Brain Struct Funct 213:329–342
Flämig R, Klingberg F (1978) Participation of thalamic nuclei in the elaboration of conditioned avoidance reflexes of rats. IV. Lesions of the nucleus reuniens. Acta Biol Med Ger 37:1779–1782
Graff-Radford NR, Tranel D, Van Hoesen GW, Brandt JP (1990) Diencephalic amnesia. Brain 113(Pt 1):1–25
Groenewegen HJ (1988) Organization of the afferent connections of the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus in the rat, related to the mediodorsal-prefrontal topography. Neuroscience 24:379–431
Groenewegen HJ, Witter MO (2004) Thalamus. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system, 3rd edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 408–453
Harrison AA, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (1997a) Central 5-HT depletion enhances impulsive responding without affecting the accuracy of attentional performance: interactions with dopaminergic mechanisms. Psychopharmacology 133:329–342
Harrison AA, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (1997b) Doubly dissociable effects of median- and dorsal-raphé lesions on the performance of the five-choice serial reaction time test of attention in rats. Behav Brain Res 89:135–149
Hembrook JR, Mair RG (2011) Lesions of reuniens and rhomboid thalamic nuclei impair radial maze win-shift performance. Hippocampus 21:815–826
Hembrook JR, Onos KD, Mair RG (2011) Inactivation of ventral midline thalamus produces selective spatial delayed conditional discrimination impairment in the rat. Hippocampus (in press)
Herkenham M (1978) The connections of the nucleus reuniens thalami: evidence for a direct thalamo-hippocampal pathway in the rat. J Comp Neurol 177:589–610
Hoover WB, Vertes RP (2007) Anatomical analysis of afferent projections to the medial prefrontal cortex in the rat. Brain Struct Funct 212:149–179
Janowsky JS, Shimamura AP, Kritchevsky M, Squire LR (1989) Cognitive impairment following frontal lobe damage and its relevance to human amnesia. Behav Neurosci 103:548–560
Kelley A, Baldo B, Pratt W (2005) Corticostriatal-hypothalamic circuitry and food motivation: integration of energy, action and reward. Physiol Behav 86:773–795
Liu YP, Wilkinson LS, Robbins TW (2004) Effects of acute and chronic buspirone on impulsive choice and efflux of 5-HT and dopamine in hippocampus, nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 173:175–185
McAlonan K, Brown VJ (2003) Orbital prefrontal cortex mediates reversal learning and not attentional set shifting in the rat. Behav Brain Res 146:97–103
McGilchrist I, Goldstein LH, Jadresic D, Fenwick P (1993) Thalamo-frontal psychosis. Br J Psychiatry 163:113–115
McKenna JT, Vertes RP (2004) Afferent projections to nucleus reuniens of the thalamus. J Comp Neurol 480:115–142
Mitchell AS, Dalrymple-Alford JC (2005) Dissociable memory effects after medial thalamus lesions in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 22:973–985
Mitchell AS, Baxter MG, Gaffan D (2007) Dissociable performance on scene learning and strategy implementation after lesions to magnocellular mediodorsal thalamic nucleus. J Neurosci 27:11888–11895
Muir JL, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (1996) The cerebral cortex of the rat and visual attentional function: dissociable effects of mediofrontal, cingulate, anterior dorsolateral, and parietal cortex lesions on a five-choice serial reaction time task. Cereb Cortex 6:470–481
Murphy ER, Dalley JW, Robbins TW (2005) Local glutamate receptor antagonism in the rat prefrontal cortex disrupts response inhibition in a visuospatial attentional task. Psychopharmacology 179:99–107
Ohtake T, Yamada H (1989) Efferent connections of the nucleus reuniens and the rhomboid nucleus in the rat: an anterograde PHA-L tracing study. Neurosci Res 6:556–568
Partlow GD, del Carpio-O’Donovan R, Melanson D, Peters TM (1992) Bilateral thalamic glioma: review of eight cases with personality change and mental deterioration. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 13:1225–1230
Passetti F, Chudasama Y, Robbins TW (2002) The frontal cortex of the rat and visual attentional performance: dissociable functions of distinct medial prefrontal subregions. Cereb Cortex 12:1254–1268
Passetti F, Dalley JW, Robbins TW (2003) Double dissociation of serotonergic and dopaminergic mechanisms on attentional performance using a rodent five-choice reaction time task. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 165:136–145
Paxinos G, Watson C (2005) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 5th edn. Elsevier Academic Press, New York
Pepin EP, Auray-Pepin L (1993) Selective dorsolateral frontal lobe dysfunction associated with diencephalic amnesia. Neurology 43:733–741
Ragozzino M, Detrick S, Kesner RP (1999) Involvement of the prelimbic–infralimbic areas of the rodent prefrontal cortex in behavioral flexibility for place and response learning. J Neurosci 19:4585–4594
Schoenbaum G, Nugent SL, Saddoris MP, Setlow B (2002) Orbitofrontal lesions in rats impair reversal but not acquisition of go, no-go odor discriminations. Neuroreport 13:885–890
Schoenbaum G, Setlow B, Nugent SL, Saddoris MP, Gallagher M (2003) Lesions of orbitofrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala complex disrupt acquisition of odor-guided discriminations and reversals. Learn Mem 10:129–140
Squire LR, Moore RY (1979) Dorsal thalamic lesion in a noted case of human memory dysfunction. Ann Neurol 6:503–506
Su HS, Bentivoglio M (1990) Thalamic midline cell populations projecting to the nucleus accumbens, amygdala, and hippocampus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 297:582–593
Swanson LW (1998) Brain maps: structure of the rat brain. Elsevier, New York
Sziklas V, Petrides M (1999) The effects of lesions to the anterior thalamic nuclei on object-place associations in rats. Eur J Neurosci 11:559–566
Takagishi M, Chiba T (1991) Efferent projections of the infralimbic (area 25) region of the medial prefrontal cortex in the rat: an anterograde tracer PHA-L study. Brain Res 566:26–39
Van Bockstaele EJ, Biswas A, Pickel VM (1993) Topography of serotonin neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus that send axon collaterals to the rat prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens. Brain Res 624:188–198
Van Der Werf YD, Weerts JG, Jolles J, Witter MP, Lindeboom J, Scheltens P (1999) Neuropsychological correlates of a right unilateral lacunar thalamic infarction. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 66:36–42
Vertes RP (2002) Analysis of projections from the medial prefrontal cortex to the thalamus in the rat, with emphasis on nucleus reuniens. J Comp Neurol 442:163–187
Vertes RP (2004) Differential projections of the infralimbic and prelimbic cortex in the rat. Synapse 51:32–58
Vertes RP, Hoover WB, Do Valle AC, Sherman A, Rodriguez JJ (2006) Efferent projections of reuniens and rhomboid nuclei of the thalamus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 499:768–796
Vertes RP, Linley SB, Hoover WB (2010) Pattern of distribution of serotonergic fibres to the thalamus of the rat. Brain Struct Funct 215:1–28
von Cramon DY, Hebel N, Schuri U (1985) A contribution to the anatomical basis of thalamic amnesia. Brain 108(Pt 4):993–1008
Winstanley CA, Chudasama Y, Dalley JW, Theobald DEH, Glennon JC, Robbins TW (2003) Intra-prefrontal 8-OH-DPAT and M100907 improve visuospatial attention and decrease impulsivity on the five-choice serial reaction time task in rats. Psychopharmacology 167:304–314
Wouterlood FG, Saldana E, Witter MP (1990) Projection from the nucleus reuniens thalami to the hippocampal region: light and electron microscopic tracing study in the rat with the anterograde tracer Phaseolus vulgaris-leucoagglutinin. J Comp Neurol 296:179–203
Zola-Morgan S, Squire LR (1985) Amnesia in monkeys after lesions of the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus. Ann Neurol 17:558–564
Zola-Morgan S, Squire LR, Amaral DG (1986) Human amnesia and the medial temporal region: enduring memory impairment following a bilateral lesion limited to field CA1 of the hippocampus. J Neurosci 6:2950–2967
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), and Canadian Foundation for Innovation-Leaders Opportunity Fund (CFI-LOF) awarded to Y. Chudasama. We wish to thank David A. Leopold, Norman M. White, Andrew R. Abela and Alana Knapman for helpful comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, J.A., Macgregor, E.M. & Chudasama, Y. Lesions of the thalamic reuniens cause impulsive but not compulsive responses. Brain Struct Funct 218, 85–96 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-012-0378-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-012-0378-5