Abstract
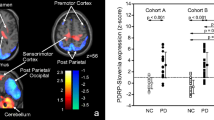
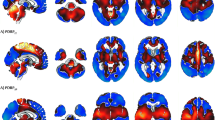
Recent cerebral blood flow (CBF) and glucose consumption (CMRglc) studies of Parkinson’s disease (PD) revealed conflicting results. Using simulated data, we previously demonstrated that the often-reported subcortical hypermetabolism in PD could be explained as an artifact of biased global mean (GM) normalization, and that low-magnitude, extensive cortical hypometabolism is best detected by alternative data-driven normalization methods. Thus, we hypothesized that PD is characterized by extensive cortical hypometabolism but no concurrent widespread subcortical hypermetabolism and tested it on three independent samples of PD patients. We compared SPECT CBF images of 32 early-stage and 33 late-stage PD patients with that of 60 matched controls. We also compared PET FDG images from 23 late-stage PD patients with that of 13 controls. Three different normalization methods were compared: (1) GM normalization, (2) cerebellum normalization, (3) reference cluster normalization (Yakushev et al.). We employed standard voxel-based statistics (fMRIstat) and principal component analysis (SSM). Additionally, we performed a meta-analysis of all quantitative CBF and CMRglc studies in the literature to investigate whether the global mean (GM) values in PD are decreased. Voxel-based analysis with GM normalization and the SSM method performed similarly, i.e., both detected decreases in small cortical clusters and concomitant increases in extensive subcortical regions. Cerebellum normalization revealed more widespread cortical decreases but no subcortical increase. In all comparisons, the Yakushev method detected nearly identical patterns of very extensive cortical hypometabolism. Lastly, the meta-analyses demonstrated that global CBF and CMRglc values are decreased in PD. Based on the results, we conclude that PD most likely has widespread cortical hypometabolism, even at early disease stages. In contrast, extensive subcortical hypermetabolism is probably not a feature of PD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe Y, Kachi T, Kato T, Arahata Y, Yamada T, Washimi Y, Iwai K, Ito K, Yanagisawa N, Sobue G (2003) Occipital hypoperfusion in Parkinson’s disease without dementia: correlation to impaired cortical visual processing. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:419–422
Agniel A, Celsis P, Viallard G, Montastruc JL, Rascol O, Demonet JF, Marc-Vergnes JP, Rascol A (1991) Cognition and cerebral blood flow in lateralised parkinsonism: lack of functional lateral asymmetries. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 54:783–786
Ahl B, Weissenborn K, van den Hoff J, Fischer-Wasels D, Kostler H, Hecker H, Burchert W (2004) Regional differences in cerebral blood flow and cerebral ammonia metabolism in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 40:73–79
Antonini A, De Notaris R, Benti R, De Gaspari D, Pezzoli G (2001) Perfusion ECD/SPECT in the characterization of cognitive deficits in Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Sci 22:45–46
Arahata Y, Hirayama M, Ieda T, Koike Y, Kato T, Tadokoro M, Ikeda M, Ito K, Sobue G (1999) Parieto-occipital glucose hypometabolism in Parkinson’s disease with autonomic failure. J Neurol Sci 163:119–126
Ben-Shachar D, Bonne O, Chisin R, Klein E, Lester H, Aharon-Peretz J, Yona I, Freedman N (2007) Cerebral glucose utilization and platelet mitochondrial complex I activity in schizophrenia: a FDG-PET study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 31:807–813
Berding G, Odin P, Brooks DJ, Nikkhah G, Matthies C, Peschel T, Shing M, Kolbe H, van Den Hoff J, Fricke H, Dengler R, Samii M, Knapp WH (2001) Resting regional cerebral glucose metabolism in advanced Parkinson’s disease studied in the off and on conditions with [(18)F]FDG-PET. Mov Disord 16:1014–1022
Bes A, Guell A, Fabre N, Dupui P, Victor G, Geraud G (1983) Cerebral blood flow studied by Xenon-133 inhalation technique in parkinsonism: loss of hyperfrontal pattern. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 3:33–37
Biesold D, Inanami O, Sato A, Sato Y (1989) Stimulation of the nucleus basalis of Meynert increases cerebral cortical blood flow in rats. Neurosci Lett 98:39–44
Bohnen NI, Minoshima S, Giordani B, Frey KA, Kuhl DE (1999) Motor correlates of occipital glucose hypometabolism in Parkinson’s disease without dementia. Neurology 52:541–546
Borghammer P, Jonsdottir KY, Cumming P, Ostergaard K, Vang K, Ashkanian M, Vafaee M, Iversen P, Gjedde A (2008) Normalization in PET group comparison studies—the importance of a valid reference region. Neuroimage 40:529–540
Borghammer P, Aanerud J, Gjedde A (2009a) Data-driven intensity normalization of PET group comparison studies is superior to global mean normalization. Neuroimage 46(4):981–988
Borghammer P, Cumming P, Aanerud J, Forster S, Gjedde A (2009b) Subcortical elevation of metabolism in Parkinson’s disease—a critical reappraisal in the context of global mean normalization. Neuroimage 47(4):1514–1521
Borghammer P, Cumming P, Aanerud J, Gjedde A (2009c) Artefactual subcortical hyperperfusion in PET studies normalized to global mean: lessons from Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimage 45:249–257
Borghammer P, Ostergaard K, Cumming P, Gjedde A, Rodell A, Hall N, Chakravarty MM (2009d) A deformation-based morphometry study of patients with early-stage Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurol [Epub ahead of print]
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:197–211
Buchsbaum MS, Buchsbaum BR, Hazlett EA, Haznedar MM, Newmark R, Tang CY, Hof PR (2007) Relative glucose metabolic rate higher in white matter in patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 164:1072–1081
Burton EJ, McKeith IG, Burn DJ, Williams ED, O’Brien JT (2004) Cerebral atrophy in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia: a comparison with Alzheimer’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and controls. Brain 127:791–800
Cudennec A, Bonvento G, Duverger D, Lacombe P, Seylaz J, MacKenzie ET (1993) Effects of dorsal raphe nucleus stimulation on cerebral blood flow and flow-metabolism coupling in the conscious rat. Neuroscience 55:395–401
Dagher A, Nagano-Saito A (2007) Functional and anatomical magnetic resonance imaging in Parkinson’s disease. Mol Imaging Biol 9:234–242
Duvernoy HM (1999) The human brain: surface, three-dimensional sectional anatomy with MRI, and blood supply. Springer, Vienna
Eberling JL, Richardson BC, Reed BR, Wolfe N, Jagust WJ (1994) Cortical glucose metabolism in Parkinson’s disease without dementia. Neurobiol Aging 15:329–335
Eckert T, Barnes A, Dhawan V, Frucht S, Gordon MF, Feigin AS, Eidelberg D (2005) FDG PET in the differential diagnosis of parkinsonian disorders. Neuroimage 26:912–921
Eckert T, Van Laere K, Tang C, Lewis DE, Edwards C, Santens P, Eidelberg D (2007) Quantification of Parkinson’s disease-related network expression with ECD SPECT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 34:496–501
Eidelberg D, Moeller JR, Dhawan V, Sidtis JJ, Ginos JZ, Strother SC, Cedarbaum J, Greene P, Fahn S, Rottenberg DA (1990) The metabolic anatomy of Parkinson’s disease: complementary [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose and [18F]fluorodopa positron emission tomographic studies. Mov Disord 5:203–213
Eidelberg D, Moeller JR, Dhawan V, Spetsieris P, Takikawa S, Ishikawa T, Chaly T, Robeson W, Margouleff D, Przedborski S et al (1994) The metabolic topography of parkinsonism. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 14:783–801
Eidelberg D, Moeller JR, Antonini A, Kazumata K, Nakamura T, Dhawan V, Spetsieris P, deLeon D, Bressman SB, Fahn S (1998) Functional brain networks in DYT1 dystonia. Ann Neurol 44:303–312
Feigin A, Antonini A, Fukuda M, De Notaris R, Benti R, Pezzoli G, Mentis MJ, Moeller JR, Eidelberg D (2002) Tc-99m ethylene cysteinate dimer SPECT in the differential diagnosis of parkinsonism. Mov Disord 17:1265–1270
Firbank MJ, Colloby SJ, Burn DJ, McKeith IG, O’Brien JT (2003) Regional cerebral blood flow in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia. Neuroimage 20:1309–1319
Fox PT, Mintun MA, Reiman EM, Raichle ME (1988) Enhanced detection of focal brain responses using intersubject averaging and change-distribution analysis of subtracted PET images. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 8:642–653
Frisina PG, Haroutunian V, Libow LS (2009) The neuropathological basis for depression in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 15:144–148
Gai WP, Halliday GM, Blumbergs PC, Geffen LB, Blessing WW (1991) Substance P-containing neurons in the mesopontine tegmentum are severely affected in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 114(Pt 5):2253–2267
German DC, Manaye KF, White CL III, Woodward DJ, McIntire DD, Smith WK, Kalaria RN, Mann DM (1992) Disease-specific patterns of locus coeruleus cell loss. Ann Neurol 32:667–676
Ghaemi M, Raethjen J, Hilker R, Rudolf J, Sobesky J, Deuschl G, Heiss WD (2002) Monosymptomatic resting tremor and Parkinson’s disease: a multitracer positron emission tomographic study. Mov Disord 17:782–788
Globus M, Mildworf B, Melamed E (1985) Cerebral blood flow and cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 35:1135–1139
Habeck C, Foster NL, Perneczky R, Kurz A, Alexopoulos P, Koeppe RA, Drzezga A, Stern Y (2008) Multivariate and univariate neuroimaging biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 40:1503–1515
Henchcliffe C, Beal MF (2008) Mitochondrial biology and oxidative stress in Parkinson disease pathogenesis. Nature clinical practice 4:600–609
Hirsch EC, Graybiel AM, Duyckaerts C, Javoy-Agid F (1987) Neuronal loss in the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus in Parkinson disease and in progressive supranuclear palsy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:5976–5980
Hosey LA, Thompson JL, Metman LV, van den Munckhof P, Braun AR (2005) Temporal dynamics of cortical and subcortical responses to apomorphine in Parkinson disease: an H2(15)O PET study. Clin Neuropharmacol 28:18–27
Hu MT, Taylor-Robinson SD, Chaudhuri KR, Bell JD, Labbe C, Cunningham VJ, Koepp MJ, Hammers A, Morris RG, Turjanski N, Brooks DJ (2000) Cortical dysfunction in non-demented Parkinson’s disease patients: a combined (31)P-MRS and (18)FDG-PET study. Brain 123(Pt 2):340–352
Huang C, Tang C, Feigin A, Lesser M, Ma Y, Pourfar M, Dhawan V, Eidelberg D (2007) Changes in network activity with the progression of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 130:1834–1846
Imon Y, Matsuda H, Ogawa M, Kogure D, Sunohara N (1999) SPECT image analysis using statistical parametric mapping in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Nucl Med 40:1583–1589
Jellinger K (1988) The pedunculopontine nucleus in Parkinson’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:540–543
Kalpouzos G, Chetelat G, Baron JC, Landeau B, Mevel K, Godeau C, Barre L, Constans JM, Viader F, Eustache F, Desgranges B (2009) Voxel-based mapping of brain gray matter volume and glucose metabolism profiles in normal aging. Neurobiol Aging 30(1):112–124
Karbe H, Holthoff V, Huber M, Herholz K, Wienhard K, Wagner R, Heiss WD (1992) Positron emission tomography in degenerative disorders of the dopaminergic system. J Neural Transm Park Dis Dement Sect 4:121–130
Kikuchi A, Takeda A, Kimpara T, Nakagawa M, Kawashima R, Sugiura M, Kinomura S, Fukuda H, Chida K, Okita N, Takase S, Itoyama Y (2001) Hypoperfusion in the supplementary motor area, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and insular cortex in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 193:29–36
Kimbrell TA, Ketter TA, George MS, Little JT, Benson BE, Willis MW, Herscovitch P, Post RM (2002) Regional cerebral glucose utilization in patients with a range of severities of unipolar depression. Biol Psychiatry 51:237–252
Kitamura S, Ujike T, Kuroki S, Sakamoto S, Soeda T, Iio M, Terashi A (1988) Cerebral blood flow and oxygen metabolism in patients with Parkinson’s disease. No To Shinkei 40:979–985
Kondo S, Tanaka M, Sun X, Okamoto K, Hirai S (1994) Cerebral blood flow and oxygen metabolism in patients with pure akinesia and progressive supranuclear palsy. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 34:531–537
Kuhl DE, Metter EJ, Riege WH (1984) Patterns of local cerebral glucose utilization determined in Parkinson’s disease by the [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose method. Ann Neurol 15:419–424
Lacombe P, Sercombe R, Verrecchia C, Philipson V, MacKenzie ET, Seylaz J (1989) Cortical blood flow increases induced by stimulation of the substantia innominata in the unanesthetized rat. Brain Res 491:1–14
Leenders KL, Wolfson L, Gibbs JM, Wise RJ, Causon R, Jones T, Legg NJ (1985) The effects of l-DOPA on regional cerebral blood flow and oxygen metabolism in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Brain 108(Pt 1):171–191
Ma Y, Tang C, Spetsieris PG, Dhawan V, Eidelberg D (2007) Abnormal metabolic network activity in Parkinson’s disease: test–retest reproducibility. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:597–605
Ma Y, Tang C, Moeller JR, Eidelberg D (2009) Abnormal regional brain function in Parkinson’s disease: truth or fiction? Neuroimage 45:260–266
Minoshima S, Frey KA, Foster NL, Kuhl DE (1995) Preserved pontine glucose metabolism in Alzheimer disease: a reference region for functional brain image (PET) analysis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 19:541–547
Mito Y, Yoshida K, Yabe I, Makino K, Hirotani M, Tashiro K, Kikuchi S, Sasaki H (2005) Brain 3D-SSP SPECT analysis in dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia, and Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 107:396–403
Moeller JR, Strother SC, Sidtis JJ, Rottenberg DA (1987) Scaled subprofile model: a statistical approach to the analysis of functional patterns in positron emission tomographic data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 7:649–658
Moeller JR, Nakamura T, Mentis MJ, Dhawan V, Spetsieres P, Antonini A, Missimer J, Leenders KL, Eidelberg D (1999) Reproducibility of regional metabolic covariance patterns: comparison of four populations. J Nucl Med 40:1264–1269
Montastruc JL, Celsis P, Agniel A, Demonet JF, Doyon B, Puel M, Marc-Vergnes JP, Rascol A (1987) Levodopa-induced regional cerebral blood flow changes in normal volunteers and patients with Parkinson’s disease. Lack of correlation with clinical or neuropsychological improvements. Mov Disord 2:279–289
Nagano-Saito A, Washimi Y, Arahata Y, Kachi T, Lerch JP, Evans AC, Dagher A, Ito K (2005) Cerebral atrophy and its relation to cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease. Neurology 64:224–229
Otsuka M, Ichiya Y, Hosokawa S, Kuwabara Y, Tahara T, Fukumura T, Kato M, Masuda K, Goto I (1991) Striatal blood flow, glucose metabolism and 18F-dopa uptake: difference in Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 54:898–904
Otsuka M, Ichiya Y, Kuwabara Y, Hosokawa S, Sasaki M, Yoshida T, Fukumura T, Kato M, Masuda K (1996) Glucose metabolism in the cortical and subcortical brain structures in multiple system atrophy and Parkinson’s disease: a positron emission tomographic study. J Neurol Sci 144:77–83
Peppard RF, Martin WR, Carr GD, Grochowski E, Schulzer M, Guttman M, McGeer PL, Phillips AG, Tsui JK, Calne DB (1992) Cerebral glucose metabolism in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia. Arch Neurol 49:1262–1268
Perlmutter JS, Raichle ME (1985) Regional blood flow in hemiparkinsonism. Neurology 35:1127–1134
Piert M, Koeppe RA, Giordani B, Minoshima S, Kuhl DE (1996) Determination of regional rate constants from dynamic FDG-PET studies in Parkinson’s disease. J Nucl Med 37:1115–1122
Playford ED, Jenkins IH, Passingham RE, Nutt J, Frackowiak RS, Brooks DJ (1992) Impaired mesial frontal and putamen activation in Parkinson’s disease: a positron emission tomography study. Ann Neurol 32:151–161
Powers WJ, Videen TO, Markham J, Black KJ, Golchin N, Perlmutter JS (2008) Cerebral mitochondrial metabolism in early Parkinson’s disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:1754–1760
Rougemont D, Baron JC, Collard P, Bustany P, Comar D, Agid Y (1984) Local cerebral glucose utilisation in treated and untreated patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47:824–830
Sasaki M, Ichiya Y, Hosokawa S, Otsuka M, Kuwabara Y, Fukumura T, Kato M, Goto I, Masuda K (1992) Regional cerebral glucose metabolism in patients with Parkinson’s disease with or without dementia. Ann Nucl Med 6:241–246
Scarmeas N, Habeck CG, Zarahn E, Anderson KE, Park A, Hilton J, Pelton GH, Tabert MH, Honig LS, Moeller JR, Devanand DP, Stern Y (2004) Covariance PET patterns in early Alzheimer’s disease and subjects with cognitive impairment but no dementia: utility in group discrimination and correlations with functional performance. Neuroimage 23:35–45
Shimada H, Hirano S, Shinotoh H, Aotsuka A, Sato K, Tanaka N, Ota T, Asahina M, Fukushi K, Kuwabara S, Hattori T, Suhara T, Irie T (2009) Mapping of brain acetylcholinesterase alterations in Lewy body disease by PET. Neurology 73(4):273–278
Spetsieris P, Ma Y, Dhawan V, Moeller JR, Eidelberg D (2006) Highly automated computer-aided diagnosis of neurological disorders using functional brain imaging. Proc SPIE: Med Imag 6144:5M1–5M12
Underwood MD, Bakalian MJ, Arango V, Mann JJ (1995) Effect of chemical stimulation of the dorsal raphe nucleus on cerebral blood flow in rat. Neurosci Lett 199:228–230
Van Laere K, Santens P, Bosman T, De Reuck J, Mortelmans L, Dierckx R (2004) Statistical parametric mapping of (99m)Tc-ECD SPECT in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy with predominant parkinsonian features: correlation with clinical parameters. J Nucl Med 45:933–942
Vander Borght T, Minoshima S, Giordani B, Foster NL, Frey KA, Berent S, Albin RL, Koeppe RA, Kuhl DE (1997) Cerebral metabolic differences in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases matched for dementia severity. J Nucl Med 38:797–802
Videbech P, Ravnkilde B, Pedersen TH, Hartvig H, Egander A, Clemmensen K, Rasmussen NA, Andersen F, Gjedde A, Rosenberg R (2002) The Danish PET/depression project: clinical symptoms and cerebral blood flow. A regions-of-interest analysis. Acta Psychiatr Scand 106:35–44
Wolfson LI, Leenders KL, Brown LL, Jones T (1985) Alterations of regional cerebral blood flow and oxygen metabolism in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 35:1399–1405
Worsley KJ, Marrett S, Neelin P, Vandal AC, Friston KJ, Evans AC (1996) A unified statistical approach for determining significant signals in images of cerebral activation. Hum Brain Mapp 4:58–73
Worsley KJ, Liao CH, Aston J, Petre V, Duncan GH, Morales F, Evans AC (2002) A general statistical analysis for fMRI data. Neuroimage 15:1–15
Yakushev I, Hammers A, Fellgiebel A, Schmidtmann I, Scheurich A, Buchholz HG, Peters J, Bartenstein P, Lieb K, Schreckenberger M (2009) SPM-based count normalization provides excellent discrimination of mild Alzheimer’s disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment from healthy aging. Neuroimage 44:43–50
Yanase D, Matsunari I, Yajima K, Chen W, Fujikawa A, Nishimura S, Matsuda H, Yamada M (2005) Brain FDG PET study of normal aging in Japanese: effect of atrophy correction. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 32:794–805
Zarow C, Lyness SA, Mortimer JA, Chui HC (2003) Neuronal loss is greater in the locus coeruleus than nucleus basalis and substantia nigra in Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. Arch Neurol 60:337–341
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by the Danish National Science Foundation (Dansk Grundforskningsfond), and Danish Parkinson’s Disease foundation (Dansk Parkinsonforening).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
These files are unfortunately not in the Publisher's archive anymore:
-
Supplementary material 1 (TIFF 3577 kb)
-
Supplementary material 2 (TIFF 3577 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borghammer, P., Chakravarty, M., Jonsdottir, K.Y. et al. Cortical hypometabolism and hypoperfusion in Parkinson’s disease is extensive: probably even at early disease stages. Brain Struct Funct 214, 303–317 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-010-0246-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-010-0246-0