Abstract
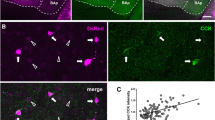
Dopaminergic (DA) inputs to the basolateral nuclear complex of the amygdala (BLC) are critical for several important functions, including reward-related learning, drug-stimulus learning, and fear conditioning. Despite the importance of the DA projection to the BLC, very little is known about which neuronal subpopulations are innervated. The present study utilized dual-labeling immunohistochemistry at the electron microscopic level to examine DA inputs to pyramidal cells in the anterior basolateral amygdalar nucleus (BLa) in the rat. DA axon terminals and BLa pyramidal cells were labeled using antibodies to tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMK), respectively. Serial section reconstructions of TH-positive (TH+) terminals were performed to determine the extent to which these axon terminals formed synapses versus non-synaptic appositions in the BLa. Our results demonstrate that at least 77% of TH+ terminals form synapses in the BLa, and that 90% of these synapses are with pyramidal cells. The distal dendritic compartment received the great majority of these synaptic contacts, with CaMK+ distal dendrites and spines receiving one-third and one-half, respectively, of all synaptic inputs to pyramidal cells. Many spines receiving innervation from TH+ terminals also received asymmetrical synaptic inputs from putative excitatory terminals. In addition, TH+ terminals often formed non-synaptic appositions with axon terminals, most of which were putatively excitatory in that they were CaMK+ and/or made asymmetrical synapses. Thus, using CaMK as a marker, the present study demonstrates that pyramidal cells, especially their distal dendritic compartments, are the primary targets of dopaminergic inputs to the basolateral amygdala.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrzejewski ME, Spencer RC, Kelley AE (2005) Instrumental learning, but not performance, requires dopamine D1-receptor activation in the amygdala. Neuroscience 135:335–345
Asan E (1993) Comparative single and double immunolabelling with antisera against catecholamine biosynthetic enzymes: criteria for the identification of dopaminergic, noradrenergic and adrenergic structures in selected rat brain areas. Histochemistry 99:427–442
Asan E (1997) Ultrastructural features of tyrosine-hydroxylase-immunoreactive afferents and their targets in the rat amygdala. Cell Tissue Res 288:449–469. doi:10.1007/s004410050832
Asan E (1998) The catecholaminergic innervation of the rat amygdala. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 142:1–118
Bissière S, Humeau Y, Lüthi A (2003) Dopamine gates LTP induction in lateral amygdala by suppressing feed forward inhibition. Nat Neurosci 6:587–592. doi:10.1038/nn1058
Blair HT, Schafe GE, Bauer EP, Rodrigues SM, LeDoux JE (2001) Synaptic plasticity in the lateral amygdala: a cellular hypothesis of fear conditioning. Learn Mem 8:229–242
Bowers D, Miller K, Mikos A, Kirsch-Darrow L, Springer U, Fernandez H et al (2006) Startling facts about emotion in Parkinson’s disease: blunted reactivity to aversive stimuli. Brain 129:3356–3365. doi:10.1093/brain/awl301
Brinley-Reed M, McDonald AJ (1999) Evidence that dopaminergic axons provide a dense innervation of specific neuronal subpopulations in the rat basolateral amygdala. Brain Res 850:127–135. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(99)02112-5
Brinley-Reed M, Mascagni F, McDonald AJ (1995) Synaptology of prefrontal cortical projections to the basolateral amygdala: an electron microscopic study in the rat. Neurosci Lett 202:45–48. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(95)12212-5
Carlsen J, Heimer L (1988) The basolateral amygdaloid complex as a cortical-like structure. Brain Res 441:377–380. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(88)91418-7
Coco ML, Kuhn CM, Ely TD, Kilts CD (1992) Selective activation of mesoamygdaloid dopamine neurons by conditioned stress: attenuation by diazepam. Brain Res 590:39–47. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(92)91079-T
Descarries L, Mechawar N (2000) Ultrastructural evidence for diffuse transmission by monoamine and acetylcholine neurons of the central nervous system. In: Agnati LF, Fuxe K, Nicholson C, Sykova E (eds) Volume transmission revisited. Prog Brain Res 125:27–47
Descarries L, Séguéla P, Watkins KC (1991) Nonjunctional relationships of monoamine axon terminals in the cerebral cortex of adult rat. In: Fuxe K, Agnati LF (eds) Volume transmission in the brain: novel mechanisms for neural transmission. Raven Press, New York, pp 53–62
Descarries L, Watkins KC, Garcia S, Bosler O, Doucet G (1996) Dual character, asynaptic and synaptic, of the dopamine innervation in adult rat neostriatum: a quantitative autoradiographic and immunocytochemical analysis. J Comp Neurol 375:167–186. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19961111)375:2<167::AID-CNE1>3.0.CO;2-0
Di Ciano P, Everitt BJ (2005) Neuropsychopharmacology of drug seeking: insights from studies with second-order schedules of drug reinforcement. Eur J Pharmacol 526:186–198. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.09.024
Erondu NE, Kennedy MB (1985) Regional distribution of type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in rat brain. J Neurosci 5:3270–3277
Faber ES, Sah P (2004) Opioids inhibit lateral amygdala pyramidal neurons by enhancing a dendritic potassium current. J Neurosci 24:3031–3039
Fallon JH, Ciofi P (1992) Distribution of monoamines within the amygdala. In: Aggleton JP (ed) The amygdala. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 97–114
Farb CR, LeDoux JE (1999) Afferents from rat temporal cortex synapse on lateral amygdala neurons that express NMDA and AMPA receptors. Synapse 33:218–229. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(19990901)33:3<218::AID-SYN6>3.0.CO;2-1
Farb CR, Aoki C, LeDoux JE (1995) Differential localization of NMDA and AMPA receptor subunits in the lateral and basal nuclei of the amygdala: a light and electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol 362:86–108. doi:10.1002/cne.903620106
Garris PA, Wightman RM (1994a) Different kinetics govern dopaminergic transmission in the amygdala, prefrontal cortex, and striatum: an in vivo voltammetric study. J Neurosci 14:442–450
Garris PA, Wightman RM (1994b) In vivo voltammetric measurement of evoked extracellular dopamine in the rat basolateral amygdaloid nucleus. J Physiol 478:239–249
Grace AA, Rosenkranz JA (2002) Regulation of conditioned responses of basolateral amygdala neurons. Physiol Behav 77:489–493. doi:10.1016/S0031-9384(02)00909-5
Hall E (1972) The amygdala of the cat: a Golgi study. Z Zellforsch 134:439–458. doi:10.1007/BF00307668
Hancock MB (1986) Two color immunoperoxidase staining: visualization of anatomic relationships between immunoreactive neural elements. Am J Anat 175:343–352. doi:10.1002/aja.1001750216
Harmer CJ, Phillips GD (1999) Enhanced dopamine efflux in the amygdala by a predictive, but not a non-predictive, stimulus: facilitation by prior repeated d-amphetamine. Neuroscience 90:119–130. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(98)00464-3
Huang YY, Kandel ER (1995) D1/D5 receptor agonists induce a protein synthesis-dependent late potentiation in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:2446–2450. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.7.2446
Huang YY, Kandel ER (1996) D1/D5 receptors mediate a protein synthesis-dependent late phase of LTP in the amygdala. Soc Neurosci, Abstracts 22:#135.16
Inglis FM, Moghaddam B (1999) Dopaminergic innervation of the amygdala is highly responsive to stress. J Neurochem 72:1088–1094. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0721088.x
Kröner S, Rosenkranz JA, Grace AA, Barrionuevo G (2005) Dopamine modulates excitability of basolateral amygdala neurons in vitro. J Neurophysiol 93:1598–1610. doi:10.1152/jn.00843.2004
Lalumiere RT, Nguyen LT, McGaugh JL (2004) Post-training intrabasolateral amygdala infusions of dopamine modulate consolidation of inhibitory avoidance memory: involvement of noradrenergic and cholinergic systems. Eur J Neurosci 20:2804–2810
Lammel S, Hetzel A, Häckel O, Jones I, Liss B, Roeper J (2008) Unique properties of mesoprefrontal neurons within a dual mesocorticolimbic dopamine system. Neuron 57:760–773
Lamprecht R, LeDoux J (2004) Structural plasticity and memory. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:45–54. doi:10.1038/nrn1301
Lanciego JL, Goede PH, Witter MP, Wouterlood FG (1997) Use of peroxidase substrate vector VIP for multiple staining in light microscopy. J Neurosci Methods 74:1–7. doi:10.1016/S0165-0270(97)02226-7
LeDoux JE, Farb CR, Milner TA (1991) Ultrastructure and synaptic associations of auditory thalamo-amygdala projections in the rat. Exp Brain Res 85:577–586. doi:10.1007/BF00231742
Lewis DA (1992) The catecholaminergic innervation of primate prefrontal cortex. J Neural Transm 36:179–200
Lorétan K, Bissière S, Lüthi A (2004) Dopaminergic modulation of spontaneous inhibitory network activity in the lateral amygdala. Neuropharmacology 47:631–639. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2004.07.015
Maren S (1999) Long-term potentiation in the amygdala: a mechanism for emotional learning and memory. Trends Neurosci 22:561–567. doi:10.1016/S0166-2236(99)01465-4
Martina M, Bergeron R (2008) D1 and D4 dopaminergic receptor interplay mediates coincident G-protein-independent and dependent regulation of glutamate NMDA receptors in the lateral amygdala. J Neurochem (Jul):23. Epub ahead of print
McDonald AJ (1992) Cell types and intrinsic connections of the amygdala. In: Aggleton JP (ed) The amygdala. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 67–96
McDonald AJ, Muller JF, Mascagni F (2002) GABAergic innervation of alpha type II calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase immunoreactive pyramidal neurons in the rat basolateral amygdala. J Comp Neurol 446:199–218. doi:10.1002/cne.10204
Muller JF, Mascagni F, McDonald AJ (2003) Synaptic connections of distinct interneuronal subpopulations in the rat basolateral amygdalar nucleus. J Comp Neurol 456:217–236. doi:10.1002/cne.10435
Muller JF, Mascagni F, McDonald AJ (2005) Coupled networks of parvalbumin-immunoreactive interneurons in the rat basolateral amygdala. J Neurosci 25:7366–7376. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0899-05.2005
Muller JF, Mascagni F, McDonald AJ (2006) Pyramidal cells of the rat basolateral amygdala: synaptology and innervation by parvalbumin immunoreactive interneurons. J Comp Neurol 494:635–650. doi:10.1002/cne.20832
Muller JF, Mascagni F, McDonald AJ (2007a) Postsynaptic targets of somatostatin-containing interneurons in the rat basolateral amygdala. J Comp Neurol 500:513–529. doi:10.1002/cne.21185
Muller JF, Mascagni F, McDonald AJ (2007b) Serotonin-immunoreactive axon terminals innervate pyramidal cells and interneurons in the rat basolateral amygdala. J Comp Neurol 505:314–335. doi:10.1002/cne.21486
Nakano Y, Lénárd L, Oomura Y, Nishino H, Aou S, Yamamoto T (1987) Functional involvement of catecholamines in reward-related neuronal activity of the monkey amygdala. J Neurophysiol 57:72–91
Neely MD, Schmidt DE, Deutch AY (2007) Cortical regulation of dopamine depletion-induced dendritic spine loss in striatal medium spiny neurons. Neuroscience 149:457–464. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.06.044
Papadopoulos GC, Parnavelas JG, Buijs RM (1989) Light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical analysis of the dopamine innervation of the rat visual cortex. J Neurocytol 18:303–310. doi:10.1007/BF01190833
Paré D, Smith Y, Paré JF (1995) Intra-amygdaloid projections of the basolateral and basomedial nuclei in the cat: Phaseolus vulgaris-leucoagglutinin anterograde tracing at the light and electron microscopic level. Neuroscience 69:567–583. doi:10.1016/0306-4522(95)00272-K
Paré D, Royer S, Smith Y, Lang EJ (2003) Contextual inhibitory gating of impulse traffic in the intra-amygdaloid network. Ann N Y Acad Sci 985:78–91
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Peters A, Harriman KM (1988) Enigmatic bipolar cell of rat visual cortex. J Comp Neurol 267:409–432. doi:10.1002/cne.902670310
Peters A, Harriman KM (1992) Different kinds of axon terminals forming symmetric synapses with the cell bodies and initial axon segments of layer II/III pyramidal cells. III. Origins and frequency of occurrence of the terminals. J Neurocytol 21:679–692. doi:10.1007/BF01191729
Peters A, Palay SL, Webster HD (1991) The fine structure of the nervous system. Oxford University Press, New York
Pezze MA, Feldon J (2004) Mesolimbic dopaminergic pathways in fear conditioning. Mesolimbic dopaminergic pathways in fear conditioning. Prog Neurobiol 74:301–320. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2004.09.004
Pickel VM, Colago EE, Mania I, Molosh AI, Rainnie DG (2006) Dopamine D1 receptors co-distribute with N-methyl-d-aspartic acid type-1 subunits and modulate synaptically-evoked N-methyl-d-aspartic acid currents in rat basolateral amygdala. Neuroscience 142:671–690. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.06.059
Pinto A, Sesack SR (2008) Ultrastructural analysis of prefrontal cortical inputs to the rat amygdala: spatial relationships to presumed dopamine axons and D1 and D2 receptors. Brain Struct Funct 213:159–175
Rademacher DJ, Kovacs B, Shen F, Napier TC, Meredith GE (2006) The neural substrates of amphetamine conditioned place preference: implications for the formation of conditioned stimulus-reward associations. Eur J Neurosci 24:2089–2097
Radley JJ, Johnson LR, Janssen WG, Martino J, Lamprecht R, Hof PR et al (2006) Associative Pavlovian conditioning leads to an increase in spinophilin-immunoreactive dendritic spines in the lateral amygdala. Eur J Neurosci 24:876–884. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04962.x
Rainnie DG, Asprodini EK, Shinnick-Gallagher P (1993) Intracellular recordings from morphologically identified neurons of the basolateral amygdala. J Neurophysiol 69:1350–1361
Robinson TE, Kolb B (2004) Structural plasticity associated with exposure to drugs of abuse. Neuropharmacology 47(Suppl 1):33–46. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2004.06.025
Rodrigues SM, Schafe GE, LeDoux JE (2004) Molecular mechanisms underlying emotional learning and memory in the lateral amygdala. Neuron 44:75–91. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2004.09.014
Rosenkranz JA, Grace AA (2001) Dopamine attenuates prefrontal cortical suppression of sensory inputs to the basolateral amygdala of rats. J Neurosci 21:4090–4103
Rosenkranz JA, Grace AA (2002a) Cellular mechanisms of infralimbic and prelimbic prefrontal cortical inhibition and dopaminergic modulation of basolateral amygdala neurons in vivo. J Neurosci 22:324–337
Rosenkranz JA, Grace AA (2002b) Dopamine-mediated modulation of odour-evoked amygdala potentials during pavlovian conditioning. Nature 417:282–287. doi:10.1038/417282a
See RE (2005) Neural substrates of cocaine-cue associations that trigger relapse. Eur J Pharmacol 526:140–146. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.09.034
Séguéla P, Watkins KC, Descarries L (1988) Ultrastructural features of dopamine axon terminals in the anteromedial and the suprarhinal cortex of adult rat. Brain Res 442:11–22. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(88)91427-8
Sesack SR (2002) Synaptology of dopamine neurons. In: Di Chiara G (ed) Handbook of experimental pharmacology, dopamine in the CNS I, vol 154/1. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 63–119
Sesack SR, Hawrylak VA, Matus C, Guido MA, Levey AI (1998) Dopamine axon varicosities in the prelimbic division of the rat prefrontal cortex exhibit sparse immunoreactivity for the dopamine transporter. J Neurosci 18:2697–2708
Sesack SR, Carr DB, Omelchenko N, Pinto A (2003) Anatomical substrates for glutamate-dopamine interactions: evidence for specificity of connections and extrasynaptic actions. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1003:36–52. doi:10.1196/annals.1300.066
Smiley JF, Goldman-Rakic PS (1993) Heterogeneous targets of dopamine synapses in monkey prefrontal cortex demonstrated by serial section electron microscopy: a laminar analysis using the silver-enhanced diaminobenzidine sulfide (SEDS) immunolabeling technique. Cereb Cortex 3:223–238. doi:10.1093/cercor/3.3.223
Smiley JF, Williams MS, Szigeti K, Goldman-Rakic PS (1992) Light and electron microscopic characterization of dopamine-immunoreactive axons in human cerebral cortex. J Comp Neurol 321:325–335. doi:10.1002/cne.903210302
Smiley JF, Morrell F, Mesulam MM (1997) Cholinergic synapses in human cerebral cortex: an ultrastructural study in serial sections. Exp Neurol 144:361–368. doi:10.1006/exnr.1997.6413
Smith Y, Paré D (1994) Intra-amygdaloid projections of the lateral nucleus in the cat: PHA-L anterograde labeling combined with postembedding GABA and glutamate immunocytochemistry. J Comp Neurol 342:232–248. doi:10.1002/cne.903420207
Smith Y, Paré J-F, Paré D (2000) Differential innervation of parvalbumin-immunoreactive interneurons of the basolateral amygdaloid complex by cortical and intrinsic inputs. J Comp Neurol 416:496–508. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(20000124)416:4<496::AID-CNE6>3.0.CO;2-N
Stefanacci L, Farb CR, Pitkänen A, Go G, LeDoux JE, Amaral DG (1992) Projections from the lateral nucleus to the basal nucleus of the amygdala: a light and electron microscopic PHA-L study in the rat. J Comp Neurol 323:586–601. doi:10.1002/cne.903230411
Tessitore A, Hariri AR, Fera F, Smith WG, Chase TN, Hyde TM et al (2002) Dopamine modulates the response of the human amygdala: a study in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 22:9099–90103
Van Haeften T, Wouterlood FG (2000) Neuroanatomical tracing at high resolution. J Neurosci Methods 103:107–116
Washburn MS, Moises HC (1992) Electrophysiological and morphological properties of rat basolateral amygdaloid neurons in vitro. J Neurosci 12:4066–4079
Wolf ME, LeWitt PA, Bannon MJ, Dragovic LJ, Kapatos G (1991) Effect of aging on tyrosine hydroxylase protein content and the relative number of dopamine nerve terminals in human caudate. J Neurochem 56:1191–1200. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb11410.x
Yoshimura N, Kawamura M, Masaoka Y, Homma I (2005) The amygdala of patients with Parkinson’s disease is silent in response to fearful facial expressions. Neuroscience 131:523–534. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.09.054
Zoli M, Torri C, Ferrari R, Jansson A, Zini I, Fuxe K et al (1998) The emergence of the volume transmission concept. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 26:136–147. doi:10.1016/S0165-0173(97)00048-9
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Courtney Pinard for assistance with the preparation of the light micrographs. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant R01-NS38998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muller, J.F., Mascagni, F. & McDonald, A.J. Dopaminergic innervation of pyramidal cells in the rat basolateral amygdala. Brain Struct Funct 213, 275–288 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-008-0196-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-008-0196-y