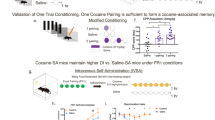
Abstract
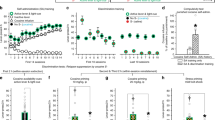
One of the most insidious features of cocaine addiction is a high rate of relapse even after extended periods of abstinence. A wide variety of drug-associated stimuli, including the context in which a drug is taken, can gain incentive motivational properties that trigger drug desire and relapse to drug-seeking. Both animal and clinical studies suggest that extensive cocaine exposure may induce a transition from cortical to striatal control over decision-making as compulsive drug-seeking emerges. Using an animal model of relapse to cocaine-seeking, the present study investigated the expression patterns of three different activity-related genes (c-fos, zif/268, and arc) in cortical and striatal brain regions implicated in compulsive drug-seeking in order to determine the neuroadaptations that occur during context-induced relapse following brief or prolonged abstinence from cocaine self-administration. Re-exposure to the environment previously associated with cocaine self-administration following 22 h or 15 days of abstinence produced a significant increase in zif/268 and arc, but not c-fos mRNA, in the caudate-putamen and nucleus accumbens. With the exception of arc mRNA levels following 15 days of abstinence, all three genes were increased in the anterior cingulate cortex of animals with a cocaine history when they were re-exposed to the operant chamber. Additionally, c-fos, zif/268, and arc expression was differentially affected in the motor and sensory cortices at both timepoints. Together, these results support convergent evidence that drug-seeking induced by a cocaine-paired context changes the activity of corticostriatal circuits.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balleine BW, Delgado MR, Hikosaka O (2007) The role of the dorsal striatum in reward and decision-making. J Neurosci 27:8161–8165
Berglind WJ, See RE, Fuchs RA, Ghee SM, Whitfield TW, Miller SW, McGinty JF (2007) A BDNF infusion into the medial prefrontal cortex suppresses cocaine-seeking in rats. Eur J NeuroSci 26:757–766
Berke JD, Hyman SE (2000) Addiction, dopamine, and the molecular mechanisms of memory. Neuron 25:515–532
Bhat RV, Baraban JM (1993) Activation of transcription factor genes in striatum by cocaine: role of both serotonin and dopamine systems. J Pharmacol Exper Ther 267:496–505
Bozon B, Kelly A, Josselyn SA, Silva AJ, Davis S, Laroche S (2003) MAPK, CREB and zif268 are all required for the consolidation of recognition memory. Phil Trans R Soc Lond 358:805–814
Breiter HC, Rosen BR (1999) Functional magnetic resonance imaging of brain reward circuitry in the human. Ann N Y Acad Sci 877:523–547
Brown EE, Robertson GS, Fibiger HC (1992) Evidence for conditional neuronal activation following exposure to a cocaine-paired environment: role of forebrain limbic structures. J Neurosci 12:4112–4121
Bush G, Vogt BA, Holmes J, Dale AM, GreveD D, Jenike MA, Rosen BR (2001) Dorsal anterior cingulate cortex: a role in reward-based decision making. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:523–528
Carter CS, Braver TS, Barch DM, Botvinick MM, Noll D, Cohen JD (1998) Anterior cingulate cortex, error detection, and the online monitoring of performance. Science 280:747–749
Childress AR, Mozley PD, McElgin W, Fitzgerald J, Reivich M, O’Brien CP (1999) Limbic activation during cue-induced cocaine craving. Am J Psychiatry 156:11–18
Chowdhury S, Shepherd JD, Okuno H, Lyford G, Petralia RS, Plath N, Kuhl D, Huganir RL, Worley PF (2006) Arc/Arg3.1 interacts with the endocytotic machiinery to regulate AMPA receptor trafficking. Neuron 52:445–459
Ciccocioppo R, Sanna PP, Weiss F (2001) Cocaine-predictive stimulus induces drug-seeking behavior and neural activation in limbic brain regions after multiple months of abstinence: reversal by D(1) antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1976–1981
Crawford CA, McDougall SA, Bolanos CA, Hall S, Berger SP (1995) The effects of the kappa agonist U-50, 488 on cocaine-induced conditioned and unconditioned behaviors and Fos immunoreactivity. Psychopharmacology 120:392–399
Crombag HS, Shaham Y (2002) Renewal of drug seeking by contextual cues after prolonged extinction in rats. Behav Neurosci 116:169–173
Curran T, Morgan JL (1995) Fos: an immediate-early transcription factor in neurons. J Neurobiol 26:403–412
Daunais JB, McGinty JF (1994) Acute and chronic cocaine administration differentially alters striatal opioid and nuclear transcription factor mRNAs. Synapse 18:35–45
Daunais JB, McGinty JF (1995) Cocaine binges differentially alter striatal preprodynorphin and zif/268 mRNAs. Brain Res 29:201–210
Davis S, Bozon B, Laroche S (2003) How necessary is the activation of the immediate early gene zif268 in synaptic plasticity and learning? Behav Brain Res 142:17–30
Ehrman RN, Robbins SJ, Childress AR, O’Brien CP (1992) Conditioned responses to cocaine-related stimuli in cocaine abuse patients. Psychopharmacology 107:523–529
Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (2000) Second-order schedules of drug reinforcement in rats and monkeys: measurement of reinforcing efficacy and drug-seeking behaviour. Psychopharmacology 153:17–30
Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (2005) Neural systems of reinforcement for drug addiction: from actions to habits to compulsion. Nat Neurosci 8:1481–1489
Everitt BJ, Wolf ME (2002) Psychomotor stimulant addiction: a neural systems perspective. J Neurosci 22:3312–3320
Everitt BJ, Dickinson A, Robbins TW (2001) The neuropsychological basis of addictive behaviour. Brain Res Rev 36:129–138
Fosnaugh JS, Bhat RV, Yamagata K, Worley PF, Baraban JM (1995) Activation of arc, a putative “effector” immediate early gene, by cocaine in rat brain. J Neurochem 64:2377–2380
Fuchs RA, Evans KA, Ledford CC, Parker MP, Case JM, Mehta RH, See RE (2005) The role of the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex, basolateral amygdala, and dorsal hippocampus in contextual reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:296–309
Fuchs RA, Branham RK, See RE (2006) Differential neural substrates mediate cocaine seeking after abstinence versus extinction training: a critical role for the dorsolateral caudate-putamen. J Neurosci 26:3584–3588
Fumagalli F, Bedogni F, Frasca A, Di Pasquale L, Racagni G, Riva MA (2006) Corticostriatal up-regulation of activity-regulated cytoskeletal-associated protein expression after repeated exposure to cocaine. Mol Pharmacol 70:1726–1734
Garavan H, Pankiewicz J, Bloom A, Cho JK, Sperry L, Ross TJ, Salmeron BJ, Risinger R, Kelley D, Stein EA (2000) Cue-induced cocaine craving: neuroanatomical specificity for drug users and drug stimuli. Am J Psychiatry 157:1789–1798
Gawin FH (1991) Cocaine addiction: psychology and neurophysiology. Science 251:1580–1586
Graybiel AM, Moratalla R, Robertson HA (1990) Amphetamine and cocaine induce drug-specific activation of the c-fos gene in striosome-matrix compartments and limbic subdivisions of the striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6912–6916
Guzowski JF, Lyford GL, Stevenson GD, Houston FP, McGaugh JL, Worley PF, Barnes CA (2000) Inhibition of activity-dependent arc protein expression in the rat hippocampus impairs the maintenance of long-term potentiation and the consolidation of long-term memory. J Neurosci 20:3993–4001
Hall J, Thomas KL, Everitt BJ (2001) Cellular imaging of zif268 expression in the hippocampus and amygdala during contextual and cued fear memory retrieval: selective activation of hippocampal CA1 neurons during the recall of contextual memories. J Neurosci 21:2186–2193
Hearing MC, Miller SW, See RE, McGinty JF (2008) Relapse to cocaine-seeking increases activity-regulated gene expression. Psychopharmacology (in press)
Hyman SE (2005) Addiction: a disease of learning and memory. Am J Psychiatry 162:1414–1422
Ito R, Dalley JW, Robbbins TW, Everitt BJ (2002) Dopamine release in the dorsal striatum during cocaine-seeking behavior under the control of a drug-associated cue. J Neurosci 22:6247–6253
James AB, Conway A-M, Morris BJ (2005) Genomic profiling of the neuronal target genes of the plasticity-related transcription factor-Zif268. J Neurochem 95:796–810
Jentsch JD, Taylor JR (1999) Impulsivity resulting from frontostriatal dysfunction in drug abuse: implications ht e control of behavior by reward-related stimuli. Psychopharmacology 146:373–390
Jog MS, Kubota Y, Connolly CI, Hillegaart V, Graybiel AM (1999) Building neural representations of habits. Science 286:1745–1749
Kerns JG (2006) Anterior cingulate and prefrontal cortex activity in an FMRI study of trial-to-trial adjustments on the Simon task. Neuroimage 33:399–405
Lu L, Grimm JW, Hope BT, Shaham Y (2004) Incubation of cocaine craving after withdrawal: a review of preclinical data. Neuropharmacology 47(Suppl 1):214–226
Macey DJ, Rice WN, Freedland CS, Whitlow CT, Porrino LJ (2004) Patterns of functional activity associated with cocaine self-administration in the rat change over time. Psychopharmacology 172:384–392
Malkani S, Wallace KJ, Donley MP, Rosen JB (2004) An egr–1 (zif268) antisense oligodeoxynucleotide infused into the amygdala disrupts fear-conditioning. Learn Mem 11:617–624
Moratalla R, Robertson HA, Graybiel AM (1992) Dynamic regulation of NGFI-A (zif268, egr1) gene expression in the striatum. J Neurosci 12:2609–2622
Neisewander JL, Baker DA, Fuchs RA, Tran-Nguyen LT, Palmer A, Marshall JF (2000) Fos protein expression and cocaine-seeking behavior in rats after exposure to a cocaine self-administration environment. J Neurosci 20:798–805
O’Brien RJ, Lau LF, Huganir RL (1998) Conditioning factors in drug abuse: can they explain compulsion? J Psychopharmacol 12:15–22
Packard MG, Knowlton BJ (2002) Learning and memory functions of the Basal Ganglia. Annu Rev Neurosci 25:563–593
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 6th edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Plath N, Ohana O, Dammermann B, Errington ML, Schmitz D, Gross C, Mao X, Engelsberg A, Mahlke C, Welzl H, Kobalz U, Stawrakakis A, Fernandez E, Waltereit R, Bick-Sander A, Therstappen E, Cooke SF, Blanquet V, Wurst W, Salmen B, Bosl MR, Lipp HP, Grant SG, Bliss TV, Wolfer DP, Kuhl D (2006) Arc/Arg3.1 is essential for the consolidation of synaptic plasticity and memories. Neuron 52:437–444
Porrino LJ, Lyons D, Smith HR, Daunais JB, Nader MA (2004) Cocaine self-administration produces a progressive involvement of limbic, association, and sensorimotor striatal domains. J Neurosci 24:3554–3562
Rial Verde EM, Lee-Osbourne J, Worley PF, Malinow R, Cline HT (2006) Increased expression of the immediate-early gene arc/arg3.1 reduces AMPA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission. Neuron 52:461–474
Tan A, Moratalla R, Lyford GL, Worley P, Graybiel AM (2000) The activity-regulated cytoskeletal-associated protein arc is expressed in different striosome-matrix patterns following exposure to amphetamine and cocaine. J Neurochem 74:2074–2078
Thomas KL, Hall J, Everitt BJ (2002) Cellular imaging with zif268 expression in the rat nucleus accumbens and frontal cortex further dissociates the neural pathways activated following the retrieval of contextual and cued fear memory. Eur J Neurosci 16:1789–1796
Thomas KL, Arroyo M, Everitt BJ (2003) Induction of the learning and plasticity-associated gene Zif268 following exposure to a discrete cocaine-associated stimulus. Eur J Neurosci 17:1964–1972
Tiffany ST (1990) A cognitive model of drug urges and drug-use behavior: role of automatic and nonautomatic processes. Psychol Rev 97(2):147–168
Torres G, Rivier C (1993) Cocaine-induced expression of c-fos in the rat is inhibited by NMDA receptro antagonisyts. Brain Res Bull 30:173–176
Valjent E, Aubier B, Corbille AG, Brami-Cherrier K, Caboche J, Topilko P, Girault JA, Herve D (2006) Plasticity-associated gene Krox24/Zif268 is required for long-lasting behavioral effects of cocaine. J Neurosci 26:4956–4960
Vanderschuren LJ, Everitt BJ (2004) Drug seeking becomes compulsive after prolonged cocaine self-administration. Science 305:1017–1019
Vanderschuren LJ, Di Ciano P, Everitt BJ (2005) Involvement of the dorsal striatum in cue-controlled cocaine seeking. J Neurosci 25:8665–8670
Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wang GJ, Swanson JM (2004) Dopamine in drug abuse and addiction: results from imaging studies and treatment implications. Mol Psychiatry 9:557–569
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Telang F, Fowler JS, Logan J, Childress AR, Jayne M, Ma Y, Wong C (2006) Cocaine cues and dopamine in dorsal striatum: mechanism of craving in cocaine addiction. J Neurosci 26:6583–6588
Wang JQ, McGinty JF (1995) Dose-dependent alteration in zif/268 and preprodynorphin mRNA expression induced by amphetamine or methamphetamine in rat forebrain. J Pharmacol Exper Ther 273:909–917
Wang JQ, Daunais JB, McGinty JF (1994a) NMDA receptors mediate amphetamine-induced upregulation of zif268 and preprodynorphin mRNA expression in rat striatum. Synapse 18:343–353
Wang JQ, Daunais JB, McGinty JF (1994b) Role of kainate/AMPA receptors in induction of zif268 and preprodynorphin mRNA by a single injection of amphetamine. Mol Brain Res 27:118–126
West AE, Griffith EC, Greenberg ME (2002) Regulation of transcription factors by neuronal activity. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:921–931
White NM, McDonald RJ (2002) Multiple parallel memory systems in the brain of the rat. Neurobiol Learn Mem 77:125–184
Worley PF, Bhat RV, Baraban JM, Erickson CA, McNaughton BL, Barnes CA (1993) Thresholds for synaptic activation of transcription factors in hippocampus: correlation with long-term enhancement. J Neurosci 13:4776–4786
Young ST, Porrino LJ, Iadarola MJ (1991) Cocaine induces striatal c-fos-immunoreactive proteins via dopaminergic D1 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:1291–1295
Zavala AR, Biswas S, Harlan RE, Neisewander JL (2007) Fos and glutamate AMPA receptor subunit coexpression associated with cue-elicited cocaine-seeking behavior in abstinent rats. Neuroscience 145:438–452
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Shannon Ghee and Anthony Carnell for excellent technical support and Scott W. Miller for statistical consultation. This research was supported by P50 DA15369 and CO6RR015455.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hearing, M.C., See, R.E. & McGinty, J.F. Relapse to cocaine-seeking increases activity-regulated gene expression differentially in the striatum and cerebral cortex of rats following short or long periods of abstinence. Brain Struct Funct 213, 215–227 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-008-0182-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-008-0182-4