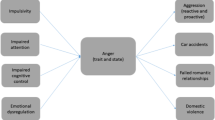
Abstract
The current review examined the research and current models of anger from three distinct literatures: psychophysiology, neuropsychology and the cognitive-behavioral perspective. Two primary conceptual difficulties are addressed in this review. First, the debate over how and when to differentiate between anger and hostility is discussed. Second, the issue regarding cognitive or emotional dominance or primacy in the experience of anger is considered. Once the conceptual ambiguity is addressed, data from the cognitive-behavioral, psychophysiological and neuropsychological literatures are reviewed with a focus on issues of laterality. Particular attention is given to research of appraisal theory from the cognitive literature, cortical arousal and related cerebral models from the psychophysiological literature, and functional cerebral systems from the neuropsychological literature. Despite significant differences appearing both within and between the bodies of literature, when viewed without the traditional ambiguity surrounding this topic, there appears to be a great deal of overlap which may be conducive to the construction of a unified theoretical model. Such a model is proposed in the final section of this paper.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolphs R, Damasio H, Tranel D (1996) Cortical systems for the recognition of emotion in facial expressions. J Neurosci 16:7678–7687
Allred KD, Smith TW (1991) Social cognition in cynical hostility. Cognit Ther Res 15:399–412
Adolphs R, Tranel D, Hamann S, Young AW, Calder AJ, Phelps E, Anderson A, Lee AR, Damasio AR (1999) Recognition of facial emotion in nine individuals with bilateral amygdale damage. Neuropsychologia 37:1111–1117
American Psychiatric Association (1994) The Diagnostic and statistic manual of mental disorders (4th edn). APA Publishers, Wasington DC
Andrews DA, Bonta J (2003) Psychology of criminal conduct. Anderson Press, Cincinnati, pp 277–299
Beauchaine D (2001) Vagal tone, development, and Gray’s motivational theory: toward an integrated model of autonomic nervous system functioning in psychopathology. Dev Psychopathol 13:183–214
Barrett LF, Wager TD (2006) The structure of emotion: Evidence from neuroimaging studies. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 15:70–83
Beauregard M, Levesque J, Bourgouin P (2001) Neural correlates of conscious self-regulation of emotion. J Neurosci 21:165
Beck R, Fernandez E (1998) Cognitive-behavioral self-regulation of the frequency, duration, and intensity of anger. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 20:217–229
Beck AT, Epstein N, Harrison R (1983) Cognitions, attitudes and personality dimensions in depression. Br J Cognit Psychother 1:1–16
Beck AT, Emery G, Greenberg RL (1996) Cognitive therapy for evaluation anxieties. In: Lindemann CG (eds) Handbook of the treatment of the anxiety disorders. Jason Aronson, Inc, Lanham, pp 26–54
Berkowitz L (1993) Aggression: its causes, consequences, and control. McGraw-Hill, New York
Biaggio MK, Supplee K, Curtis N (1981) Reliability and validity of 4 anger scales. Pers Assess 45:639–648
Block GW, Nanson JL, Lowry NJ, (1999) Attention, memory and language after pediatric ischemic stroke. Child Neuropsychol 5:81–91
Bolmont B, Thullier F, Abraini JH (2000) Relationships between mood states and performances in reaction time, psychomotor ability and mental efficiency during a 31-day gradual decompression in a hypobaric chamber from sea level to 8848 m equivalent altitude. Physiol Behav 71:469–476
Borod JC, Koff E, White B (1983) Facial asymmetry in posed and spontaneous expressions of emotion. Brain Cogn 2:165–175
Borod JC, Cicero BA, Obler LK (1998) Right hemisphere emotional perception: Evidence across multiple channels. Neuropsychology 12:446–458
Buck R (1977) Nonverbal communication of affect in preschool children: relationships with personality and skin conductance. J Pers Soc Psychol 35:225–236
Buss AH (1961) The psychology of aggression. Wiley, Oxford
Carver CS, White TL (1994) Behavioral inhibition, behavioral activation, and affective responses to impending reward and punishment: The BIS/BAS Scales. J Pers Soc Psychol 67:279–301
Christie IC, Friedman BH (2003) Autonomic specificity of discrete emotion and dimensions of affective space: A multivariate approach. Int J Psychophysiol 51:143–153
Cole HW, Ray WJ (1985) EEG correlates of emotional tasks related to attentional demands. Int J Psychophysiol 3:33–41
Cook WW, Medley DM (1954) Proposed hostility and Pharisaic-virtue scales for the MMPI. J Appl Psychol 38:414–418
Critchley HD, Elliot R, Mathias CJ, Dolan RJ (2000) Neural activity relating to the generation and representation of galvanic skin conductance responses: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Neurosci 20:3033–3040
Damasio AR (1989) Time-locked multiregional retroactivation: A systems-level proposal for the neural substrates of recall and recognition. Cognition 33:25–62
Damasio H, Damasio AR (2000) Emotion, decision making and the orbitofrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 10:295–307
Davidson RJ (2000) Affective style, psychopathology, and resilience: brain mechanisms and plasticity. Am Psychol 55:1196–1214
Davidson RJ (1998) Affective style and affective disorders: Perspectives from affective neuroscience. Cogn Emot 12:307–330
Davidson RJ (1995) Cerebral asymmetry, emotion, and affective style. In: Davidson RJ, Hugdahl K (eds) Brain asymmetry. The MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 127–143
Davidson RJ (1994) Asymmetric brain function, affective style, and psychopathology: the role of early experience and plasticity. Dev Psychopathol 6:741–758
Davidson RJ (1993) Cerebral asymmetry and emotion: conceptual and methodological conundrums. Cogn Emot 7:115–138
Davidson RJ (1992) Anterior cerebral asymmetry and the nature of emotion. Brain Cogn 20:125–151
Davidson RJ, Fox NA (1982) Asymmetrical brain activity discriminates between positive and negative affective stimuli in human infants. Science 218:235–1237
Davidson RJ, Schwartz GE (1977) Brain mechanisms subserving self-generated imagery: electrophysiological specificity and patterning. Psychophysiology 14:598–602
Davidson RJ, Ekman P, Saron CD, Senulis A, Friesen BR (1990) Approach/withdrawal and cerebral asymmetry: emotional expression and brain physiology. J Pers Soc Psychol 58:330–341
Davidson RJ, Abercrombie H, Nitschke JB, Putnam K (1999) Regional brain function, emotion and disorders of emotion. Curr Opin Neurobiol 9:228–234
Day A, Howells K (2002) Psychological treatments for rehabilitating offenders: evidence-based practice comes of age. Aust Psychol 37:39–47
Deffenbacher JL (1994) Anger reduction: issues, assessment, and intervention strategies. In: Siegman AW, Smith TW (eds) Anger, hostility, and the heart. Earlbaum, Hillsdale, pp 319–337
Deffenbacher JL, Oetting ER, Huff ME (1996) Evaluation of two cognitive-behavioral approaches to general anger reduction. Cogn Ther Res 20:551–573
Deffenbacher JL, Petrilli RT, Lynch RS, Oetting PD, Swain C (2003) The Driver’s angry thoughts questionnaire: a measure of angry cognitions when driving. Cognit Ther Res 27:383–402
Demaree HA (2000) Analysis of quantitative electroencephalographic and cardiovascular responses to stress among low- and high-hostiles. Diss Abstr Int B Sci Eng 61(1-B):526
Demaree HA, Harrison DW (1997) Physiological and neuropsychological correlates of hostility. Neuropsychologia 35:1405–1411
Demaree HA, Higgins DA, Williamson J, Harrison DW (2002) Asymmetry in hand grip strength and fatigue in low- and high-hostile men. Int J Neurosci 112:415–428
Demaree HA, Robinson JL, Everhart DE, Schmeichel BJ (2004) Resting RSA is associated with natural and self-regulated responses to negative emotional stimuli. Brain Cogn 56:14–23
Demaree HA, Everhart ED, Youngstrom EA, Harrison DW (2005) Brain lateralization of emotional processing: historical roots and a future incorporating ‘dominance’. Behav Cogn Neurosci Rev 4:3–20
Eckhardt CI, Deffenbacher J (1995) Diagnosis of anger disorders. In: Kassinove H (eds) Anger disorders: definition, diagnosis and treatment. Taylor & Francis, Washington DC
Eckhardt CI, Kassinove H (1998) Articulated cognitive distortions and cognitive deficiencies in maritally violent men. J Cognit Psychother 12:231–250
Eckhardt CI, Barbour KA, Stuart GL (1997) Anger and hostility in martially violent men: conceptual distinctions, measurement issues, and literature review. Clin Psychol Rev 17:333–358
Eckhardt CI, Norlander B, Deffenbacher J (2004) The assessment of anger and hostility: a critical review. Aggress Violent Behav 9:17–43
Ehrlichman H, Barrett J (1983) Right hemispheric specialization for mental imagery: a review of the evidence. Brain Cogn 2:55–76
Ekman P, Davidson RJ (1993) Voluntary smiling changes regional brain activity. Psychol Sci 4:342–345
Ekman P, Friesen WV (1971) Constants across cultures in the face and emotion. J Pers Soc Psychol 17:124–129
Ekman PJ, Levenson RW, Friesen WV (1983) Autonomic nervous system activity distinguishes among emotions. Science 221:1208–1210
Ekman PJ, Davidson RJ, Friesen WV (1990) The Duchenne smile: emotional expression and brain physiology. J Pers Soc Psychol 58:342–353
Everhart DE, Harrison DW (1995) Hostility following right CVA: support for right orbital frontal deactivation and right temporal activation. J Neurother 1:55–59
Everhart DE, Harrison DW (2000) Facial affect perception in anxious and nonanxious men. Psychobiology 28:90–98
Everhart DE, Harrison DW, Shenal BV, Williamson J, Wuensch KL (2002) Grip-strength, fatigue, and motor perseveration in anxious men without depression. Neuropsychiatry Neuropsychol Behav Neurol 15:133–142
Everhart DE, Demaree H, Harrison DW (2005) The Merging of cognitive and affective neuroscience: studies of the affective auditory verbal learning test. In: Clark AV (ed) Causes, role and influence of mood states. Nova Biomedical Books, Hauppauge
Fava M, Anderson K, Rosenbaum JF (1990) Anger attacks: possible variants of panic and major depressive disorder. Am J Psychiatry 147:867–870
Fernandez E, Beck AT (2001) Cognitive-behavioral self-intervention versus self-monitoring of anger: effects on anger frequency, duration and intensity. Behav Cogn Psychother 29:345–356
Foster PS, Harrison DW (2002) The relationship between magnitude of cerebral activation and intensity of emotional arousal. Int J Neurosci 112:1463–1477
Foster PS, Williamson JB, Harrison DW (2005) The Ruff Figural Fluency Test: heightened right frontal lobe delta activity as a function of performance. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 20:427–434
Fowles DC (1998) Biological variables in psychopathology: a biological perspective. In: Sutker PB, Adams HE (eds) Comprehensive book of psychopathology, 2nd edn. Plenum Press, New York, pp 157–182
Frijda NH (1986) Passions: Emotion and socially consequential behavior. In: Kavanaugh RD, Zimmerberg B, Fein S (eds) Emotion: interdisciplinary perspectives. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc, Hillsdale
Frijda NH (2005) Emotion experience. Cogn Emot 19:473–497
Gläscher J, Adolphs R (2003) Processing of the arousal of subliminal and supraliminal emotional stimuli by the human amygdala. J Neurosci 23:10274–10282
Graham S, Hoehn S (1995) Children’s understanding of aggression and withdrawal as social stigmas: an attributional analysis. Child Dev 66:1143–1161
Gray JA (1982) The neuropsychology of anxiety: an enquiry into the functions of the septo-hippocampal system. Clarendon Press/Oxford University Press, New York
Gray JA (1990) Brain systems that mediate both emotion and cognition. Cogn Emot 4:69–288
Hagemann D, Naumann E, Thayer JF (2001) The quest for the EEG reference revisited: a glance from brain asymmetry research. Psychophysiology 38:847–857
Hare RD (1999) Psychopathy as a risk factor for violence. Psychiatr Q 70:181–197
Harrison DW, Gorelczenko PM (1990) Functional asymmetry for facial affect perception in high and low hostile men and women. Int J Neurosci 55:89–97
Harmon-Jones E (2003) Clarifying the emotive functions of asymmetrical frontal cortical activity. Psychophysiology 40:838–848
Harmon-Jones E, Allen JHB (1998) Anger and frontal brain activity: EEG asymmetry consistent with approach motivation despite negative affective valence. J Pers Soc Psychol 74:1310–1316
Harmon-Jones E, Sigelman JD, Bohlig A, Harmon-Jones C (2003) Anger, coping, and frontal cortical activity: the effect of coping potential on anger-induced left frontal activity. Cogn Emot 17:1–24
Harmon-Jones E, Vaughn-Scott K, Mohr S, Sigelman J, Harmon-Jones C (2004) The effect of manipulated sympathy and anger on left and right frontal cortical activity. Emotion 4:95–101
Heilman K (1997) The neurobiology of emotional experience. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 9:439–448
Heilman KM (2000) Emotional experience: a neurological model. In: Lane RD, Nadel L (eds) Cognitive neuroscience of emotion. Oxford University Press, New York
Heilman KM, Bowers D (1990) Neuropsychological studies of emotional changes induced by right and left hemispheric lesions. In: Stein NL, Nancy B. Leventhal, Trabasso T (eds) Psychological and biological approaches to emotion. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc, Hillsdale
Hellige JB, Cox PJ, Litvac L (1979) Information processing in the cerebral hemispheres: Selective hemispheric activation and capacity limitations. J Exp Psychol Gen 10:251–279
Heller W (1993) Neuropsychological mechanisms of individual differences in emotion, personality, and arousal. Neuropsychology 7:476–489
Heller W, Nitschke JB (1997) Regional brain activity in emotion: A framework for understanding cognition in depression. Cogn Emot 11:637–661
Heller W, Nitschke JB, Miller GA (1998) Lateralization in emotion and emotional disorders. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 7:26–32
Henriques JB, Davidson RJ (1991) Left frontal hypoactivation in depression. J Abnorm Psychol 100:535–545
Herridge ML, Harrison DW, Mollet GA, Shenal B (2004) Hostility and facial affect recognition: Effects of a cold pressor stressor on accuracy and cardiovascular reactivity. Brain Cogn 55:564–571
Hewig J, Hagemann D, Seifert J, Naumann E, Batussek B (2004) On the selective relation of frontal cortical asymmetry and anger-out versus anger-control. J Pers Soc Psychol 87:926–939
Hollon SD, Kendall PC (1980) Cognitive self-statements in depression: development of an automatic thoughts questionnaire. Cognit Ther Res 4:383–395
Izard CE (1993) Organizational and motivational functions of discrete emotions. In: Lewis M, Haviland JM (eds) Handbook of emotions. Guilford Press, New York
Jones J, Trower P (2004) Irrational and evaluative beliefs in individuals with anger disorders. J Ration Emot Cogn Behav Ther 22:153–169
Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM (2000) Principles of neural science (4th ed). McGraw-Hill Publishers, New York
Kassinove H, Suckhodolsky DG (1995) Anger disorders: basic science and practice issues. Issues Compr Pediatr Nurs 18:173–205
Kassinove H, Tafrate RC (2002) Anger management: The complete treatment guidebook. Impact Publishers, Atascadero
Kestenbaum R, Nelson CA (1992) Neural and behavioral correlates of emotion recognition in children and adults. J Exp Child Psychol 54:1–18
Kettunen J, Ravaja N, Keltikangas-Jarvinen L, Näätänen P (2000) The relationship of respiratory sinus arrhythmia to the co-activation of autonomic and facial responses during the Rorschach test. Psychophysiology 37:242–250
Killgore WD, Yurgelun-Todd DA (2001) Sex differences in amygdala activation during the perception of facial affect. Neuroreport 12:2543–2547
Kimbrell TA, George M, Parekh PI (1999) Regional brain activity during transient self-induced anxiety and anger in healthy adults. Biol Psychiatry 46:454–465
Kinsbourne M (1978) Asymmetrical function of the brain. Cambridge University Press, Oxford
Kinsbourne M (1985) Deviant development of lateralization and cerebral function. Psychiatr Ann 15:439–444
Kunst-Wilson WR, Zajonc RB (1981) Affective discrimination of stimuli that cannot be recognized. Science 207:557–558
Lane RD, Fink GR, Chau PM (1997) Neural activation during selective attention to subjective emotional responses. Neuroreport 8:3969–3972
Lang PJ (1994) The varieties of emotional experience: A meditation on James-Lange theory. Psychol Rev 101:211–221
Lazarus RS (1982) Thoughts on the relations between emotion and cognition. Am Psychol 37:1019–1024
Lazarus RS (1984) On the primacy of cognition. Am Psychol 39:124–129
Lazarus RS (1991) Emotion and adaptation. Oxford, New York
Lazarus RS, Smith CA (1988) Knowledge and appraisal in the cognition-emotion relationship. Cogn Emot 2:281–300
LeDoux JD (1994) Cognitive-emotional interactions in the brain. In: Eckman P, Davidson RJ (eds) The nature of emotion. Oxford University Press, New York
Lemerise EA, Arsenio WF (2000) An integrated model of emotion processes and cognition in social information processing. Child Dev 71:107–118
Levenson RW (1988) Emotion and the autonomic nervous system: a prospectus for research on autonomic specificity. In: Wagner HL (eds) Social psychophysiology and emotion: theory and clinical applications. Wiley, Oxford
Lezak MD (1983) Neuropsychological assessment, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Loeber R, Coie J (2001) Continuities and discontinuities of development, with particular emphasis on emotional and cognitive components of disruptive behaviour. In: Hill J, Maughan B (eds) Conduct disorders in childhood and adolescence. Oxford University Press, New York
Luria AR (1973) The frontal lobes and the regulation of behavior. In: Pribram KH, Luria AR (eds) Psychophysiology of the frontal lobes. Academic Press, Oxford
Maitlin MW (1998) Cognition. 4th edn. Harcourt Brace, NY
Martin R, Wan C, David JP, Wegner E, Olson BD, Watson D (2000) Style of anger expression: relation to expressivity, personality, and health. Pers Soc Psychol Bull 25:1196–1207
Mauss IB, Levenson RW, McCarter L, Wilhelm FH, Gross JJ (2005) The tie that binds? Coherence among emotion experience, behavior, and physiology. Emotion 5:175–190
Max JE (2004) Effect of side of lesion on neuropsychological performance in childhood stroke. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 10:698–708
Maxwell JS, Shackman AJ, Davidson RJ (2005) Unattended facial expressions asymmetrically bias the concurrent processing of nonemotional information. J Cogn Neurosci 17:1386–1395
McKeever WF, Dixon MS (1981) Right-hemisphere superiority for discriminating memorized from nonmemorized faces: Affective imagery, sex, and perceived emotionality effects. Brain Lang 12:246–260
McNaughton N, Gray JA (2000) Anxiolytic action on the behavioural inhibition system implies multiple types of arousal contribute to anxiety. J Affect Disord 61:161–176
Mills CK (1912) Preliminary note on a new symptom complex due to lesion of the cerebellum and cerebello-rubro-thalamic system, etc. J Nerv Ment Dis 39:73–76
Miller TQ, Smith TW, Turner CW, Guijarro ML, Hallet AJ (1996) A meta-analytic review of research on hostility and physical health. Psychol Bull 119:322–348
Mollet GA (2004) Hostility and negative emotion induction: implications for verbal learning and cardiovascular regulation. Unpublished Master’s Thesis. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA
Mollet G (2006) Emotion and pain: a functional cerebral systems integration. Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA
Murphy FC, Nimmo-Smith I, Lawrence AD (2003) Functional neuroanatomy of emotions: a meta-analysis. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 3:207–233
Narumoto J, Okada T, Sadato N, Fukui K, Yonekura Y (2001) Attention to emotion modulates fMRI activity in human right superior temporal sulcus. Cogn Brain Res 12:225–231
Pakaslahti L (2000) Children’s and adolescents’ aggressive behavior in context: The development and application of aggressive problem-solving strategies. Aggress Violent Behav 5:467–490
Phan KL, Wager TD, Taylor SF, Liberzon I (2004) Functional imaging studies of human emotions. CNS Spectr 9:258–256
Porges SW (1991) Vagal mediation of respiratory sinus arrhythmia: Implications for drug delivery. In: Hrushesky WJ, Langer R, Theeuwes F (eds) Temporal control of drug delivery. New York Academy of Sciences, New York
Rao SM (2000) Neuropsychological evaluation. In: Fogel BS, Schiffer RB, Rao SM (eds) Synopsis of neuropsychiatry. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins Publishers, Philadelphia
Reuter-Lorenz PA, Givis RP, Moscovitch M (1983) Hemispheric specialization and the perception of emotion: Evidence from right-handers and from inverted and noninverted left-handers. Neuropsychologia 21:687–692
Robinson RG, Downhill JE (1995) Lateralization of psychopathology in response to focal brain injury. In: Davidson RJ, Hugdahl K (eds) Brain asymmetry. The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Robinson RG, Manes F (2000) Elation, mania, and mood disorders: evidence from neurological disease. In: Borod JC (ed) The neuropsychology of emotion. Oxford University Press, New York
Roseman IJ (1991) Appraisal determinants of discrete emotions. Cogn Emot 5:161–200
Ross P (2000) Electrophysiology of working memory: Task modality and load effects. Diss Abstr Int B Sci Eng 61:3319
Ruff RM, Light RH, Evans RW (1987) The Ruff Figural Fluency Test: a normative study with adults. Dev Neuropsychol 3:37–51
Schachter S, Singer J (1962) Cognitive, social, and physiological determinants of emotional state. Psychol Rev 69:379–399
Scherer KR, Ellsworth PC, Forgas JP (2003) Part V: Cognitive components of emotion. In: Davidson RJ, Scherer KR, Goldsmith HH (eds) Handbook of affective sciences. Oxford University Press, New York
Schutter DJG, deHaan EHV, van Honk J (2004) Functionally dissociated aspects in anterior and posterior electrocortical processing of facial threat. Int J Psychophysiol 53:29–36
Schwartz GE, Davidson RJ, Maer F (1975) Right hemisphere lateralization for emotion in the human brain: interactions with cognition. Science 190:286–288
Siegel JM (1985) Anger and cardiovascular risk in adolescents. Health Psychol 3:293–313
Siegman AW, Snow SC (1997) The outward expression of anger, the inward experience of anger and CVR: the role of vocal expression. J Behav Med 20:29–45
Smith TW (1994) Concepts and methods in the study of anger, hostility and health. In: Siegman AW, Smith TW (eds) Anger, hostility and the heart. Earlbaum, Hillsdale
Smith TW, Pope MK (1990) Cynical hostility as a health risk: current status and future directions. J Soc Behav Pers 5:77–88
Smith TW, Galzer K, Ruiz JM, Gallo LC (2004) Hostility, anger, and aggressiveness and coronary heart disease: an interpersonal perspective on emotion and health. J Pers 72:1217–1270
Snyder KA, Harrison DW (1997) The affective auditory verbal learning test. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 12:477–482
Snyder CR, Crowson JJ, Houston BK, Kurylo M, Poirier J (1997) Assessing hostile automatic thoughts: development and validation of the HAT Scale. Cognit Ther Res 21:477–492
Spielberger CD, Johnson EH, Russell SF, Crane RS, Jacobs G, Worden TJ (1983) Assessment of anger: the state-trait scale. In: Butcher JN, Spielberger CD (eds) Advances in personality assessment, 2. Earlbaum, Hillside
Spielberger CD, Reheiser EC, Sydeman SJ (1995) Measuring the experience, expression, and control of anger. Issues Compr Pediatr Nurs 18:207–232
Stuss DT (1992) Biological and psychological development of executive functions. Brain Cogn 20:8–23
Suberi M, McKeever WF (1977) Differential right hemispheric memory storage of emotional and non-emotional faces. Neuropsychologia 15:757–768
Suls J, Bunde J (2005) Anger, anxiety, and depression as risk factors for cardiovascular disease: the problems and implications of overlapping affective dispositions. Psychol Bull 131:260–300
Tabert M, Borod JC, Tang CY, Lange G, Wei T, Johnson R, Nusbaum A, Bushbaum M (2001) Differential amygdala activation during emotional decision and recognition memory tasks using unpleasant words: an fMRI study. Neuropsychologia 39:556–573
Thayer JF, Lane BH (2000) Phasic heart period reactions to cued threat and nonthreat stimuli in generalized anxiety disorder. Psychophysiology 37:361–368
Thayer JF, Friedman BH, Borkovec TD (1996) Autonomic characteristics of generalized anxiety disorder and worry. Biol Psychiatry 39:255–266
Tomarken AJ, Davidson RJ, Henriques JB (1990) Resting frontal brain asymmetry predicts affective responses to films. J Pers Soc Psychol 59:791–801
Tomarken AJ, Davidson RJ, Wheeler RE, Doss E (1992) Psychometric properties of resting anterior EEG asymmetry: temporal stability and internal consistency. Psychophysiology 29:576–592
Tucker DM (1981) Lateral brain function, emotion, and conceptualization. Psychol Bull 89:19–46
Tucker DM, Dawson SL (1984) Asymmetric EEG changes as method actors generated emotions. Biol Psychol 19:63–75
Tucker DM, Williamson PA (1984) Asymmetric neural control systems in human self-regulation. Psychol Rev 91:185–215
Vanderploeg RD, Brown WS, Marsh JT (1987) Judgments of emotion in words and faces: ERP correlates. Int J Psychophysiol 5:193–205
Vigne JJ, Dale JA, Klions HL (1988) Facial electromyogram and heart-rate correlates of a paradoxical attitude change to antinuclear war information. Percept Mot Skills 67:755–762
Wacker J, Heldmann M, Stemmler G (2003) Separating emotion and motivational direction in fear and anger: Effects on frontal asymmetry. Emotion 3:167–193
Wager TD, Barrett LF, Bliss-Moreau E, Lindquist, K, Duncan S, Kober H, Joseph J, Davidson M, Mize J (2007) The neuroimaging of emotion. In: Lewis M (ed) Handbook of Emotion (3rd edn). Guilford Press, New York (in Press)
Wager TD, Phan KL, Liberzon I, Taylor SF (2003) Valence, gender, and lateralization of functional brain anatomy in emotion: a meta-analysis of findings from neuroimaging. Neuroimage 19:513–531
Waldstein SR, Kop WJ, Schmidt LA, Haufler AJ, Krantz DS, Fox NA (2000) Frontal electrocortical and cardiovascular reactivity during happiness and anger. Biol Psychol 55:3–23
Weiner B (1995) Inferences of responsibility and social motivation. In: Zanna MP (ed) Advances in experimental social psychology. Academic Press, San Diego
Williams TM, Zabrack ML, Joy LA (1982) The portrayal of aggression on North American television. J Appl Soc Psychol 1:360–380
Wingrove J, Bond AJ (2005) Correlates between trait hostility and faster reading times for sentences describing angry reactions to ambiguous situations. Cogn Emot 19:463–472
Wittling W (1995) Brain asymmetry in the control of autonomic-physiologic activity. In: Davidson RJ, Hugdahl K (eds) Brain asymmetry. The MIT Press, Cambridge
Zajonc RB (1980) Feeling and thinking: preferences need no inferences. Am Psychol 35:151–175
Zajonc RB (1984) On the primacy of affect. Am Psychol 29:117–123
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cox, D.E., Harrison, D.W. Models of anger: contributions from psychophysiology, neuropsychology and the cognitive behavioral perspective. Brain Struct Funct 212, 371–385 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-007-0168-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-007-0168-7