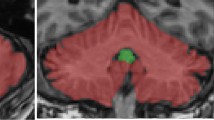
Abstract
‘Non-traditional’ large neurons of the granular layer of the cerebellar cortex include all its large neuronal types, except the Golgi neuron, which is instead one of the five ‘classic’ types of corticocerebellar neurons. The morphological, chemical and functional characteristics of the ‘non-traditional’ large neurons have not been entirely ascertained. The aim of this study was to ascertain whether morphological evidence can be provided of GABA synthesis within the ‘non-traditional’ large neurons of the human cerebellar cortex by means of immunocytochemistry for glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD). Fragments of postmortem cerebellar cortex of various lobules from the hemispheres and vermis were studied. Immunoreactions revealed large neurons distributed throughout the granular layer in all lobules examined. They were discriminated by analyzing the morphological features of their bodies and processes and were identified as Golgi neurons and as some ‘non-traditional’ types, such as the candelabrum, Lugaro and synarmotic neurons. In addition, immunoreactive large neurons, with their bodies and processes closely adjacent to microvessels, were observed throughout the layer: these perivascular neurons could represent a new type of ‘non-traditional’ neuron of the cerebellar cortex. This study supplies the first indication that in the human cerebellar cortex some types of ‘non-traditional’ large neurons are GAD-immunoreactive, in addition to those neurons already known to be GABAergic (i.e., stellate, basket, Purkinje and Golgi neurons). These morphological data further point out possible functional roles for GABA as a neurotransmitter/neuromodulator in intrinsic, associative and projective circuits of the cerebellar cortex.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman J, Bayer SA (1977) Time of origin and distribution of a new cell type in the rat cerebellar cortex. Exp Brain Res 29:265–274
Aoki E, Semba R, Kashiwamata S (1986) New candidate for GABAergic neurons in the rat cerebellum: an immunocytochemical study with anti-GABA antibody. Neurosci Lett 68:267–271
Benagiano V, Flace P, Virgintino D, Rizzi A, Roncali L, Ambrosi G (2000) Immunolocalization of glutamic acid decarboxylase in postmortem human cerebellar cortex. A light microscopy study. Histochem Cell Biol 114:191–195
Benagiano V, Roncali L, Virgintino D, Flace P, Errede M, Rizzi A, Girolamo F, Robertson D, Bormann J, Ambrosi G (2001) GABA immunoreactivity in the human cerebellar cortex: a light and electron microscopical study. Histochem J 33:537–543
Braak H (1974) On the intermediate cells of Lugaro within the cerebellar cortex of man. A pigmentarchitectonic study. Cell Tiss Res 149:399–411
Braak E, Braak H (1983) On three types of large nerve cells in the granular layer of the human cerebellar cortex. Anat Embryol 166:67–86
Braak E, Braak H (1993) The new monodendritic neuronal type within the adult human cerebellar granule cell layer shows calretinin-immunoreactivity. Neurosci Lett 154:199–202
Castejon OJ, Castejon HV (2000) Correlative microscopy of cerebellar Golgi cells. Biocell 24:13–30
Christ H (1985) Fusiform nerve cells of the granular layer in the cerebellar cortex of the baboon. Neurosci Lett 56:195–198
Clements JR, Monaghan PL, Beitz AJ (1987) An ultrastructural description of glutamate-like immunoreactivity in the rat cerebellar cortex. Brain Res 421:343–348
Diño MR, Nunzi MG, Anelli R, Mugnaini E (2000) Distribution of unipolar brush cells of the vestibulocerebellum: afferents and targets. Prog Brain Res 124:123–137
Eccles JC, Ito M, Szentàgothai J (1967) The cerebellum as a neuronal machine. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Floris A, Diño M, Jacobowitz DM, Mugnaini E (1994) The unipolar brush cells of the rat cerebellar cortex and cochlear nucleus are calretinin-positive: a study by light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Anat Embryol 189:495–520
Fortin M, Marchand R, Parent A (1998) Calcium-binding proteins in primate cerebellum. Neurosci Res 30:155–168
Fox CA (1959) The intermediate cells of Lugaro in the cerebellar cortex of the monkey. J Comp Neurol 112:39–51
Gabbott PL, Somogyi P, Stewart MG, Hamori J (1986) GABA-immunoreactive neurons in the rat cerebellum: a light and electron microscope study. J Comp Neurol 251:474–490
Geurts FJ, Timmermans J-P, Shigemoto R, De Shutter E (2001) Morphological and neurochemical differentiation of large granular layer interneurons in the adult rat cerebellum. Neuroscience 104:499–512
Golgi C (1874) Sulla fina anatomia del cervelletto umano. In: Opera Omnia Chapter V, vol 1. Istologia Normale, Hoepli, Milan, pp 99–111
Gragera RR, Muniz E, Martinez-Rodriguez R (1993) Electron microscopic immunolocalization of GABA and glutamic acid decarboxylase in cerebellar capillaries and their microenvironment. Cell Mol Biol 39:809–817
Houk JC, Mugnaini E (2003) Cerebellum. In: Squire LR, Bloom FE, McConnell SK, Roberts JL, Spitzer NC, Zigmond MJ (eds) Fundamental Neuroscience. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 841–872
Jansen J, Brodal A (1958) Das Kleinhirn. In: Bargmann W (ed) Handbuch der Mikroskopischen Anatomie des Menschen, vol 4. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 91–149
Katsetos CD, Frankfurter A, Christakos S, Mancall EL, Vlachos IN, Urich H (1993) Differential localization of class III, beta-tubulin isotype and calbindin-D28 k defines distinct neuronal types in the developing human cerebellar cortex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 52:655–666
Lainé J, Axelrad H (1994) The candelabrum cell: a new interneuron in the cerebellar cortex. J Comp Neurol 339:159–173
Lainé J, Axelrad H (1996) Morphology of the Golgi impregnated Lugaro cell in the rat cerebellar cortex: a reappraisal with a description of its axon. J Comp Neurol 375:618–640
Lainé J, Axelrad H (1998) Lugaro cells target basket and stellate cells in the cerebellar cortex. Neuroreport 9:2399–2403
Lainé J, Axelrad H (2002) Extending the cerebellar Lugaro cell class. Neuroscience 111:363–374
Landau E (1933) La cellule synarmotique dans le cervelet humain. Arch Anat 17:273–285
Lugaro E (1894) Sulle connessioni tra gli elementi nervosi della corteccia cerebellare con considerazioni generali sul significato fisiologico dei rapporti tra gli elementi nervosi. Riv Sper Freniat 20:297–331
Melik-Musian AB, Fanardzhian VV (1998) Histological identification of Lugaro cells in the cat cerebellum. Neurosci Behav Physiol 28:1486–1489
Mugnaini E (1972) The histology and cytology of the cerebellar cortex. In: Larsell O, Jansen J (eds) The comparative anatomy and histology of the cerebellum: the human cerebellum, cerebellar connections and cerebellar cortex. Minnesota Press, Minneapolis, pp 201–264
Mugnaini E (2000) GABAergic inhibition in the cerebellar system. In: Martin DL, Olsen RW (eds) GABA in the Nervous System: the view at fifty years. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 383–407
Mugnaini E, Floris A (1994) The unipolar brush cell: a neglected neuron of the mammalian cerebellar cortex. J Comp Neurol 339:174–180
Mugnaini E, Oertel WH (1985) An atlas of the distribution of GABAergic neurons and terminals in the rat CNS as revealed by GAD immunohistochemistry. In: Björklund A, Hökfelt T (eds) Handbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy, vol 4: GABA and Neuropeptides in the CNS - Part I. Elsevier, Vancouver, pp 436–608
Müller T (1994) Large nerve cells with long axons in the granular layer and white matter of the murine cerebellum. J Anat 184:419–423
Munoz DG (1990) Monodendritic neurons: a cell type in the human cerebellar cortex identified by chromogranin A-like immunoreactivity. Brain Res 528:335–338
Nunzi MG, Birnstiel S, Bhattacharyya BJ, Slater NT, Mugnaini E (2001) Unipolar brush cell form a glutamatergic projection system within the mouse cerebellar cortex. J Comp Neurol 434:329–341
Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J, Somogyi P (1988) Colocalization of glycine-like and GABA-like immunoreactivities in Golgi cell terminals in the rat cerebellum: a postembedding light and electron microscopy study. Brain Res 450:342–353
Palay SL, Chan-Palay V (1974) Cerebellar cortex. Cytology and organization. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Pensa A (1931) Osservazioni e considerazioni sulla struttura della corteccia cerebellare dei mammiferi. Mem R Accad Naz Lincei, Sci Fis Mat Nat, ser VI 5:25–50
Ramón y Cajal S (1911) Histologie du Système Nerveux de l’Homme et des Vertébrés, vol II. Maloine, Paris
Ribak CE, Vaughn JE, Saito K (1978) Immunocytochemical localization of glutamic acid decarboxylase in neuronal somata following colchicine inhibition of axonal transport. Brain Res 140:315–332
Storm-Mathisen J, Lecknes AK, Bore AT, Vaalant JL, Edminson P, Haug FM, Ottersen OP (1983) First visualization of glutamate and GABA in neurones by immunocytochemistry. Nature 301:517–520
Voogd J, Glickstein M (1998) Anatomy of the cerebellum. Trends Neurosci 21:370–375
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Ms. Mary Victoria Pragnell B.A., for linguistic help, and Mr. Francesco Fumai, for technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from the University of Bari to G. Ambrosi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
To our Master, Professor Rodolfo Amprino, with our great admiration, gratefulness and affection, on the occasion of his ninety-second birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flace, P., Benagiano, V., Lorusso, L. et al. Glutamic acid decarboxylase immunoreactive large neuron types in the granular layer of the human cerebellar cortex. Anat Embryol 208, 55–64 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-003-0374-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-003-0374-x