Abstract.
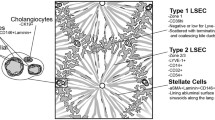
This study reports the effects of altered hepatic perfusion on the sinusoidal bed and the phenotypic characteristics of sinusoidal endothelial cells (SECs). Sinusoids were studied by the application of endothelial cell markers (CD31, CD34, CD105, and ATZ 11) in lesions with localized increased perfusion (liver cell adenoma, focal nodular hyperplasia, and macroregenerative nodule), in chronic congestion, in decreased portovenous inflow (portal vein thrombosis), and in decreased arteriohepatic perfusion (obliterative arteriopathy in chronic allograft rejection). SECs react in a sensitive and uniform way to all investigated conditions of different pathologic liver perfusion: expression of CD31, CD34, and ATZ 11 by SEC is found in inflow areas, CD105-positive SECs are found at the end of the sinusoidal blood stream. This blood flow-orientated phenotypic shift of SECs was accompanied by a perisinusoidal accumulation of activated hepatic stellate cells and collagen IV. These findings are helpful in liver biopsies and provide new insights into the angioarchitecture of benign nodular lesions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Theuerkauf, I., Zhou, H. & Fischer, HP. Immunohistochemical patterns of human liver sinusoids under different conditions of pathologic perfusion. Virchows Arch 438, 498–504 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004280000364
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004280000364