Abstract.
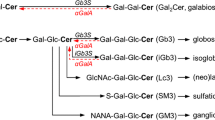
The inherited deficiency of arylsulfatase A (ASA) in humans causes lysosomal accumulation of sulfatides in visceral organs and in the nervous system and leads to wide-spread demyelination (metachromatic leukodystrophy, MLD). ASA-deficient mice have previously been generated by means of targeted gene disruption. In the present study, visceral organs of ASA-deficient mice were investigated. A simple technique for the histochemical detection of accumulated sulfatides was elaborated using pre-embedding staining with alcian blue. The gall bladder, intrahepatic bile ducts, exocrine pancreatic ducts, respiratory epithelium and, with low degree, testicular Sertoli cells, showed sulfolipid storage. The storage pattern in the kidney will be described in a separate publication. Hepatocytes, pancreatic islets, adrenal glands, and gastric epithelium were unaffected. Ultrastructurally, the intralysosomal storage material displayed parallel and concentric lamellar patterns. Apart from some differences, the topographic distribution of the sulfatide storage resembled that in human MLD. In addition to being an animal model of the human disease, the ASA-deficient mouse may be useful for investigating the cell biology of sulfolipids in visceral organs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schott, I., Hartmann, D., Gieselmann, V. et al. Sulfatide storage in visceral organs of arylsulfatase A-deficient mice. Virchows Arch 439, 90–96 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004280000360
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004280000360