Abstract
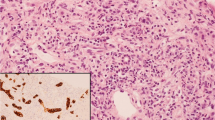
Baseline clinical and biochemical parameters fail to predict non-response to steroids in severe alcoholic hepatitis patients. Liver biopsy features have not been adequately assessed for predicting response to steroid therapy in severe alcoholic hepatitis. We aimed to identify histological parameters, which can predict steroid response in severe alcoholic hepatitis (SAH). We analyzed histological data of 107 SAH patients (71 in a derivative and 36 in a validation cohort) who presented within 4 weeks after inset of jaundice and were prospectively treated with steroids (40 mg/day). Histopathological parameters were semi-quantitatively scored in the pre-therapy biopsies in the derivative cohort, and a histological scoring system of SAH was developed which differentiated between steroid responders (Lille score < 0.45 at day 7) and non-responders. Seventeen of the 71 (24%) patients in the derivation cohort and 9 of 36 (25%) in the validation cohort were non-responders to steroids. In the derivation cohort, in comparison to responders, non-responders had higher severity of ballooning degeneration (BD) (mean 3.87 ± 0.91 versus 2.92 ± 1.33; p = 0.013) and density of Mallory-Denk bodies (MD) (mean 2.27 ± 0.79 versus. 1.69 ± 0.97; p = 0.028) on liver histology. A score derived using BD and MD (range 0–8) had high sensitivity (81%), specificity (64%), and negative predictive value (91%) in identifying patients who did not respond to steroids. The AUROC for a combined MD and BD score of > 5 for predicting steroid non-response was 0.731. Baseline histological parameters in SAH, ballooning degeneration, and Mallory-Denk bodies can reliably identify non-response to corticosteroids and help to stratify patients prior to introduction of therapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AH:
-
Alcoholic hepatitis
- BD:
-
Ballooning degeneration
- MD:
-
Mallory-Denk bodies
- LI:
-
Lobular inflammation
References
McCullough AJ, O'Connor JF (1998) Alcoholic liver disease: proposed recommendations for the American College of Gastroenterology. Am J Gastroenterol 93(11):2022–2036
Teli MR, Day CP, Burt AD, Bennett MK, James OF (1995) Determinants of progression to cirrhosis or fibrosis in pure alcoholic fatty liver. Lancet 346(8981):987–990
Adang RP, Wensing JW, Stockbrügger RW (1998) Alcohol consumption and alcohol-related liver disease in the Netherlands. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl 225:70–74
Tome S, Lucey MR (2004) Review article: Current management of alcoholic liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 19:707–714
Maddrey WC, Boitnott JK, Bedine MS, Weber FL Jr, Mezey E, White RI Jr (1978) Corticosteroid therapy of alcoholic hepatitis. Gastroenterology 75:193–199
Forrest EH, Evans CD, Stewart S, Phillips M, Oo YH, McAvoy N, Fisher NC, Singhal S, Brind A, Haydon G, O'Grady J, Day CP, Hayes PC, Murray LS, Morris AJ (2005) Analysis of factors predictive of mortality in alcoholic hepatitis and derivation and validation of the Glasgow alcoholic hepatitis score. Gut 54:1174–1179
Louvet A, Wartel F, Mathurin P et al (2009) Infection in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis treated with steroids: early response to therapy is the key factor. Gastroenterology 137:541–548
Mathurin P, O’Grady J, Morgan TR et al (2011) Corticosteroids improve short-term survival in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis: meta-analysis of individual patient data. Gut 60:255e260
Louvet A, Naveau S, Mathurin P et al (2007) The Lille model: a new tool for therapeutic strategy in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis treated with steroids. Hepatology 45(6):1348–1354
Mookerjee RP, Lackner C, Jalan R, Lackner C, Stauber R, Stadlbauer V, Deheragoda M, Aigelsreiter A, Jalan R (2011) The role of liver biopsy in the diagnosis and prognosis of patients with acute deterioration of alcoholic cirrhosis. J Hepatol 55(5):1103–1111
Altamirano J, Miquel R, Katoonizadeh A et al (2014) A histologic scoring system for prognosis of patients with alcoholic hepatitis. Gastroenterology 146(5):1231-9.e1-6
Rastogi A, Kumar A, Sarin SK et al (2011) Liver histology as predictor of outcome in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF). Virchows Arch 459(2):121–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-011-1115-9
Lucey MR, Mathurin P, Morgan TR (2009) Alcoholic hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 360(26):2758–2769
Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB et al (1992) Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest 101(6):1644–1655
Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver (APASL) Working Party on Portal Hypertension (2011) Diagnosis and management of acute variceal bleeding: Asian Pacific Association for Study of the liver recommendations. Hepatol Int 5(2):607–624
Garg V, Garg H, Khan A, Trehanpati N, Kumar A, Sharma BC, Sakhuja P, Sarin SK (2012) Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor mobilizes CD34(+) cells and improves survival of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. Gastroenterology 142(3):505–512 e1
Hardy T, Wells C, Stewart SF et al (2013) White cell count and platelet count associate with histological alcoholic hepatitis in jaundiced harmful drinkers. BMC Gastroenterol 13(1):55. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-230X-13-55
MacSween RN, Burt AD (1986) Histologic spectrum of alcoholic liver disease. Semin Liver Dis 6(3):221–232
O’Shea RS, Dasarathy S, McCullough AJ (2010) Alcoholic liver disease, practice guidelines. Hepatology 51:307–332
Louvet A, Mathurin P (2015) Alcoholic liver disease: mechanisms of injury and targeted treatment. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 12(4):231–242
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SMS, RV, VA, MS, and SKS did the patient enrollment, data collection, MS preparation, and correction; AR and CB did the histological scoring and grading,
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Institutional review board acceptance was sought before enrolling the patients and the current study is part of the registered trial NCT01820208.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shasthry, S.M., Rastogi, A., Bihari, C. et al. Histological activity score on baseline liver biopsy can predict non-response to steroids in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis. Virchows Arch 472, 667–675 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-018-2330-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-018-2330-4