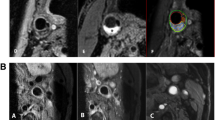
Abstract
Intraplaque hemorrhage (IPH) is a crucial factor in progression and destabilization of an atherosclerotic plaque. Anti-thromboembolic drugs are widely used as prophylactic treatment against arterial and venous thrombotic diseases, but a major complication is bleeding. We investigated the association between exposure to anti-thromboembolic therapy and IPH in postmortem coronary arteries. Coronary arteries with postmortem angiographically confirmed extensive atherosclerosis were obtained at autopsy from patients who had received oral anticoagulants (n = 10), platelet aggregation inhibitors (n = 10), or no anti-thrombotic drugs (n = 10) before death. Coronary arteries were cut at 3-mm interval, and all plaque-containing segments were immunohistochemically screened for IPH and microvessels. These data were related to overall plaque composition and the use of anti-thromboembolic therapies. IPH was found in 483 out of 904 (53 %) coronary segments with advanced atherosclerotic plaques and more frequently in patients on oral anticoagulants (174/284, 61 %) than in patients on anti-platelets (198/376, 53 %) or without therapy (111/244, 46 %) (P = 0.02 and P = 0.001, respectively). Also, intraplaque microvascular leakage was more frequently observed in patients on anticoagulants than in non-treated patients (P = 0.03). Finally, the IPH appeared to be larger in plaques of patients on anticoagulant treatment (P < 0.001). Density of intraplaque microvessels was highest in plaques of patients on platelet inhibitors (P < 0.05), but this was not associated with increased hemorrhagic burden. Prophylactic therapy with oral coumarin-type anticoagulants appears to be associated with a higher hemorrhagic burden in atherosclerotic coronary arteries, which may lead to increase in plaque volume over time, in this selected subgroup of patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davies MJ, Thomas AC (1985) Plaque fissuring–the cause of acute myocardial infarction, sudden ischaemic death, and crescendo angina. Br Heart J 53:363–373
van der Wal AC, Becker AE (1999) Atherosclerotic plaque rupture—pathologic basis of plaque stability and instability. Cardiovasc Res 41:334–344
Wartman W (1938) Occlusion of the coronary arteries by hemorrhage into their walls. Am Heart J 15:459–470
Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Farb A, Schwartz SM (2000) Lessons from sudden coronary death: a comprehensive morphological classification scheme for atherosclerotic lesions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:1262–1275
Kolodgie FD, Gold HK, Burke AP, Fowler DR, Kruth HS, Weber DK, Farb A, Guerrero LJ, Hayase M, Kutys R, Narula J, Finn AV, Virmani R (2003) Intraplaque hemorrhage and progression of coronary atheroma. N Engl J Med 349:2316–2325
Takaya N, Yuan C, Chu B, Saam T, Polissar NL, Jarvik GP, Isaac C, McDonough J, Natiello C, Small R, Ferguson MS, Hatsukami TS (2005) Presence of intraplaque hemorrhage stimulates progression of carotid atherosclerotic plaques: a high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging study. Circulation 111:2768–2775
Davies MJ (2000) The pathophysiology of acute coronary syndromes. Heart 83:361–366
Kockx MM, Cromheeke KM, Knaapen MW, Bosmans JM, De Meyer GR, Herman AG, Bult H (2003) Phagocytosis and macrophage activation associated with hemorrhagic microvessels in human atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:440–446
Lin HL, Xu XS, Lu HX, Zhang L, Li CJ, Tang MX, Sun HW, Liu Y, Zhang Y (2007) Pathological mechanisms and dose dependency of erythrocyte-induced vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaques. J Mol Cell Cardiol 43:272–280
Furie B, Furie BC (2008) Mechanisms of thrombus formation. N Engl J Med 359:938–949
Mackman N (2008) Triggers, targets and treatments for thrombosis. Nature 451:914–918
Bousser MG, Eschwege E, Haguenau M, Lefaucconnier JM, Thibult N, Touboul D, Touboul PJ (1983) “AICLA” controlled trial of aspirin and dipyridamole in the secondary prevention of athero-thrombotic cerebral ischemia. Stroke 14:5–14
Baigent C, Collins R, Appleby P, Parish S, Sleight P, Peto R (1998) ISIS-2: 10 year survival among patients with suspected acute myocardial infarction in randomised comparison of intravenous streptokinase, oral aspirin, both, or neither. The ISIS-2 (Second International Study of Infarct Survival) Collaborative Group. BMJ 316:1337–1343
Hirsh J (1991) Oral anticoagulant drugs. N Engl J Med 324:1865–1875
Nobuyoshi M, Tanaka M, Nosaka H, Kimura T, Yokoi H, Hamasaki N, Kim K, Shindo T, Kimura K (1991) Progression of coronary atherosclerosis: is coronary spasm related to progression? J Am Coll Cardiol 18:904–910
Landefeld CS, Beyth RJ (1993) Anticoagulant-related bleeding: clinical epidemiology, prediction, and prevention. Am J Med 95:315–328
Serebruany VL, Malinin AI, Eisert RM, Sane DC (2004) Risk of bleeding complications with antiplatelet agents: meta-analysis of 338,191 patients enrolled in 50 randomized controlled trials. Am J Hematol 75:40–47
Wolff T, Miller T, Ko S (2009) Aspirin for the primary prevention of cardiovascular events: an update of the evidence for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern Med 150:405–410
Derksen WJ, Peeters W, Tersteeg C, de Vries JP, de Kleijn DP, Moll FL, van der Wal AC, Pasterkamp G, Vink A (2011) Age and coumarin-type anticoagulation are associated with the occurrence of intraplaque hemorrhage, while statins are associated less with intraplaque hemorrhage: a large histopathological study in carotid and femoral plaques. Atherosclerosis 214:139–143
DeVito CL, Little WA (1988) Fractal sets associated with functions: the spectral lines of hydrogen. Phys Rev A 38:6362–6364
Arbustini E, Morbini P, D’Armini AM, Repetto A, Minzioni G, Piovella F, Vigano M, Tavazzi L (2002) Plaque composition in plexogenic and thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: the critical role of thrombotic material in pultaceous core formation. Heart 88:177–182
Meijer-Jorna LB, Mekkes JR, van der Wal AC (2002) Platelet involvement in cutaneous small vessel vasculitis. J Cutan Pathol 29:176–180
Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Finn AV, Gold HK, Tulenko TN, Wrenn SP, Narula J (2005) Atherosclerotic plaque progression and vulnerability to rupture: angiogenesis as a source of intraplaque hemorrhage. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:2054–2061
Ammar AD, Wilson RL, Travers H, Lin JJ, Farha SJ, Chang FC (1984) Intraplaque hemorrhage: its significance in cerebrovascular disease. Am J Surg 148:840–843
Jorgensen L, Chandler AB, Borchgrevink CF (1971) Acute lesions of coronary arteries in anticoagulant-treated and in untreated patients. Atherosclerosis 13:21–44
Fisher M, Sacoolidge JC, Taylor CR (1987) Patterns of fibrin deposits in carotid artery plaques. Angiology 38:393–399
Ernst RL, Ammar AD, Lin JJ, Travers H (1986) The effect of antiplatelet therapy on the incidence of carotid plaque hemorrhage. Stroke 17:540–541
AbuRahma AF, Boland JP, Robinson P, Decanio R (1990) Antiplatelet therapy and carotid plaque hemorrhage and its clinical implications. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 31:66–70
Glagov S, Zarins C, Giddens DP, Ku DN (1988) Hemodynamics and atherosclerosis. Insights and perspectives gained from studies of human arteries. Arch Pathol Lab Med 112:1018–1031
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the Netherlands Heart Foundation.
Authors’ contribution
XL, RJW, and ACW are responsible for the conception and design of the study. XL, AV, JK, OB, HJP, JGPT, and ACW are responsible for the acquisition of data or analysis and interpretation of data. XL, AV, HNJP, RW, and ACW are responsible for drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content. XL and ACW are responsible for the final approval of the version published. ACW and XL are responsible for the overall content.
Conflict of interest
No competing interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Vink, A., Niessen, H.W.M. et al. Total burden of intraplaque hemorrhage in coronary arteries relates to the use of coumarin-type anticoagulants but not platelet aggregation inhibitors. Virchows Arch 465, 723–729 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-014-1654-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-014-1654-y