Abstract
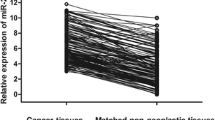
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short non-coding RNAs that exert a critical influence on tumorigenesis through post-transcriptional modification and are considered to be potential biomarkers for the diagnosis or prognosis of various cancers. Although several miRNAs have been proposed as relevant biomarkers for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), detailed working mechanisms and validated prognostic significance of these miRNAs remain controversial. In this study, we evaluated expression levels of miRNA-126 (miR-126) and miR-200c in 72 NSCLCs and 30 benign lung tissues by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and analyzed the correlation of miRNA expression with a variety of clinicopathological factors and patient survival. Compared with the benign control group, miR-126 expression was significantly downregulated in NSCLCs (p < 0.001), while miR-200c expression was significantly upregulated in NSCLCs (p < 0.001). The expression of miR-126 was significantly higher in NSCLCs with a tumor size of ≤3 cm than in those with a tumor size of >3 cm (p = 0.026). There were no other significant associations between miRNA expression and clinicopathological features. In univariate survival analysis for all NSCLC patients, high miR-200c expression (p = 0.037), large tumor size (p = 0.026), and lymphovascular invasion (p = 0.012) were significantly correlated with worse overall survival. High miR-126 expression was significantly associated with favorable prognosis only in patients with adenocarcinoma (p = 0.033). In multivariate analysis, miR-200c and tumor size remained as independent prognostic factors. Our results suggest that miR-126 might play tumor-suppressive and miR-200c an oncogenic role, and these miR’s are potential prognostic biomarkers for NSCLC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM (2001) Global cancer statistics in the year 2000. Lancet Oncol 55:371–377
Spira A, Ettinger DS (2004) Multidisciplinary management of lung cancer. N Eng J Med 59:225–249
Eulalio A, Huntzinger E, Nishihara T, Rehwinkel J, Fauser M, Izaurralde E (2009) Deadenylation is a widespread effect of miRNA regulation. RNA 15:21–32
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19:92–105
Caldas C, Brenton JD (2005) Sizing up miRNAs as cancer genes. Nat Med 11:712–714
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhurt R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2001) Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 294:853–858
Bandres E, Agirre X, Ramire N, Zarate R, Garcia-Foncillas J (2007) MicroRNAs as cancer players: potential clinical and biological effects. DNA Cell Biol 26:273–282
Sassen S, Miska EA, Caldas C (2008) MicroRNA: implications for cancer. Virchows Arch 452:1–10
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:259–269
Schmidt M, Paes K, De Mazière A, Smyczek T, Yang S, Gray A, French D, Kasman I, Klumperman J, Rice DS, Ye W (2007) EGFL7 regulates the collective migration of endothelial cells by restricting their spatial distribution. Development 134:2913–2923
Sun Y, Bai Y, Zhang F, Wang Y, Guo Y, Guo L (2010) miR-126 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cells proliferation by targeting EGFL7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391:1483–1489
Crawford M, Brawner E, Batte K, Yu L, Hunter MG, Otterson GA, Nuovo G, Marsh CB, Nana-Sinkam SP (2008) MicroRNA-126 inhibits invasion in non-small cell lung carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 373:607–612
Liu B, Peng XC, Zheng XL, Wang J, Qin YW (2009) MiR-126 restoration down-regulate VEGF and inhibit the growth of lung cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Lung Cancer 66:169–175
Hurteau GJ, Carlson JA, Spivack SD, Brock GJ (2007) Overexpression of the microRNA has-miR-200c leads to reduced expression of transcription factor 8 and increased expression of E-cadherin. Cancer Res 67:7972–7976
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G, Kang Y (2008) The miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem 283:14910–14914
Guarino M, Rubino B, Ballabio G (2007) The role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology. Pathology 39:305–318
Thiery JP (2002) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2:442–454
Yang J, Lan H, Huang X, Liu B, Tong Y (2012) MicroRNA-126 inhibits tumor cell growth and its expression level correlates with poor survival in non-small cell lung cancer patients. PLoS ONE 7:e42978
Jusufović E, Rijavec M, Keser D, Korošec P, Sodja E, Iljazović E, Radojević Z, Košnik M (2012) Let-7b and miR-126 are down-regulated in tumor tissue and correlate with microvessel density and survival outcomes in non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 7:e45577
Donnem T, Lonvik K, Eklo K, Berg T, Sorbye SW, Al-Shibli K, Al-Saad S, Andersen S, Stenvold H, Bremnes RM, Busund LT (2011) Independent and tissue-specific prognostic impact of miR-126 in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer 117:3193–3200
Ceppi P, Mudduluru G, Kumarswamy R, Rapa I, Scagliotti GV, Papotti M, Allgayer H (2010) Loss of miR-200c expression induces an aggressive, invasive, and chemoresistant phenotype in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Res 8:1207–1216
Liu XG, Zhu WY, Huang YY, Ma LN, Zhou SQ, Wang YK, Zeng F, Zhou JH, Zhang YK (2012) High expression of serum miR-21 and tumor miR-200c associated with poor prognosis in patients with lung cancer. Med Oncol 29:618–626
Tsim S, O'Dowd CA, Milroy R, Davidson S (2010) Staging of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): a review. Respir Med 104:1767–1774
Võsa U, Vooder T, Kolde R, Vilo J, Metspalu A, Annilo T (2013) Meta-analysis of microRNA expression in lung cancer. Int J Cancer 132:2884–2893
Landi MT, Zhao Y, Rotunno M, Koshiol J, Liu H, Bergen AW, Rubagotti M, Goldstein AM, Linnoila I, Marincola FM, Tucker MA, Bertazzi PA, Pesatori AC, Caporaso NE, McShane LM, Wang E (2010) MicroRNA expression differentiates histology and predicts survival of lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16:430–441
Yu SL, Chen HY, Chang GC, Chen CY, Chen HW, Singh S, Cheng CL, Yu CJ, Lee YC, Chen HS, Su TJ, Chiang CC, Li HN, Hong QS, Su HY, Chen CC, Chen WJ, Liu CC, Chan WK, Chen WJ, Li KC, Chen JJ, Yang PC (2008) MicroRNA signature predicts survival and relapse in lung cancer. Cancer Cell 13:48–57
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, Calin GA, Liu CG, Croce CM, Harris CC (2006) Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 9:189–198
Hamano R, Miyata H, Yamasaki M, Kurokawa Y, Hara J, Moon JH, Nakajima K, Takiguchi S, Fujiwara Y, Mori M, Doki Y (2011) Overexpression of miR-200c induces chemoresistance in esophageal cancers mediated through activation of the Akt signaling pathway. Clin Cancer Res 17:3029–3038
Chen J, Wang W, Zhang Y, Hu T, Chen Y (2014) The roles of miR-200c in colon cancer and associated molecular mechanisms. Tumor Biol. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-1860-x
Park YA, Lee JW, Choi JJ, Jeon HK, Cho Y, Choi C, Kim TJ, Lee NW, Kim BG, Bae DS (2012) The interactions between microRNA-200c and BRD7 in endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 124:125–133
Iorio MV, Visone R, Di Leva G, Donati V, Petrocca F, Casalini P, Taccioli C, Volinia S, Liu CG, Alder H, Calin GA, Ménard S, Croce CM (2007) MicroRNA signatures in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 67:8699–8707
Meng F, Henson R, Lang M, Wehbe H, Maheshwari S, Mendell JT, Jiang J, Schmittgen TD, Patel T (2006) Involvement of human micro-RNA in growth and response to chemotherapy in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. Gastroenterology 130:2113–2129
Kopp F, Wagner E, Roidl A (2014) The proto-oncogene KRAS is targeted by miR-200c. Oncotarget 5:185–195
Tsunoda T, Takashima Y, Yoshida Y, Doi K, Tanaka Y, Fujimoto T, Machida T, Ota T, Koyanagi M, Kuroki M, Sasazuki T, Shirasawa S (2011) Oncogenic KRAS regulates miR-200c and miR-221/222 in a 3D-specific manner in colorectal cancer cells. Anticancer Res 31:2453–2460
Hu Y, Correa AM, Hoque A, Guan B, Ye F, Huang J, Swisher SG, Wu TT, Ajani JA, Xu XC (2011) Prognostic significance of differentially expressed miRNAs in esophageal cancer. Int J Cancer 128:132–143
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M.K., Jung, S.B., Kim, JS. et al. Expression of microRNA miR-126 and miR-200c is associated with prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Virchows Arch 465, 463–471 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-014-1640-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-014-1640-4