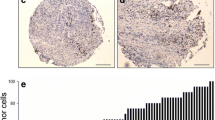
Abstract
Locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) is associated with a 25 % rate of metastases. The prognostic and predictive relevances of the expression of five proteins (c-FLIPL/s, HIF-1α, β-catenin, p65, and p105/p50 NF-κβ) were assessed. This is a retrospective study. From 1998 to 2009, 152 patients with stage II/III rectal cancer were treated with radio-chemotherapy. TMAs constructed with tumor and normal tissue from the diagnostic endoscopic biopsy and the surgical specimen after chemoradiotherapy were subjected to immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis. Results were correlated with clinical and pathological data, including progression-free survival (PFS). Four different IHC conditions were independent prognostic parameters for PFS: (1) cytoplasmic c-FLIPL/s (p = 0.007), (2) nuclear HIF-1α (p = 0.020), (3) a change in the cytoplasmic p65 between the diagnostic biopsy and the post-treatment specimen (p = 0.004), and (4) a change in the cytoplasmic c-FLIPL/s between the diagnostic biopsy and the post-treatment specimen (p = 0.021). Three different protein expression profiles, combining biomarkers, showed prognostic significance. IHC evaluation of these biomarkers in our three protein expression profiles may help to identify patients with worse prognosis and design more effective therapeutic strategies to personalize the treatment of rectal cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baba Y, Nosho K, Shima K, Irahara N, Chan AT, Meyerhardt JA, Chung DC, Giovannucci EL, Fuchs CS, Ogino S (2010) HIF1A overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in a cohort of 731 colorectal cancers. Am J Pathol 176:2292–2301
Ben Lassoued A, Beaufils N, Dales JP, Gabert J (2013) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha as prognostic marker. Expert Opin Med Diagn 7:53–70. doi:10.1517/17530059.2012.719022
Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND (2010) WHO classification of tumors of the digestive system.
Brennan DJ, O'Connor DP, Rexhepaj E, Ponten F, Gallagher WM (2010) Antibody-based proteomics: fast-tracking molecular diagnostics in oncology. Nat Rev Cancer 10:605–617. doi:10.1038/nrc2902
Dolcet X, Llobet D, Pallares J, Matias-Guiu X (2005) NF-kB in development and progression of human cancer. Virchows Arch 446:475–482. doi:10.1007/s00428-005-1264-9
Ellis RD, Goodlad JR, Limb GA, Powell JJ, Thompson RP, Punchard NA (1998) Activation of nuclear factor kappa B in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Res 47:440–445
Evertsson S, Sun XF (2002) Protein expression of NF-kappaB in human colorectal adenocarcinoma. Int J Mol Med 10:547–550
Ferlay J, Parkin DM, Steliarova-Foucher E (2010) Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2008. Eur J Cancer 46:765–781. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2009.12.014
Furlan D, Sahnane N, Carnevali I, Cerutti R, Bertoni F, Kwee I, Uccella S, Bertolini V, Chiaravalli AM, Capella C (2008) Up-regulation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1 transcriptional pathway in colorectal carcinomas. Hum Pathol 39:1483–1494
Gorlach A, Bonello S (2008) The cross-talk between NF-kappaB and HIF-1: further evidence for a significant liaison. Biochem J 412:e17–e19
Kaidi A, Williams AC, Paraskeva C (2007) Interaction between beta-catenin and HIF-1 promotes cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Nat Cell Biol 9:210–217
Korkolopoulou P, Saetta AA, Levidou G, Gigelou F, Lazaris A, Thymara I, Scliri M, Bousboukea K, Michalopoulos NV, Apostolikas N, Konstantinidou A, Tzivras M, Patsouris E (2007) c-FLIP expression in colorectal carcinomas: association with Fas/FasL expression and prognostic implications. Histopathology 51:150–156
Lee CH, Jeon YT, Kim SH, Song YS (2007) NF-kappaB as a potential molecular target for cancer therapy. Biofactors 29:19–35
Lu XG, Xing CG, Feng YZ, Chen J, Deng C (2006) Clinical significance of immunohistochemical expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha as a prognostic marker in rectal adenocarcinoma. Clin Colorectal Cancer 5:350–353
Ludwig JA, Weinstein JN (2005) Biomarkers in cancer staging, prognosis and treatment selection. Nat Rev Cancer 5:845–856. doi:10.1038/nrc1739
Mann B, Gelos M, Siedow A, Hanski ML, Gratchev A, Ilyas M, Bodmer WF, Moyer MP, Riecken EO, Buhr HJ, Hanski C (1999) Target genes of beta-catenin-T cell-factor/lymphoid-enhancer-factor signaling in human colorectal carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:1603–1608
Micheau O, Lens S, Gaide O, Alevizopoulos K, Tschopp J (2001) NF-kappaB signals induce the expression of c-FLIP. Mol Cell Biol 21:5299–5305. doi:10.1128/mcb.21.16.5299-5305.2001
Musio D, De Felice F, Bulzonetti N, Guarnaccia R, Caiazzo R, Bangrazi C, Raffetto N, Tombolini V (2013) Neoadjuvant-intensified treatment for rectal cancer: time to change? World J Gastroenterol 19:3052–3061. doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3052
Naito M, Katayama R, Ishioka T, Suga A, Takubo K, Nanjo M, Hashimoto C, Taira M, Takada S, Takada R, Kitagawa M, Matsuzawa S, Reed JC, Tsuruo T (2004) Cellular FLIP inhibits beta-catenin ubiquitylation and enhances Wnt signaling. Mol Cell Biol 24:8418–8427. doi:10.1128/mcb.24.19.8418-8427.2004
Pallares J, Santacana M, Puente S, Lopez S, Yeramian A, Eritja N, Sorolla A, Llobet D, Dolcet X, Matias-Guiu X (2009) A review of the applications of tissue microarray technology in understanding the molecular features of endometrial carcinoma. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 31:217–226
Rimm DL, Camp RL, Charette LA, Costa J, Olsen DA, Reiss M (2001) Tissue microarray: a new technology for amplification of tissue resources. Cancer J 7:24–31
Schoenfeld DA (1983) Sample-size formula for the proportional-hazards regression model. Biometrics 39:499–503
Simiantonaki N, Taxeidis M, Jayasinghe C, Kurzik-Dumke U, Kirkpatrick CJ (2008) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha expression increases during colorectal carcinogenesis and tumor progression. BMC Cancer 8:320
Thakur R, Mishra DP (2013) Pharmacological modulation of beta-catenin and its applications in cancer therapy. J Cell Mol Med 17:449–456. doi:10.1111/jcmm.12033
Theodoropoulos GE, Lazaris AC, Theodoropoulos VE, Papatheodosiou K, Gazouli M, Bramis J, Patsouris E, Panoussopoulos D (2006) Hypoxia, angiogenesis and apoptosis markers in locally advanced rectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis 21:248–257
Ullenhag GJ, Mukherjee A, Watson NF, Al-Attar AH, Scholefield JH, Durrant LG (2007) Overexpression of FLIPL is an independent marker of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 13:5070–5075. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-06-2547
Valentini V, van Stiphout RG, Lammering G, Gambacorta MA, Barba MC, Bebenek M, Bonnetain F, Bosset JF, Bujko K, Cionini L, Gerard JP, Rodel C, Sainato A, Sauer R, Minsky BD, Collette L, Lambin P (2011) Nomograms for predicting local recurrence, distant metastases, and overall survival for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer on the basis of European randomized clinical trials. J Clin Oncol 29:3163–3172
Voboril R, Voborilova J, Rychterova V, Jirasek T, Dvorak J (2008) Dissociated invasively growing cancer cells with NF-kappaB/p65 positivity after radiotherapy: a new marker for worse clinical outcome in rectal cancer? Preliminary data Clin Exp Metastasis 25:491–496. doi:10.1007/s10585-008-9155-5
Voboril R, Weberova-Voborilova J (2007) Sensitization of colorectal cancer cells to irradiation by IL-4 and IL-10 is associated with inhibition of NF-kappaB. Neoplasma 54:495–502
Wilson TR, McLaughlin KM, McEwan M, Sakai H, Rogers KM, Redmond KM, Johnston PG, Longley DB (2007) c-FLIP: a key regulator of colorectal cancer cell death. Cancer Res 67:5754–5762
Yu HG, Yu LL, Yang Y, Luo HS, Yu JP, Meier JJ, Schrader H, Bastian A, Schmidt WE, Schmitz F (2003) Increased expression of RelA/nuclear factor-kappa B protein correlates with colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncology 65:37–45. doi:10.1159/000071203
Yu HG, Zhong X, Yang YN, Luo HS, Yu JP, Meier JJ, Schrader H, Bastian A, Schmidt WE, Schmitz F (2004) Increased expression of nuclear factor-kappaB/RelA is correlated with tumor angiogenesis in human colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis 19:18–22. doi:10.1007/s00384-003-0494-z
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. F. Badia and Dr. R. Oncins and the members of the Colorectal Cancer Tumor Boards in Lleida for providing the pathological material and follow-up data. Work supported by the Xarxa de Bancs de Tumors de Catalunya sponsored by Pla Director d’Oncología de Catalunya (XBTC) and IRBLleida Biobank (B.0000682) and Plataforma Biobancos PT13/0010/0014.
Funding sources for this work
This work was supported by grants 2009SGR794, RD12/0036/0013.
All financial disclosures
No financial disclosures.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Antonieta Salud and Xavier Matias-Guiu are both senior co-authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Novell, A., Martínez-Alonso, M., Mira, M. et al. Prognostic value of c-FLIPL/s, HIF-1α, and NF-κβ in stage II and III rectal cancer. Virchows Arch 464, 645–654 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-014-1572-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-014-1572-z