Abstract
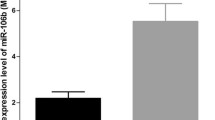
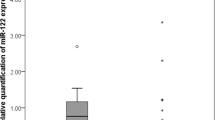
Hepatoblastoma (HB) is the most common primary liver cancer in childhood. The fetal and mixed embryonal/fetal epithelial subtypes of HB differ not only in grade of differentiation but probably also in prognosis. We aimed to determine microRNA (miRNA) expression patterns of the main subtypes of epithelial HBs to reveal differences and relate them to survival. We studied 20 cases of epithelial HB, subtyped as pure fetal (n = 12) or embryonal/fetal (n = 8). Tissues were sampled according to subtype to arrive at 15 purely fetal and eight purely embryonal samples (n = 8) and 15 samples of non-tumorous surrounding liver (SL). Relative expression of miR-17-5p, miR-18a, miR-21, miR-34a, miR-96, miR-122, miR-181a, miR-195, miR-210, miR-214, miR-221, miR-222, miR-223, and miR-224 was determined by TaqMan MicroRNA Assays applying miR-140 as reference. A higher level of miR-18a (p < 0.01) was found in embryonal samples than in fetal samples. Lower miR-17-5p, miR-195, miR-210, miR-214, and higher miR-221 levels were detected in fetal samples (p < 0.02) in comparison with SL samples, whereas a lower miR-122 level was observed in embryonal samples (p < 0.003). Histological subtype did not correlate with survival; however, high miR-21, low miR-222, and low miR-224 levels proved to be independently prognostic for HB with significantly increased overall survival (p < 0.03). The fetal and embryonal components of epithelial HB, as well as SL, revealed different miRNA expression patterns. Furthermore, miR-21, miR-222, and miR-224 levels predict overall survival of HB patients regardless of epithelial subtype.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwala S (2012) Primary malignant liver tumors in children. Indian J Pediatr 79:793–800
Lopez-Terrada D, Zimmermann A (2012) Current issues and controversies in the classification of pediatric hepatocellular tumors. Pediatr Blood Cancer 59:780–784
Allan BJ, Parikh PP, Diaz S, Perez EA, Neville HL, Sola JE (2013) Predictors of survival and incidence of hepatoblastoma in the paediatric population. HPB (Oxford) 15:741–746
Purcell R, Childs M, Maibach R, Miles C, Turner C, Zimmermann A, Sullivan M (2011) HGF/c-Met related activation of beta-catenin in hepatoblastoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 30:96
Dezso K, Halasz J, Bisgaard HC, Paku S, Turanyi E, Schaff Z, Nagy P (2008) Delta-like protein (DLK) is a novel immunohistochemical marker for human hepatoblastomas. Virchows Arch 452:443–448
Halasz J, Holczbauer A, Paska C, Kovacs M, Benyo G, Verebely T, Schaff Z, Kiss A (2006) Claudin-1 and claudin-2 differentiate fetal and embryonal components in human hepatoblastoma. Hum Pathol 37:555–561
Purcell R, Childs M, Maibach R, Miles C, Turner C, Zimmermann A, Czauderna P, Sullivan M (2012) Potential biomarkers for hepatoblastoma: results from the SIOPEL-3 study. Eur J Cancer 48:1853–1859
Kiss A, Szepesi A, Lotz G, Nagy P, Schaff Z (1998) Expression of transforming growth factor-alpha in hepatoblastoma. Cancer 83:690–697
Adesina AM, Lopez-Terrada D, Wong KK, Gunaratne P, Nguyen Y, Pulliam J, Margolin J, Finegold MJ (2009) Gene expression profiling reveals signatures characterizing histologic subtypes of hepatoblastoma and global deregulation in cell growth and survival pathways. Hum Pathol 40:843–853
Cairo S, Armengol C, Buendia MA (2012) Activation of Wnt and Myc signaling in hepatoblastoma. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 4:480–486
Ciesla M, Skrzypek K, Kozakowska M, Loboda A, Jozkowicz A, Dulak J (2011) MicroRNAs as biomarkers of disease onset. Anal Bioanal Chem 401:2051–2061
Farazi TA, Spitzer JI, Morozov P, Tuschl T (2011) miRNAs in human cancer. J Pathol 223:102–115
Braconi C, Henry JC, Kogure T, Schmittgen T, Patel T (2011) The role of microRNAs in human liver cancers. Semin Oncol 38:752–763
Cairo S, Wang Y, de Reynies A, Duroure K, Dahan J, Redon MJ, Fabre M, McClelland M, Wang XW, Croce CM, Buendia MA (2010) Stem cell-like micro-RNA signature driven by Myc in aggressive liver cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:20471–20476
Kerr TA, Korenblat KM, Davidson NO (2011) MicroRNAs and liver disease. Transl Res 157:241–252
Lakner AM, Bonkovsky HL, Schrum LW (2011) microRNAs: fad or future of liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 17:2536–2542
Rong M, Chen G, Dang Y (2013) Increased miR-221 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues and its role in enhancing cell growth and inhibiting apoptosis in vitro. BMC Cancer 13:21
Magrelli A, Azzalin G, Salvatore M, Viganotti M, Tosto F, Colombo T, Devito R, Di Masi A, Antoccia A, Lorenzetti S, Maranghi F, Mantovani A, Tanzarella C, Macino G, Taruscio D (2009) Altered microRNA expression patterns in hepatoblastoma patients. Transl Oncol 2:157–163
Haas JE, Feusner JH, Finegold MJ (2001) Small cell undifferentiated histology in hepatoblastoma may be unfavorable. Cancer 92:3130–3134
Perilongo G, Malogolowkin M, Feusner J (2012) Hepatoblastoma clinical research: lessons learned and future challenges. Pediatr Blood Cancer 59:818–821
Perilongo G, Shafford E, Maibach R, Aronson D, Brugieres L, Brock P, Childs M, Czauderna P, MacKinlay G, Otte JB, Pritchard J, Rondelli R, Scopinaro M, Staalman C, Plaschkes J (2004) Risk-adapted treatment for childhood hepatoblastoma. Final report of the second study of the international society of paediatric oncology—SIOPEL 2. Eur J Cancer 40:411–421
Doleshal M, Magotra AA, Choudhury B, Cannon BD, Labourier E, Szafranska AE (2008) Evaluation and validation of total RNA extraction methods for microRNA expression analyses in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. J Mol Diagn 10:203–211
Karakatsanis A, Papaconstantinou I, Gazouli M, Lyberopoulou A, Polymeneas G, Voros D (2013) Expression of microRNAs, miR-21, miR-31, miR-122, miR-145, miR-146a, miR-200c, miR-221, miR-222, and miR-223 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma or intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and its prognostic significance. Mol Carcinog 52:297–303
Varnholt H, Drebber U, Schulze F, Wedemeyer I, Schirmacher P, Dienes HP, Odenthal M (2008) MicroRNA gene expression profile of hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 47:1223–1232
Pineau P, Volinia S, McJunkin K, Marchio A, Battiston C, Terris B, Mazzaferro V, Lowe SW, Croce CM, Dejean A (2010) miR-221 overexpression contributes to liver tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:264–269
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Orntoft TF (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res 64:5245–5250
Ismail H, Broniszczak D, Kalicinski P, Dembowska-Baginska B, Perek D, Teisseyre J, Kluge P, Kosciesza A, Lembas A, Markiewicz M (2012) Changing treatment and outcome of children with hepatoblastoma: analysis of a single center experience over the last 20 years. J Pediatr Surg 47:1331–1339
Shenouda SK, Alahari SK (2009) MicroRNA function in cancer: oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer Metastasis Rev 28:369–378
Lopez-Terrada D, Gunaratne PH, Adesina AM, Pulliam J, Hoang DM, Nguyen Y, Mistretta TA, Margolin J, Finegold MJ (2009) Histologic subtypes of hepatoblastoma are characterized by differential canonical Wnt and Notch pathway activation in DLK + precursors. Hum Pathol 40:783–794
Chopra A, Iyer VK, Agarwala S, Mathur SR, Aron M, Gupta SD, Verma K (2010) Apoptotic protein expression, glycogen content, DNA ploidy and cell proliferation in hepatoblastoma subtyping and their role in prognostication. Pediatr Surg Int 26:1173–1178
von Frowein J, Pagel P, Kappler R, von Schweinitz D, Roscher A, Schmid I (2011) MicroRNA-492 is processed from the keratin 19 gene and up-regulated in metastatic hepatoblastoma. Hepatology 53:833–842
Scisciani C, Vossio S, Guerrieri F, Schinzari V, De Iaco R, D’Onorio de Meo P, Cervello M, Montalto G, Pollicino T, Raimondo G, Levrero M, Pediconi N (2012) Transcriptional regulation of miR-224 upregulated in human HCCs by NFkappaB inflammatory pathways. J Hepatol 56:855–861
Boutz DR, Collins PJ, Suresh U, Lu M, Ramirez CM, Fernandez-Hernando C, Huang Y, Abreu Rde S, Le SY, Shapiro BA, Liu AM, Luk JM, Aldred SF, Trinklein ND, Marcotte EM, Penalva LO (2011) Two-tiered approach identifies a network of cancer and liver disease-related genes regulated by miR-122. J Biol Chem 286:18066–18078
Hu J, Xu Y, Hao J, Wang S, Li C, Meng S (2012) MiR-122 in hepatic function and liver diseases. Protein Cell 3:364–371
Xu T, Zhu Y, Xiong Y, Ge YY, Yun JP, Zhuang SM (2009) MicroRNA-195 suppresses tumorigenicity and regulates G1/S transition of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 50:113–121
Chen L, Jiang M, Yuan W, Tang H (2012) miR-17-5p as a novel prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Invest Surg 25:156–161
Yang W, Sun T, Cao J, Liu F, Tian Y, Zhu W (2012) Downregulation of miR-210 expression inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis and enhances radiosensitivity in hypoxic human hepatoma cells in vitro. Exp Cell Res 318:944–954
El Tayebi HM, Omar K, Hegy S, El Maghrabi M, El Brolosy M, Hosny KA, Esmat G, Abdelaziz AI (2013) Repression of miR-17-5p with elevated expression of E2F-1 and c-MYC in non-metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma and enhancement of cell growth upon reversing this expression pattern. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 434:421–427
Wang X, Chen J, Li F, Lin Y, Zhang X, Lv Z, Jiang J (2012) MiR-214 inhibits cell growth in hepatocellular carcinoma through suppression of beta-catenin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 428:525–531
Wu W, Takanashi M, Borjigin N, Ohno SI, Fujita K, Hoshino S, Osaka Y, Tsuchida A, Kuroda M (2013) MicroRNA-18a modulates STAT3 activity through negative regulation of PIAS3 during gastric adenocarcinogenesis. Br J Cancer 108:653–661
Brock M, Trenkmann M, Gay RE, Gay S, Speich R, Huber LC (2011) MicroRNA-18a enhances the interleukin-6-mediated production of the acute-phase proteins fibrinogen and haptoglobin in human hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 286:40142–40150
Wong QW, Ching AK, Chan AW, Choy KW, To KF, Lai PB, Wong N (2010) MiR-222 overexpression confers cell migratory advantages in hepatocellular carcinoma through enhancing AKT signaling. Clin Cancer Res 16:867–875
Garofalo M, Quintavalle C, Romano G, Croce CM, Condorelli G (2012) miR221/222 in cancer: their role in tumor progression and response to therapy. Curr Mol Med 12:27–33
Ma D, Tao X, Gao F, Fan C, Wu D (2012) miR-224 functions as an onco-miRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating AKT signaling. Oncol Lett 4:483–488
Shen SN, Wang LF, Jia YF, Hao YQ, Zhang L, Wang H (2013) Upregulation of microRNA-224 is associated with aggressive progression and poor prognosis in human cervical cancer. Diagn Pathol 8:69
Lu S, Wang S, Geng S, Ma S, Liang Z, Jiao B (2013) Upregulation of microRNA-224 confers a poor prognosis in glioma patients. Clin Transl Oncol 15:569–574
Zhu Q, Wang Z, Hu Y, Li J, Li X, Zhou L, Huang Y (2012) miR-21 promotes migration and invasion by the miR-21-PDCD4-AP-1 feedback loop in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 27:1660–1668
Bao L, Yan Y, Xu C, Ji W, Shen S, Xu G, Zeng Y, Sun B, Qian H, Chen L, Wu M, Chen J, Su C (2013) MicroRNA-21 suppresses PTEN and hSulf-1 expression and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through AKT/ERK pathways. Cancer Lett 337:226–236
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mrs. Elvira Kálé Rigóné for the English proofreading and Mrs. Magdolna Zoltánné Pekár for her assistance in sectioning and manually guided dissection. This study was supported by grants OTKA K101435 and K108548 from the National Scientific Research Foundation.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to be identified.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gyugos, M., Lendvai, G., Kenessey, I. et al. microRNA expression might predict prognosis of epithelial hepatoblastoma. Virchows Arch 464, 419–427 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-014-1549-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-014-1549-y