Abstract
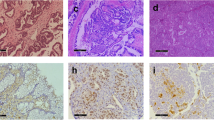
In order to study survivin, matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2), membranous type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP), and tissue inhibitor metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2) expression immunohistochemically in endometriotic tissues and normal endometrium, our retrospective study considered 194 patients affected by endometriosis and 71 patients with normal endometrium. Tissue microarrays were created from paraffin-embedded blocks; immunohistochemistry was used to assess protein expression. In endometriotic tissues, survivin was expressed at a higher level than in normal endometrium; its glandular expression level was higher in non-ovarian than in ovarian endometriotic tissues and lower in stromal components. Endometrial tissues from women without endometriosis and endometriotic tissues had different matrix metalloproteinase expression profiles. MMP-2 and MT1-MMP correlated with TIMP-2 in endometriotic tissues. Furthermore, in endometriotic tissues, expression of survivin, aurora B kinase, and Ki-67 showed a significant positive correlation, which indicates a role in cellular proliferation that could be closely linked to its anti-apoptotic activity in endometriosis development. Our results imply a role for matrix metalloproteinases in endometriosis invasiveness; correlation of their expression with that of TIMP-2 underscores its possible key regulatory role.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABK:
-
Aurora B kinase
- APC:
-
Adenomatous polyposis coli
- ASRM:
-
American Society of Reproductive Medicine
- ET:
-
Endometriotic tissue
- IAP:
-
Inhibitor of apoptosis protein
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- MMP-2:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-2
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- MT1-MMP:
-
Membranous type 1 matrix metalloproteinase
- PR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- TIMP-2:
-
Tissue inhibitor metalloproteinase-2
- TMA:
-
Tissue microarray
References
Leyendecker G, Kunz G, Noe M, Herbertz M, Mall G (1998) Endometriosis: a dysfunction and disease of the archimetra. Hum Reprod Update 4:752–762
Fujino K, Ueda M, Takehara M et al (2006) Transcriptional expression of survivin and its splice variants in endometriosis. Mol Hum Reprod 12:383–388. doi:10.1093/molehr/gal042
Fauvet R, Poncelet C, Hugol D, Lavaur A, Feldmann G, Daraï E (2003) Expression of apoptosis-related proteins in endometriomas and benign and malignant ovarian tumours. Virchows Arch 443:38–43. doi:10.1007/s00428-003-0813-3
Ueda M, Yamashita Y, Takehara M et al (2002) Survivin gene expression in endometriosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:3452–3459
Imai A, Takagi A, Tamaya T (2000) Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analog repairs reduced endometrial cell apoptosis in endometriosis in vitro. Am J Obstet Gynecol 182:1142–1146
Gebel HM, Braun DP, Tambur A, Frame D, Rana N, Dmowski WP (1998) Spontaneous apoptosis of endometrial tissue is impaired in women with endometriosis. Fertil Steril 69:1042–1047
Ai Z, Yin L, Zhou X, Zhu Y, Zhu D, Yu Y, Feng Y (2006) Inhibition of survivin reduces cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in human endometrial cancer. Cancer 107:746–756. doi:10.1002/cncr.22044
Kelly AE, Ghenoiu C, Xue JZ, Zierhut C, Kimura H, Funabiki H (2010) Survivin reads phosphorylated histone H3 threonine 3 to activate the mitotic kinase Aurora B. Science 330:235–239. doi:10.1126/science.1189505
Musacchio A (2010) Molecular biology. Surfing chromosomes (and Survivin). Science 330:183–184, doi:10.1126/science.1197261.
Chu Y, Yao PY, Wang W et al (2010) Aurora B kinase activation requires survivin priming phosphorylation by PLK1. J Mol Cell Biol. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjq037
Chung HW, Lee JY, Moon HS, Hur SE, Park MH, Wen Y, Polan ML (2002) Matrix metalloproteinase-2, membranous type 1 matrix metalloproteinase, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 expression in ectopic and eutopic endometrium. Fertil Steril 78:787–795
Will H, Atkinson SJ, Butler GS, Smith B, Murphy G (1996) The soluble catalytic domain of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase cleaves the propeptide of progelatinase A and initiates autoproteolytic activation. Regulation by TIMP-2 and TIMP-3. J Biol Chem 271:17119–17123
Zucker S, Drews M, Conner C et al (1998) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2) binds to the catalytic domain of the cell surface receptor, membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MT1-MMP). J Biol Chem 273:1216–1222
Strongin AY, Collier I, Bannikov G, Marmer BL, Grant GA, Goldberg GI (1995) Mechanism of cell surface activation of 72-kDa type IV collagenase. Isolation of the activated form of the membrane metalloprotease. J Biol Chem 270:5331–5338
Murphy G (2011) Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases. Genome Biol 12:233. doi:10.1186/gb-2011-12-11-233
Kokorine I, Marbaix E, Henriet P, Okada Y, Donnez J, Eeckhout Y, Courtoy PJ (1996) Focal cellular origin and regulation of interstitial collagenase (matrix metalloproteinase-1) are related to menstrual breakdown in the human endometrium. J Cell Sci 109(Pt 8):2151–2160
Osteen KG, Keller NR, Feltus FA, Melner MH (1999) Paracrine regulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression in the normal human endometrium. Gynecol Obstet Invest 48(Suppl 1):2–13
Bruner-Tran KL, Eisenberg E, Yeaman GR, Anderson TA, McBean J, Osteen KG (2002) Steroid and cytokine regulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression in endometriosis and the establishment of experimental endometriosis in nude mice. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:4782–4791
Uzan C, Cortez A, Dufournet C, Fauvet R, Siffroi JP, Daraï E (2004) Eutopic endometrium and peritoneal, ovarian and bowel endometriotic tissues express a different profile of matrix metalloproteinases-2, -3 and -11, and of tissue inhibitor metalloproteinases-1 and -2. Virchows Arch 445:603–609. doi:10.1007/s00428-004-1117-y
Ria R, Loverro G, Vacca A, Ribatti D, Cormio G, Roccaro AM, Selvaggi L (2002) Angiogenesis extent and expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 agree with progression of ovarian endometriomas. Eur J Clin Invest 32:199–206
Calcagno A, Grassi T, Mariuzzi L et al (2011) Expression patterns of Aurora A and B kinases, Ki-67 and the estrogen and progesterone receptors determined using an endometriosis tissue microarray model. Hum Reprod 26:2731–2741. doi:10.1093/humrep/der264
Noyes R, Hertig A, Rock J (1950) Dating the endometrial biopsy. Fertil Steril 1:3–25
ASRM (1997) Revised American Society for Reproductive Medicine classification of endometriosis: 1996. Fertil Steril 67:817–821
Dilly M, Hambruch N, Shenavai S et al (2011) Expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-14 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase (TIMP)-2 during bovine placentation and at term with or without placental retention. Theriogenology 75:1104–1114. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2010.11.019
Mazzoni A, Pashley DH, Tay FR et al (2009) Immunohistochemical identification of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in human dentin: correlative FEI-SEM/TEM analysis. J Biomed Mater Res A 88:697–703. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.31920
Zhang H, Li M, Zheng X, Sun Y, Wen Z, Zhao X (2009) Endometriotic stromal cells lose the ability to regulate cell-survival signaling in endometrial epithelial cells in vitro. Mol Hum Reprod 15:653–663. doi:10.1093/molehr/gap069
Tamm I, Wang Y, Sausville E, Scudiero DA, Vigna N, Oltersdorf T, Reed JC (1998) IAP-family protein survivin inhibits caspase activity and apoptosis induced by Fas (CD95), Bax, caspases, and anticancer drugs. Cancer Res 58:5315–5320
Konno R, Yamakawa H, Utsunomiya H, Ito K, Sato S, Yajima A (2000) Expression of survivin and Bcl-2 in the normal human endometrium. Mol Hum Reprod 6:529–534
Donjacour AA, Cunha GR (1991) Stromal regulation of epithelial function. Cancer Treat Res 53:335–364
Gaide Chevronnay HP, Selvais C, Emonard H, Galant C, Marbaix E, Henriet P (2012) Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases activity studied in human endometrium as a paradigm of cyclic tissue breakdown and regeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta 1824:146–156. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap. 2011.09.003
Sotnikova NY, Antsiferova YS, Posiseeva LV, Shishkov DN, Posiseev DV, Filippova ES (2010) Mechanisms regulating invasiveness and growth of endometriosis lesions in rat experimental model and in humans. Fertil Steril 93:2701–2705. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.11.024
Di Carlo C, Bonifacio M, Tommaselli GA, Bifulco G, Guerra G, Nappi C (2009) Metalloproteinases, vascular endothelial growth factor, and angiopoietin 1 and 2 in eutopic and ectopic endometrium. Fertil Steril 91:2315–2323. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.03.079
Wenzl RJ, Heinzl H (1998) Localization of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in uterine endometrium and ectopic implants. Gynecol Obstet Invest 45:253–257
Mönckedieck V, Sannecke C, Husen B et al (2009) Progestins inhibit expression of MMPs and of angiogenic factors in human ectopic endometrial lesions in a mouse model. Mol Hum Reprod 15:633–643. doi:10.1093/molehr/gap063
Bruner-Tran KL, Zhang Z, Eisenberg E, Winneker RC, Osteen KG (2006) Down-regulation of endometrial matrix metalloproteinase-3 and -7 expression in vitro and therapeutic regression of experimental endometriosis in vivo by a novel nonsteroidal progesterone receptor agonist, tanaproget. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:1554–1560. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-2024
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Enrica Stella for her help in this study, Matteo De Luca for the technical assistance in realizing TMA, and to Dr. Serena Bertozzi for her help in preparation of this manuscript. Dr. Giorgio Zaccagna, Dr. Guido Borgna and Dr. Marco Pittino are thanked for their helpful collaboration. This study was financially supported by the University of Udine.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ambrogio P. Londero and Angelo Calcagno equally contributed to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 215 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Londero, A.P., Calcagno, A., Grassi, T. et al. Survivin, MMP-2, MT1-MMP, and TIMP-2: their impact on survival, implantation, and proliferation of endometriotic tissues. Virchows Arch 461, 589–599 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-012-1301-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-012-1301-4