Abstract
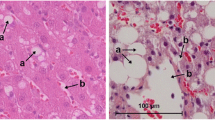
The issue of adequately quantitatively evaluating hepatic steatosis is still unresolved. Therefore, we compared three methods of quantitative assessment. Two groups of mice (n = 10 each) were fed standard chow (10% fat, SC group) or a high-fat diet (60% fat, HF group) for 16 weeks, and hepatic triglyceride (HT) and liver tissue were then studied. Paraplast-embedded tissues stained by hematoxylin and eosin (H-E) were compared to frozen sections stained by Oil Red-O (ORO). In addition, the volume density of steatosis (Vv[steatosis, liver]) was measured by point counting (P-C, sections H-E or ORO) or by image analysis (I-A, sections ORO). HT was significantly higher in the HF group (104% greater, P = 0.0004) than in the SC group. With P-C and H-E, Vv[steatosis, liver] was 4.80 ± 0.90% in the SC group and 33.50 ± 3.17% in the HF group (600% greater, P < 0.0001). With P-C and ORO, Vv[steatosis, liver] was 4.86 ± 0.89% in the SC group and 25.21 ± 1.27% in the HF group (420% greater, P < 0.0001). With I-A and ORO, Vv[steatosis, liver] was 4.17 ± 0.85% in the SC group and 23.35 ± 1.58% in the HF group (460% greater, P < 0.0001). Correlations between Vv[steatosis, liver] and HT were strong and significant in all methods. In conclusion, all methods were appropriate and reproducible. In P-C and H-E, there is a slight overestimation of steatosis in the HF animals in comparison to frozen sections and ORO; in frozen sections, differences between P-C and I-A are insignificant.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Erickson SK (2009) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Lipid Res 50(Suppl):S412–416
Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, Nuremberg P, Horton JD, Cohen JC, Grundy SM, Hobbs HH (2004) Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology 40:1387–1395
Farrell GC, Larter CZ (2006) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: from steatosis to cirrhosis. Hepatology 43:S99–S112
Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG (2010) Histopathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 16:5286–5296
Burt AD, Mutton A, Day CP (1998) Diagnosis and interpretation of steatosis and steatohepatitis. Semin Diagn Pathol 15:246–258
Sherlock S (1995) Alcoholic liver disease. Lancet 345:227–229
Tannapfel A, Denk H, Dienes H-P, Langner C, Schirmacher P, Trauner M, Flott-Rahmel B (2011) Histopathological diagnosis of non-alcoholic and alcoholic fatty liver disease. Virchows Archiv 458:511–523
van Werven JR, Marsman HA, Nederveen AJ, Smits NJ, ten Kate FJ, van Gulik TM, Stoker J (2010) Assessment of hepatic steatosis in patients undergoing liver resection: comparison of US, CT, T1-weighted dual-echo MR imaging, and point-resolved 1H MR spectroscopy. Radiology 256:159–168
El-Badry AM, Breitenstein S, Jochum W, Washington K, Paradis V, Rubbia-Brandt L, Puhan MA, Slankamenac K, Graf R, Clavien PA (2009) Assessment of hepatic steatosis by expert pathologists: the end of a gold standard. Ann Surg 250:691–697
Adams LA, Angulo P (2007) Role of liver biopsy and serum markers of liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Liver Dis 11:25–35, viii.
Contos MJ, Sanyal AJ (2002) The clinicopathologic spectrum and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Adv Anat Pathol 9:37–51
Franzen LE, Ekstedt M, Kechagias S, Bodin L (2005) Semiquantitative evaluation overestimates the degree of steatosis in liver biopsies: a comparison to stereological point counting. Mod Pathol 18:912–916
Liquori GE, Calamita G, Cascella D, Mastrodonato M, Portincasa P, Ferri D (2009) An innovative methodology for the automated morphometric and quantitative estimation of liver steatosis. Histol Histopathol 24:49–60
Reeves PG, Nielsen FH, Fahey GC Jr (1993) AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J Nutr 123:1939–1951
Fraulob JC, Ogg-Diamantino R, Fernandes-Santos C, Aguila MB, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA (2010) A mouse model of metabolic syndrome: insulin resistance, fatty liver and non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease (NAFPD) in C57BL/6 mice fed a high fat diet. J Clin Biochem Nutr 46:212–223
Souza-Mello V, Gregorio BM, Cardoso-de-Lemos FS, de Carvalho L, Aguila MB, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA (2010) Comparative effects of telmisartan, sitagliptin and metformin alone or in combination on obesity, insulin resistance, and liver and pancreas remodelling in C57BL/6 mice fed on a very high-fat diet. Clin Sci (Lond) 119:239–250
Vieira VJ, Valentine RJ, Wilund KR, Woods JA (2009) Effects of diet and exercise on metabolic disturbances in high-fat diet-fed mice. Cytokine 46:339–345
Aguila MB, Pinheiro AR, Parente LB, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA (2003) Dietary effect of different high-fat diet on rat liver stereology. Liver Int 23:363–370
Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA, Fernandes-Santos C, Aguila MB (2010) Image analysis and quantitative morphology. Methods Mol Biol 611:211–225
Marques CM, Motta VF, Torres TS, Aguila MB, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA (2010) Beneficial effects of exercise training (treadmill) on insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat fed C57BL/6 mice. Braz J Med Biol Res 43:467–475
Nascimento FA, Barbosa-da-Silva S, Fernandes-Santos C, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA, Aguila MB (2010) Adipose tissue, liver and pancreas structural alterations in C57BL/6 mice fed high-fat-high-sucrose diet supplemented with fish oil (n − 3 fatty acid rich oil). Exp Toxicol Pathol 62:17–25
Brunt EM (2010) Pathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:195–203
Ahishali E, Demir K, Ahishali B, Akyuz F, Pinarbasi B, Poturoglu S, Ibrisim D, Gulluoglu M, Ozdil S, Besisik F, Kaymakoglu S, Boztas G, Cakaloglu Y, Mungan Z, Canberk Y, Okten A (2010) Electron microscopic findings in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: is there a difference between hepatosteatosis and steatohepatitis? J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25:619–626
Straub BK, Schirmacher P (2010) Pathology and biopsy assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Dis 28:197–202
Garcia Urena MA, Colina Ruiz-Delgado F, Moreno Gonzalez E, Jimenez Romero C, Garcia Garcia I, Loinzaz Segurola C, Gonzalez P, Gomez Sanz R (1998) Hepatic steatosis in liver transplant donors: common feature of donor population? World J Surg 22:837–844
Brunt EM, Janney CG, Di Bisceglie AM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Bacon BR (1999) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J Gastroenterol 94:2467–2474
Turlin B, Mendler MH, Moirand R, Guyader D, Guillygomarc’h A, Deugnier Y (2001) Histologic features of the liver in insulin resistance-associated iron overload. A study of 139 patients. Am J Clin Pathol 116:263–270
Sanyal AJ (2002) AGA technical review on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 123:1705–1725
Turlin B, Ramm GA, Purdie DM, Laine F, Perrin M, Deugnier Y, Macdonald GA (2009) Assessment of hepatic steatosis: comparison of quantitative and semiquantitative methods in 108 liver biopsies. Liver Int 29:530–535
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, Ferrell LD, Liu YC, Torbenson MS, Unalp-Arida A, Yeh M, McCullough AJ, Sanyal AJ (2005) Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 41:1313–1321
Wieckowska A, Feldstein AE (2008) Diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: invasive versus noninvasive. Semin Liver Dis 28:386–395
Lee JH, Kim D, Kim HJ, Lee CH, Yang JI, Kim W, Kim YJ, Yoon JH, Cho SH, Sung MW, Lee HS (2010) Hepatic steatosis index: a simple screening tool reflecting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Liver Dis 42:503–508
Lee SS, Park SH, Kim HJ, Kim SY, Kim MY, Kim DY, Suh DJ, Kim KM, Bae MH, Lee JY, Lee SG, Yu ES (2010) Non-invasive assessment of hepatic steatosis: prospective comparison of the accuracy of imaging examinations. J Hepatol 52:579–585
Cruz-Orive LM, Weibel ER (1990) Recent stereological methods for cell biology: a brief survey. Am J Physiol 258:L148–156
Weibel ER (1989) Measuring through the microscope: development and evolution of stereological methods. J Microsc 155:393–403
Souza-Mello V, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA, Aguila MB (2007) Hepatic structural alteration in adult programmed offspring (severe maternal protein restriction) is aggravated by post-weaning high-fat diet. Br J Nutr 98:1159–1169
Rawlins SR, El-Zammar O, Zinkievich JM, Newman N, Levine RA (2010) Digital quantification is more precise than traditional semiquantitation of hepatic steatosis: correlation with fibrosis in 220 treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C. Dig Dis Sci 55:2049–2057
Nakano S, Nagasawa T, Ijiro T, Inada Y, Tamura T, Maruyama K, Kuroda J, Yamazaki Y, Kusama H, Shibata N (2008) Bezafibrate prevents hepatic stellate cell activation and fibrogenesis in a murine steatohepatitis model, and suppresses fibrogenic response induced by transforming growth factor-beta1 in a cultured stellate cell line. Hepatol Res 38:1026–1039
Neves RH, de Barros M, Alencar AC, Costa-Silva M, Aguila MB, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA, Machado-Silva JR, Gomes DC (2007) Long-term feeding a high-fat diet causes histological and parasitological effects on murine schistosomiasis mansoni outcome. Exp Parasitol 115:324–332
DeLeve LD, Wang X, Kanel GC, Atkinson RD, McCuskey RS (2008) Prevention of hepatic fibrosis in a murine model of metabolic syndrome with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Pathol 173:993–1001
Neves RH, Alencar AC, Aguila MB, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA, Machado-Silva JR, Gomes DC (2007) Light and confocal microscopic observations of adult Schistosoma mansoni from mice fed on a high-fat diet. J Helminthol 81:361–368
Tschanz SA, Burri PH, Weibel ER (2011) A simple tool for stereological assessment of digital images: the STEPanizer. J Microsc 243(Pt 1):47–59
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Thatiany Marinho and Angelica Figueiredo for their technical assistance. This research was supported by the Brazilian agencies CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Ciencia e Tecnologia, www.cnpq.br) and FAPERJ (Fundacao para o Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, www.faperj.br).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Catta-Preta, M., Mendonca, L.S., Fraulob-Aquino, J. et al. A critical analysis of three quantitative methods of assessment of hepatic steatosis in liver biopsies. Virchows Arch 459, 477–485 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-011-1147-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-011-1147-1