Abstract
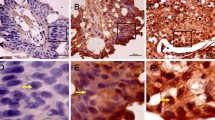
Distinguishing urinary bladder muscularis propria (MP) from muscularis mucosae (MM) is crucial in bladder cancer staging. Immunohistochemical staining for the smooth muscle-specific protein smoothelin has been reported to be a robust marker for MP. The aim of this study was to investigate how smoothelin immunostaining in the bladder varies with pretreatment techniques and if it can be used to discriminate between MM and MP. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) for smoothelin was performed on nontumoral sections from 18 cystectomy specimens using three different pretreatment protocols. The immunoreactivity of MM, MP and blood vessels was scored semiquantitatively. Staining intensity depended strongly on the different pretreatment protocols used. Heat-induced epitope retrieval (HIER) in alkaline buffer resulted in the strongest staining with a moderate or strong immunostaining of the MP in 18/18 (100%) of cases, but in 11/18 (61%), the MM was moderately or strongly stained. HIER in acidic buffer resulted in a suboptimal staining of the MP. Enzymatic pretreatment resulted in absent or weak staining. In conclusion, smoothelin IHC is strongly dependent on epitope retrieval, and smoothelin staining did not discriminate reliably between MP and MM with any of the tested pretreatment protocols.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM (2008) The global burden of urinary bladder cancer. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl 218:12–20
Ploeg M, Aben KK, Kiemeney LA (2009) The present and future burden of urinary bladder cancer in the world. World J Urol 27:289–293
Greene FLPD, Fleming ID et al (2002) AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. Springer, New York, 2002
Dixon JS, Gosling JA (1983) Histology and fine structure of the muscularis mucosae of the human urinary bladder. J Anat 136:265–271
Aydin A, Ucak R, Karakok M, Guldur ME, Kocer NE (2002) Vascular plexus is a differentation criterion for muscularis mucosa from muscularis propria in small biopsies and transurethral resection materials of urinary bladder? Int Urol Nephrol 34:315–319
Ro JY, Ayala AG, el-Naggar A (1987) Muscularis mucosa of urinary bladder. Importance for staging and treatment. Am J Surg Pathol 11:668–673
Vakar-Lopez F, Shen SS, Zhang S, Tamboli P, Ayala AG, Ro JY (2007) Muscularis mucosae of the urinary bladder revisited with emphasis on its hyperplastic patterns: a study of a large series of cystectomy specimens. Ann Diagn Pathol 11:395–401
Kuijpers KA, Heesakkers JP, Jansen CF, Schalken JA (2007) Cadherin-11 is expressed in detrusor smooth muscle cells and myofibroblasts of normal human bladder. Eur Urol 52:1213–1221
Paner GP, Ro JY, Wojcik EM, Venkataraman G, Datta MW, Amin MB (2007) Further characterization of the muscle layers and lamina propria of the urinary bladder by systematic histologic mapping: implications for pathologic staging of invasive urothelial carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 31:1420–1429
Paner GP, Shen SS, Lapetino S, Venkataraman G, Barkan GA, Quek ML, Ro JY, Amin MB (2009) Diagnostic utility of antibody to smoothelin in the distinction of muscularis propria from muscularis mucosae of the urinary bladder: a potential ancillary tool in the pathologic staging of invasive urothelial carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 33:91–98
Council L, Hameed O (2009) Differential expression of immunohistochemical markers in bladder smooth muscle and myofibroblasts, and the potential utility of desmin, smoothelin, and vimentin in staging of bladder carcinoma. Mod Pathol 22:639–650
van der Loop FT, Schaart G, Timmer ED, Ramaekers FC, van Eys GJ (1996) Smoothelin, a novel cytoskeletal protein specific for smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol 134:401–411
Miyamoto H, Sharma RB, Illei PB, Epstein JI (2010) Pitfalls in the use of smoothelin to identify muscularis propria invasion by urothelial carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 34:418–422
Paner GP, Brown JG, Lapetino S, Nese N, Gupta R, Shen SS, Hansel DE, Amin MB (2010) Diagnostic use of antibody to smoothelin in the recognition of muscularis propria in transurethral resection of urinary bladder tumor (TURBT) specimens. Am J Surg Pathol 34:792–799
Bovio IM, Al-Quran SZ, Rosser CJ, Algood CB, Drew PA, Allan RW (2010) Smoothelin immunohistochemistry is a useful adjunct for assessing muscularis propria invasion in bladder carcinoma. Histopathology 56:951–956
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindh, C., Nilsson, R., Lindstrom, M.L. et al. Detection of smoothelin expression in the urinary bladder is strongly dependent on pretreatment conditions: a critical analysis with possible consequences for cancer staging. Virchows Arch 458, 665–670 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-011-1076-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-011-1076-z