Abstract
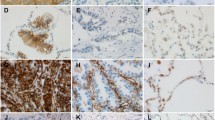
Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) plays a role in integrin signaling-mediated cell-extracellular matrix interactions and is involved in signal transduction pathways to control cell survival, differentiation, and proliferation in mammalian cells. ILK has been implicated in the progression of several human malignancies. However, its function in malignant tumors is not fully enunciated. Previous in vitro studies also implicated ILK in the regulation of E-cadherin expression and vascular endothelial growth factor expression. In the current study, we investigated the protein expression of ILK and its correlation with clinicopathological profiles, E-cadherin expression, microvessel density (MVD) and clinical outcome in 57 lung squamous cell carcinoma and 44 adenocarcinoma, using immunohistochemistry. No ILK was detected in normal bronchial epithelium, while it was positively expressed in 39 (68.42%) squamous cell carcinoma cases and 27 (61.36%) adenocarcinoma cases. Positive ILK expression was significantly associated with advanced TNM stage (P = 0.022) in adenocarcinoma, and associated with high MVD in lung squamous cell carcinoma (P < 0.001) and adenocarcinoma (P = 0.049). The Spearman's correlation test revealed that increased ILK expression was correlated with reduced E-cadherin expression in lung squamous cell carcinoma (correlation coefficient = 0.364, P = 0.005). Moreover, the Kaplan–Meier survival analysis showed that ILK, E-cadherin, and MVD were all statistically significant prognostic factors in patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Measuring ILK and E-cadherin expression, and MVD may contribute to a better understanding of the prognosis of patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dedhar S (2000) Cell-substrate interactions and signaling through ILK. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12:250–256
Hannigan GE, Leung-Hagesteijn C, Fitz-Gibbon L et al (1996) Regulation of cell adhesion and anchorage-dependent growth by a new beta 1-integrin-linked protein kinase. Nature 379:91–96
Attwell S, Roskelley C, Dedhar S (2000) The integrin-linked kinase (ILK) suppresses anoikis. Oncogene 19:3811–3815
Radeva G, Petrocelli T, Behrend E et al (1997) Overexpression of the integrin-linked kinase promotes anchorage-independent cell cycle progression. J Biol Chem 272:13937–13944
Wu C, Keightley SY, Leung-Hagesteijn C et al (1998) Integrin-linked protein kinase regulates fibronectin matrix assembly, E-cadherin expression, and tumorigenicity. J Biol Chem 273:528–536
Ito R, Oue N, Zhu X et al (2003) Expression of integrin-linked kinase is closely correlated with invasion and metastasis of gastric carcinoma. Virchows Arch 442:118–123
Graff JR, Deddens JA, Konicek BW et al (2001) Integrin-linked kinase expression increases with prostate tumor grade. Clin Cancer Res 7:1987–1991
Bravou V, Klironomos G, Papadaki E et al (2003) Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) expression in human colon cancer. Br J Cancer 89:2340–2341
Ahmed N, Riley C, Oliva K et al (2003) Integrin-linked kinase expression increases with ovarian tumour grade and is sustained by peritoneal tumour fluid. J Pathol 201:229–237
Dai DL, Makretsov N, Campos EI et al (2003) Increased expression of integrin-linked kinase is correlated with melanoma progression and poor patient survival. Clin Cancer Res 9:4409–4414
Takanami I (2005) Increased expression of integrin-linked kinase is associated with shorter survival in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 5:1
Eke I, Hehlgans S, Cordes N (2009) There's something about ILK. Int J Radiat Biol 85:929–936
Tan C, Costello P, Sanghera J et al (2001) Inhibition of integrin linked kinase (ILK) suppresses beta-catenin-Lef/Tcf-dependent transcription and expression of the E-cadherin repressor, snail, in APC-/- human colon carcinoma cells. Oncogene 20:133–140
McPhee TR, McDonald PC, Oloumi A et al (2008) Integrin-linked kinase regulates E-cadherin expression through PARP-1. Dev Dyn 237:2737–2747
Tan C, Cruet-Hennequart S, Troussard A et al (2004) Regulation of tumor angiogenesis by integrin-linked kinase (ILK). Cancer Cell 5:79–90
Edwards LA, Woo J, Huxham LA et al (2008) Suppression of VEGF secretion and changes in glioblastoma multiforme microenvironment by inhibition of integrin-linked kinase (ILK). Mol Cancer Ther 7:59–70
Weidner N (1995) Current pathologic methods for measuring intratumoral microvessel density within breast carcinoma and other solid tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 36:169–180
McDonald PC, Fielding AB, Dedhar S (2008) Integrin-linked kinase–essential roles in physiology and cancer biology. J Cell Sci 121:3121–3132
McDonald PC, Oloumi A, Mills J et al (2008) Rictor and integrin-linked kinase interact and regulate Akt phosphorylation and cancer cell survival. Cancer Res 68:1618–1624
Troussard AA, Costello P, Yoganathan TN et al (2000) The integrin linked kinase (ILK) induces an invasive phenotype via AP-1 transcription factor-dependent upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9). Oncogene 19:5444–5452
Delcommenne M, Tan C, Gray V et al (1998) Phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase-dependent regulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 and protein kinase B/AKT by the integrin-linked kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:11211–11216
Haase M, Gmach CC, Eke I et al (2008) Expression of integrin-linked kinase is increased in differentiated cells. J Histochem Cytochem 56:819–829
Chung DH, Lee JI, Kook MC et al (1998) ILK (beta1-integrin-linked protein kinase): a novel immunohistochemical marker for Ewing's sarcoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumour. Virchows Arch 433:113–117
Goulioumis AK, Bravou V, Varakis J et al (2008) Integrin-linked kinase cytoplasmic and nuclear expression in laryngeal carcinomas. Virchows Arch 453:511–519
Acconcia F, Barnes CJ, Singh RR et al (2007) Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of nuclear localization and functions of integrin-linked kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:6782–6787
Fielding AB, Dobreva I, McDonald PC et al (2008) Integrin-linked kinase localizes to the centrosome and regulates mitotic spindle organization. J Cell Biol 180:681–689
Banerjee S, Saxena N, Sengupta K et al (2003) 17alpha-estradiol-induced VEGF-A expression in rat pituitary tumor cells is mediated through ER independent but PI3K-Akt dependent signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 300:209–215
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Shi, R., Zhang, D. et al. Expression of integrin-linked kinase in lung squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma: correlation with E-cadherin expression, tumor microvessel density and clinical outcome. Virchows Arch 458, 99–107 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-010-1016-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-010-1016-3