Abstract
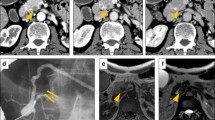
The first case of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma arising in an infant is presented. The tumor arose at the anal verge of a 1-year-old girl. The diagnosis of this CD99-positive tumor was supported by expression of epithelial (keratins, EMA, and Ep-CAM) and neuroendocrine (chromogranin A, synaptophysin, and neuron-specific enolase) markers and absence of immunoreactivity for Fli-1. No fusion of EWSR1 with FLI-1 or ERG was detected by polymerase chain reaction. However, the split of the EWSR1 gene was demonstrated by fluorescence in situ hybridization. This case adds to the few epithelial tumors in which an EWSR1 rearrangement was demonstrated. Because the tumor was initially misclassified as an extraskeletal Ewing’s sarcoma, the patient was treated according to the Ewing’s sarcoma treatment protocol. She remains free of tumor 8 years after initial diagnosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broaddus RR, Herzog CE, Hicks MJ (2003) Neuroendocrine tumors (carcinoid and neuroendocrine carcinoma) presenting at extra-appendiceal sites in childhood and adolescence. Arch Pathol Lab Med 127:1200–1203
Corpron CA, Black CT, Herzog CE, Sellin RV, Lally KP, Andrassy RJ (1995) A half century of experience with carcinoid tumors in children. Am J Surg 170:606–608
Moertel CL, Weiland LH, Telander RL (1990) Carcinoid tumor of the appendix in the first two decades of life. J Pediatr Surg 25:1073–1075
Schmid CH, Beham A, Feichtinger J, Aubock L, Dietze O (1992) Recurrent and subsequently metastasizing Merkel cell carcinoma in a 7-year-old girl. Histopathology 20:437–439
Spunt SL, Pratt CB, Rao BN, Pritchard M, Jenkins JJ, Hill DA, Cain AM, Pappo AS (2000) Childhood carcinoid tumors: the St Jude Children’s Research Hospital experience. J Pediatr Surg 35:1282–1286
Harms D (1995) Soft tissue sarcomas in the Kiel Pediatric Tumor Registry. In: Harms D, Schmidt D (eds) Current topics in pathology. Springer, Berlin, pp 31–45
Collini P, Sampietro G, Bertulli R, Casali PG, Luksch R, Mezzelani A, Sozzi G, Pilotti S (2001) Cytokeratin immunoreactivity in 41 cases of ES/PNET confirmed by molecular diagnostic studies. Am Surg Pathol 25:273–274
Folpe AL, Goldblum JR, Rubin BP, Shehata BM, Liu W, Dei Tos AP, Weiss SW (2005) Morphologic and immunophenotypic diversity in Ewing family tumors: a study of 66 genetically confirmed cases. Am J Surg Pathol 29:1025–1033
Gu M, Antonescu CR, Guiter G, Huvos AG, Ladanyi M, Zakowski MF (2000) Cytokeratin immunoreactivity in Ewing’s sarcoma: prevalence in 50 cases confirmed by molecular diagnostic studies. Am J Surg Pathol 24:410–416
Shuangshoti S, Mujananon S, Chaipipat M, Keetacheeva K, Shuangshoti S (2005) Expression of neuronal nuclear antigen (NeuN) in epithelial neuroendocrine carcinoma. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 13:265–267
Vakar-Lopez F, Ayala AG, Raymond AK, Czerniak B (2000) Epithelial phenotype in Ewing’s sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Int J Surg Pathol 8:59–65
Srivastava A, Rosenberg AE, Selig M, Rubin BP, Nielsen GP (2005) Keratin-positive Ewing’s sarcoma: an ultrastructural study of 12 cases. Int J Surg Pathol 13:43–50
Gardner LJ, Polski JM, Fallon R, Dunphy CH (1998) Identification of CD56 and CD57 by flow cytometry in Ewing’s sarcoma or primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Virchows Arch 433:35–40
Wick MR (2000) Immunohistology of neuroendocrine and neuroectodermal tumors. Semin Diagn Pathol 17:194–203
Ali A, Serra S, Asa SL, Chetty R (2006) The predictive value of CK19 and CD99 in pancreatic endocrine tumors. Am J Surg Pathol 30:1588–1594
Pelosi G, Rraggetta F, Sonzogni A, Fazio N, Cavallon A, Viale G (2000) CD99 immunoreactivity in gastrointestinal and pulmonary neuroendocrine tumours. Virchows Arch 437:270–274
Folpe AL, Hill CE, Parham DM, O’Shea PA, Weiss SW (2000) Immunohistochemical detection of FLI-1 protein expression: a study of 132 round cell tumors with emphasis on CD99-positive mimics of Ewing’s sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Am J Surg Pathol 24:1657–1662
Parker JR, Armstrong DL, Strother D, Rudman DM, Dauser RC, Laurent JP, Deyd J, Rouah PE (2001) Anti-neuronal nuclei immunohistochemical staining pattern in childhood ependymomas. J Child Neurol 16:548–552
Willoughby V, Sonawala A, Werlang-Perurena A, Donner LR (2008) A comparative immunohistochemical analysis of small round cell tumors of childhood: utility of peripherin and α-internexin as markers for neuroblastomas. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 16:344–348
Mackay B, Donner L, Ordonez NG (1986) Small round cell tumors. In: Russo J, Sommers SC (eds) Tumor diagnosis by electron microscopy, 3rd edn. Field, Rich, and Associates, New York, pp 281–313
Sandberg AA, Bridge JA (2000) Updates on cytogenetics and molecular genetics of bone and soft tissue tumors: Ewing sarcoma and peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 123:1–26
Szuhai K, Ijszenga M, de Jong D, Karseladze A, Tanke HJ, Hogendoorn PC (2009) The NFATc2 gene is involved in a novel cloned translocation in a Ewing sarcoma variant that couples its function in immunology to oncology. Clin Cancer Res 15:2259–2268
Mastrangelo T, Modena P, Tornielli S, Bullrich F, Testi MA, Mezzelani A, Radice P, Azzarelli A, Pilotti S, Croce CM, Pierotti MA, Sozzi G (2000) A novel zinc finger gene is fused to EWS in small round cell tumor. Oncogene 19:3799–3804
Berg T, Kalsaas AH, Buechner J, Busund LT (2009) Ewing sarcoma–peripheral neuroectodermal tumor of the kidney with a FUS–ERG fusion transcript. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 194:53–57
Ng TL, Nielsen T, Hayes M et al (2007) Novel Ewing sarcoma translocation identified in a case lacking EWS gene rearrangement. Pediatr Dev Pathol 10:83A
Shing DC, McMullan DJ, Roberts P, Smith K, Chin SF, Nicholson J, Tillman RM, Ramani P, Cullinane C, Coleman N (2003) FUS/ERG gene fusion in Ewing’s tumors. Cancer Res 63:4568–4576
Weinreb I, Goldstein D, Perez-Ordonez B (2008) Primary extraskeletal Ewing family tumor with complex epithelial differentiation: a unique case arising in the lateral neck presenting with Horner syndrome. Am J Surg Pathol 32:1742–1748
Romeo S, Dei Tos AP (2010) Soft tissue tumors associated with EWSR1 translocation. Virchows Arch 456:219–234
Tanas MR, Goldblum JR (2009) Fluorescence in situ hybridization in the diagnosis of soft tissue neoplasms: a review. Adv Anat Pathol 16:838–391
Sirvent N, Trassard M, Ebran N, Attias R, Pedeutour F (2009) Fusion of EWSR1 with the DUX4 facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy region resulting from t(4;22)(q35;q12) in a case of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 195:12–18
Moller E, Stenman G, Mandahl N, Hamberg H, Molne L, van den Oord JJ, Brosjo O, Mertens F, Panagopoulos I (2008) POU5F1, encoding a key regulator of stem cell pluripotency, is fused to EWSR1 in hidradenoma of the skin and mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the salivary glands. J Pathol 215:78–86
Brandal P, Panagopoulos I, Bjerkehagen B, Gorunova L, Skjeldal S, Micci F, Hein S (2008) Detection of a t(1;22)(q23;q12) translocation leading to an EWSR1–PBX1 fusion gene in a myoepithelioma. Genes Chromosom Cancer 47:558–564
Brandal P, Panagopoulos I, Bjerkehagen B, Heim S (2009) T(19;22)(q13;q12) translocation leading to the novel fusion gene EWSR1–ZNF444 in soft tissue myoepithelial carcinoma. Genes Chromosom Cancer 48:1051–1056
Balachandra B, Marcus V, Jass JR (2007) Poorly differentiated tumours of the anal canal: a diagnostic strategy for the surgical pathologist. Histopathology 50:163–174
Bernick PE, Klimstra DS, Shia J, Minsky B, Saltz L, Shi W, Thaler H, Guillem J, Paty P, Cohen AM, Wong WD (2004) Neuroendocrine carcinomas of the colon and rectum. Dis Colon Rectum 47:163–169
Ferrari A, Rognone A, Casanova M, Zaffignani E, Piva L, Collini P, Bertario L, Sala P, Leo E, Belli F, Gallino G (2008) Colorectal carcinoma in children and adolescents: the experience of the Istituto Nazionale Tumori of Milan, Italy. Pediatr Blood Cancer 50:588–593
Ahlman A, Nilsson DO, McNicol AM, Ruszniewski P, Niederle B, Ricke J, Jensen R, Kos-Kudla B, Oberg K, O’Connor JM, Pavel ME, Vullierme MP, Frascati Consensus Conference participants (2008) Poorly differentiated endocrine carcinomas of midgut and hindgut origin. Neuroendocrinology 87:40–46
Plockinger U, Rindi G, Arnold R, Eriksson B, Krenning EP, de Herder WW, Goede A, Caplin M, Oberg K, Reubi JC, Nilsson O, Delle Fave G, Ruszniewski P, Ahlman H, Weidenmann B, Society European Neuroendocrine Tumour (2004) Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of neuroendocrine gastrointestinal tumours. A consensus statement on behalf of the European Neuroendocrine Tumour Society (ENETS). Neuroendocrinology 80:394–424
Moertel CG, Kvols LK, O’Connell MJ, Rubin J (1991) Treatment of neuroendocrine carcinomas with combined etoposide and cisplatin. Evidence of major therapeutic activity in the anaplastic variants of these neoplasms. Cancer 68:227–232
Rindi G, Kloppel G, Ahlman H, Caplin M, Couvelard A, de Herder WW, Erikssson B, Falchetti A, Falconi M, Komminoth P, Korner M, Lopes JM, McNicol AM, Nilsson O, Perren A, Scarpa A, Scoazec JY, Wiedenmann B, Frascati Consensus Conference participants (2006) TNM staging of foregut (neuro)endocrine tumors: a consensus proposal including a grading system. Virchows Arch 449:395–401
Acknowledgments
Consultation with Professor Dr. Gunter Kloppel, Institute of Pathology, and Professor Dr. Ivo Leuschner, Institute of Pediatric Pathology, University of Kiel, Kiel, Germany is gratefully acknowledged.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malone, V.S., Dobin, S.M., Jones, K.A. et al. CD99-positive large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma with rearranged EWSR1 gene in an infant: a case of prognostically favorable tumor. Virchows Arch 457, 389–395 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-010-0944-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-010-0944-2