Abstract
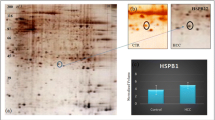
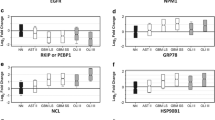
Neuroblastoma (NB) and Ewing’s sarcoma (ES) cell lines were analysed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) searching for new diagnostic/prognostic markers. Protein expression profiles displayed a high degree of similarity with the exception of marked heat shock protein (HSP) 27 and less marked HSP60 and HSP70 family up-modulations in NB cells. HSP27, which showed peculiar variability in different NB cell preparations, responded to all trans-retinoic acid treatment in NB cells but not in ES cells at gene and protein expression levels. Immunohistochemistry studies showed different behaviours of HSP27 and HSP70 expression in NB and ES biopsies. HSP27 was less expressed, whereas HSP70 was more expressed in the immature areas of NB. HSP27 expression showed positive and statistically significant correlation with favourable prognosis, and HSP27 expression also negatively correlated with increasing aggressiveness of histological type. In ES, both chaperones were expressed without characteristic patterns. Our results suggest that HSP27, after further clinical validations, could be used as a marker of neuronal differentiation in vivo for the assessment of the biological behaviour of NB and for the risk stratification of patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong BK, White E, Saracci R (1992) Principles exposure measurement in epidemiology. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 66–67
Bando Y, Katayama T, Kasai K, Taniguchi M, Tamatani M, Tohyama M (2003) GRP94 (94 kDa glucose-regulated protein) suppresses ischemic neuronal cell death against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Eur J Neurosi 18:829–40
Biedler JL, Roffler-Tarlov S, Shachner M, Freedman LS (1978) Multiple neurotransmitter synthesis by human neuroblastoma cell lines and clones. Cancer Res 38:3751–3757
Biedler JL, Spengler BA, Chang TD, Ross RA (1988) Transdifferentiation of human neuroblastoma cells results in coordinate loss of neuronal and malignant properties. Prog Clin Biol Res 271:265–276
Brodeur GM, Maris JM (2002) Neuroblastoma. In: Pizzo PA, Poplack DG (eds) Principles and practice of pediatric oncology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadhelphia, pp 895–937
Bruey JM, Ducasse C, Bonniaud P, Ravagnan L, Susin SA, Diaz-Latoud C, Gurbuxani S, Arrigo AP, Kroemer G, Solary E, Garrido C (2000) Hsp27 negatively regulates cell death by interacting with cytochrome c. Nat Cell Biol 2:645–652
Carta F, Demuro PP, Zanini C, Santona A, Castiglia D, D’Atri S, Ascierto PA, Napoletano M, Cossu A, Tavolini B, Turrini F, Manca A, Sini MC Palmieri G, Rozzo AC (2005) Analysis of candidate genes through a proteomics-based approach in primary cell lines from malignant melanomas and their metastases. Melanoma Res 15:235–244
Charette SJ, Lavoie JN, Lambert H, Landry J (2000) Inhibition of Daxx-mediated apoptosis by heat shock protein 27. Mol Cell Biol 20:7602–7612
Cimmino F, Spano D, Capasso M, Zambrano N, Russo R, Zollo M, Iascolan A (2007) Comparative proteomic expression profile in all-trans retinoic acid differentiated neuroblastoma cell line. J Proteome Res 6:2550–2564
Ginsberg JP, Woo SY, Johnson ME, Hicks MJ, Horowitz ME (2002) Ewing’s sarcoma family of tumors: Ewing’s sarcoma of bone and soft tissue and the peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors. In: Pizzo PA, Poplack DG (eds) Principles and practice of pediatric oncology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadhelphia, pp 937–1016
Giribaldi G, Ulliers D, Mannu F, Arese P, Turrini F (2001) Growth of Plasmodium falciparum induces stage-dependent haemichrome formation, oxidative aggregation of band 3, membrane deposition of complement and antibodies, and phagocytosis of parasitized erythrocytes. Br J Haematol 13:492–499
Harris MN, Ozpolat B, Abdi F, Gu S, Legler A, Mawuenyega KG, Tirado-Gomez M, Lopez-Berestein G, Chen X (2004) Comparative proteomic analysis of all-trans-retinoic acid treatment reveals systematic posttranscriptional control mechanisms in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood 104:1314–1323
Hasegawa SL, Davison JM, Rutten A, Fletcher JA, Fletcher CD (1998) Primary cutaneous Ewing’s sarcoma: immunophenotypic and molecular cytogenetic evaluation of five cases. Am J Surg Pathol 22:310–8
Hoang AT, Huang J, Rudra-Ganguly N, Zheng J, Powell WC, Rabindran SK, Wu C, Roy-Burman P (2000) A novel association between the human heat shock transcription factor 1 (HSF1) and prostate adenocarcinoma. Am J Pathol 156:857–864
Ishiguro Y, Kato K, Akatsuka H, Iwata H, Nagaya M (1997) Chemotherapy-induced expression of alpha B-crystallin in neuroblastoma. Med Pediatr Oncol 29:11–5
Jolly C, Morimoto RI (2000) Role of the heat shock response and molecular chaperones in oncogenesis and cell death. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:1564–1572
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Miyazaki T, Kato H, Faried A, Sohda M, Nakajima M, Fukai Y, Masuda R, Fukuchi M, Ojima H, Tsukada K, Kuwano H (2005) Predictors of response to chemo-radiotherapy and radiotherapy for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 25:2749–2755
Oakley BR, Kirsch DR, Morris NR (1980) A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 105:361–363
Peuchmaur M, d’Amore SG, Joshi VV, Hata J, Roald B, Dehner LP, Gerbing RB, Stram DO, Lukens JN, Matthay KK, Shimada H (2003) Revision of the International Neuroblastoma Pathology Classification: confirmation of favorable and unfavorable prognostic subsets in ganglioneuroblastoma, nodular. Cancer 98:2274–2281
Ponthan F, Borgstrom P, Hassan M, Wassberg E, Redfem CP, Kogner P (2001) The vitamin A analogues: 13-cis retinoic acid, 9-cis retinoic acid, and Ro 13-6307 inhibit neuroblastoma tumour growth in vivo. Med Pediatr Oncol 36:127–131
Rane MJ, Pan Y, Singh S, Powell DW, Wu R, Cummins T, Chen Q, McLeish KR, Klein JB (2003) Heat shock protein 27 controls apoptosis by regulating Akt activation. J Biol Chem 278:27828–27835
Rettig WJ, Splenger BA, Chesa PG, Old LJ, Biedler JL (1987) Coordinate changes in neuronal phenotype and surface antigen expression in human neuroblastoma cell variants. Cancer Res 47:1383–1389
Rocchi P, Ferreri AM, Simone G, Prodi G (1987) Epirubicin-induced differentiation of human neuroblastoma cells in vitro. Anticancer Res 7:247–250
Sarto C, Valsecchi C, Magni F, Tremolada L, Arizzi C, Cordani N, Cesellato S, Doro G, Favoni P, Perego RA, Raimondo F, Ferrero S, Mocarelli P, Galli-Kienle M (2004) Expression of heat shock protein 27 in human renal cell carcinoma. Proteomics 4:2252–2260
Schlesinger HR, Gerson JM, Moorhead PS, Maguire H, Hummeler K (1976) Establishment and characterization of human neuroblastoma cell lines. Cancer Res 36:3094–3100
Schwab M, Shimada H, Joshi V, Brodeur GM (2000) Neuroblastic tumours of adrenal gland and sympathetic nervous system. In: Kleihues P, Canavee WK (eds) Pathology and genetics of tumours of the nervous system. IARC, Lyon, pp 153–161
SIOP (2004) Europe Neuroblastoma AIEOP LNESG2 Study: guidelines for the treatment of patients with localized resectable neuroblastoma and analysis of prognostic factors. Ist. G. Gaslini
Thanner F, Sutterlin MW, Kapp M, Rieger L, Morr AK, Kristen P, Dietl J, Gassel AM, Muller T (2005) Heat shock protein 27 is associated with decreased survival in node-negative breast cancer patients. Anticancer Res 25:1649–1653
Thiele CJ, McKeon C, Triche TJ, Ross RA Reynolds CP, Israel MA (1987) Differential protooncogene expression characterizes histopathologically indistinguishable tumors of the peripheral nervous system. J Clin Invest 80:804–811
Thomas X, Campos L, Mounier C, Cornillon J, Flandrin P, Le QH, Piselli S, Guyotat D (2005) Expression of heat-shock proteins is associated with major adverse prognostic factors in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res 29:1049–1058
Triche T, Askin FB, Kissane JM (1986) Neuroblastoma, Ewing Sarcoma and the differential diagnosis of small- round- blue-cell tumor. In: Finegold M (ed) Pathology of neoplasia in children and adolescents. Sauders, Philadelphia, pp 145–195
Ungar DR, Hailat N Strahler JR, Kuick RD, Brodeur GM, Seeger RC, Reynolds CP, Hanash SM (1994) Hsp27 expression in neuroblastoma: correlation with disease stage. J Nat Can Inst 86:780–4
Ushigome S, Machinami R, Soresens PH (2002) Ewing sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumour (PNET). In: Fletcher CDM, Unni KK, Mertens F (eds) Pathology and genetics of tumours of soft tissue and bone. IARC, Lyon, pp 298–300
Voight A, Zintl F (2003) Effects of retinoic acid on proliferation, apoptosis, cytotoxicity, migration, and invasion of neuroblastoma cells. Med Pediatr Oncol 40:205–213
Woolson RF, Clarke WR (2002) Statistical methods for the analysis of biomedical data, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 226–232, 286–288
Yenari MA (2002) Heat shock proteins and neuroprotection. Adv Exp Med Biol 513:281–289
Zanini C, Giribaldi G, Mandili G, Carta F, Crescenzio N, Bisaro B, Doria A, Foglia L, di Montezemolo LC, Timeus F, Turrini F (2007) Inhibition of heat shock proteins (HSP) expression by quercetin and differential doxorubicin sensitization in neuroblastoma and Ewing’s sarcoma cell lines. J Neurochem 103:1344–1354
Acknowledgement
We thank Paola Angelini MD—Centre of Reference—Gaslini Istitute, Genoa, Italy, and Daniele Bertin, Ospedale Infantile Regina Margherita, Turin, Italy. This study was partially supported by the “ONCOLOGY SPECIAL PROJECT” Compagnia di San Paolo/FIRMS and Regione Piemonte, Turin, Italy.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zanini, C., Pulerà, F., Carta, F. et al. Proteomic identification of heat shock protein 27 as a differentiation and prognostic marker in neuroblastoma but not in Ewing’s sarcoma. Virchows Arch 452, 157–167 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-007-0549-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-007-0549-6