Abstract
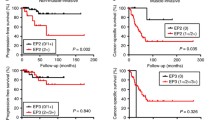
The prostaglandin E2 receptor, EP4 receptor (EP4R), plays an important role in the development of transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract (TCC-UUT). However, the clinical significance of other EP receptors (EP1R–3R) is not clear. Furthermore, the pathological function of EP receptors in such patients is not understood. In the present study, we examined the expression of EP1R–3R in 101 TCC-UUT tissues by immunohistochemistry. Furthermore, we defined the relationship between cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 and EP receptor expression, proliferation index (PI), microvessel density (MVD), and expression of metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA), and exon v6 containing CD44 isoform (CD44 v6) by multivariate analysis. The expression of EP1R, EP2R, and EP3R was positive in 20 (19.8%), 26 (25.7%), and 14 (13.9%) tumor samples, respectively. Expression of these receptors was not associated with pathological findings or survival. COX-2 and EP4R were independently associated with MVD and MMP-2, and uPA or PI and MMP-2, respectively. Other EP receptors were not influenced by any factors. Our results suggest that EP1R–3R play a minimal role in cancer progression in patients with TCC-UUT. On the other hand, EP4R regulates tumor progression via cancer cell proliferation and MMP-2, distinct from COX-2.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arber N, Levin B (2005) Chemoprevention of colorectal cancer: ready for routine use? Recent Results Cancer Res 166:213–230
Asano T, Shoda J, Ueda T, Kawamoto T, Todoroki T, Shimonishi M, Tanabe T, Sugimoto Y, Ichikawa A, Mutoh M, Tanaka N, Miwa M (2002) Expression of cyclooxygenase-1 and prostaglandin E-receptors in carcinoma of the gallbladder: crucial role of arachidonate metabolism in tumor growth and progression. Clin Cancer Res 8:1157–1167
Braun JR, DuBois RN (2005) COX-2: a molecular target for colorectal cancer prevention. J Clin Oncol 23:2840–2855
Chang SH, Liu CH, Conway R, Han DK, Nithipatikom K, Trifan OC, Lane TF, Hla T (2004) Role of prostaglandin E2-dependent angiogenic switch in cyclooxygenase 2-induced breast cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:591–596
Chen Y, Hugh-Fulfold M (2000) Prostaglandin E2 and the protein kinase A pathway mediate arachidonic acid induction of c-fos in human prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 82:2000–2006
Coleman RA, Smith WL, Narumiya S (1994) International union of pharmacology classification of prostanoid receptors: properties, distribution, and structure of the receptors and their subtypes. Pharmacol Rev 46:205–229
Dohadwala M, Luo J, Zhu L, Lin Y, Dougherty GJ, Sharma S, Huang M, Pold M, Batra RK, Dubinett SM (2001) Non-small cell cancer cyclooxygenase-dependent invasion is mediated by CD44. J Biol Chem 276:20809–20812
Dohadwala M, Bartra RK, Luo J, Lin Y, Krysan K, Põld M, Sharma S, Dubinett SM (2002) Autocrine/paracrine PGE2 production by non-small cell lung cancer cells regulates MMP-2 and CD44 in COC-2 dependent invasion. J Biol Chem 52:50828–50833
Dubois RN, Abramson SB, Crofford L, Gupta RA, Simon LS, Van De Putte LB, Lipsky PE (1998) Cyclooxygenase in biology and disease. FASEB J 12:1063–1073
Eschwege P, Ferlicot S, Droupy S, Ba N, Conti M, Loric S, Coindard G, Denis I, Ferretti L, Cornelius A, Legrand A, Bedossa P, Benoit G, Jardin A, Scardiono P (2003) A histopathologic investigation of PGE(2) pathways as predictors of proliferation and invasion in urothelial carcinomas of the bladder. Eur Urol 44:435–441
Hansen-Petrik MB, McEntee MF, Jull B, Shi H, Zemel MB, Whelan J (2003) Prostaglandin E2 protects intestinal tumors from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced regression in APCmin/+ mice. Cancer Res 62:403–408
Hong RL, Pu YS, Hsieh TS, Chu JS, Lee WJ (1996) Expressions of E-cadherin and exon v6-containing isoforms of CD44 and their prognostic values in human transitional cell carcinoma. J Urol 153:2025–2028
Inoue K, Kamada M, Salton JW, Fukata S, Yoshikawa C, Tamboli P, Dinney CF, Shuin T (2002) The prognostic value of angiogenesis and metastasis-related genes for progression of transitional cell carcinoma of the renal pelvis and ureter. Clin Cancer Res 8:1863–1870
Jabbour HN, Milne SA, Williams AR, Anderson RA, Boddy SC (2001) Expression of COX-2 and PGE synthase and synthesis of PGE(2) in endometrial adenocarcinoma: a possible autocrine/paracrine regulation of neoplastic cell function via EP2/EP4 receptors. Br J Cancer 85:1023–1031
Kawamori T, Uchiya N, Nakatsugi S, Watanabe K, Ohuchida S, Yamamoto H, Maruyama T, Kondo K, Sugimura T, Wakabayashi K (2002) Chemopreventive effects of ONO-8711, a selective prostaglandin E receptor EP1 antagonists, on breast cancer development. Carcinogenesis 22:2001–2004
Kinugasa Y, Hatori M, Ito H, Kurihara Y, Ito D, Nagumo M (2004) Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 suppresses invasiveness of oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines via down-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and CD44. Clin Exp Metastasis 21:737–745
Kömhoff M, Guan Y, Shappell HW, Davis L, Jack G, Shyr Y, Koch MO, Shapper SB, Breyer MD (2000) Enhanced expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in high grade human transitional cell bladder carcinomas. Am J Pathol 157:29–35
Krysan K, Reckamp KL, Dalwadi H, Sharma S, Rozengurt E, Dohadwala M, Dubinett SM (2005) Prostaglandin E2 activates mitogen-activated protein kinase/Erk pathway signaling and cell proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer cells in an epidermal growth factor receptor-independent manner. Cancer Res 65:6275–6281
Li G, Yang T, Yan J (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2 increased the angiogenic and metastatic potential of tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 299:886–890
Masferrer JL, Leahy KM, Koki AT, Zweifel BS, Settle SL, Woerner BM, Edwards DA, Flickinger AG, Moore RJ, Seibert K (2000) Antiangiogenic and antitumor activities of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Cancer Res 60:1306–1311
Miyata Y, Koga S, Kanda S, Nishikido M, Hayashi T, Kanetake H (2003) Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in renal cell carcinoma: correlation with tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2, and survival. Clin Cancer Res 9:1741–1749
Miyata Y, Shigeru K, Nomata K, Hayashida Y, Kanetake H (2004) Expression of metalloproteinase-2, -9, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 and -2 in transitional cells carcinoma of the upper urinary tract: correlation with tumor stage and survival. Urology 63:602–608
Miyata Y, Shigeru K, Nomata K, Eguchi J, Kanetake H (2005) Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and EP4 receptor in transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. J Urol 173:56–60
Mohammed SI, Knapp DW, Bostwick DG, Foster RS, Khan KNM, Masferrer JL, Woerner Snyder PW, Koki AT (1999) Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in human invasive transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) of the urinary bladder. Cancer Res 59:987–990
Munkarah A, Ali-Fehmi R (2005) COX-2: a protein with an active role in gynecological cancers. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 17:49–53
Mutoh M, Watanabe K, Kitamura T, Shoji Y, Takahashi M, Kawamori T, Tani K, Kobayashi M, Maruyama T, Kobayashi K, Ohuchida S, Sugimoto Y, Narumiya S, Sugimura T, Wakabayshi K (2002) Involvement of prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP4 in colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 62:28–32
Nakanishi K, Kawai T, Torikata C, Aurues T, Ikeda T (1998) Urokinase-type plasminogen activator, its inhibitor, and its receptor in patients with upper urinary tract carcinoma. Cancer 82:724–732
Nakanishi K, Kawai T, Sato H, Aida S, Kasamatsu H, Aurues T, Ikeda T (2000) Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and of membrane-type-1matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) in transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. Hum Pathol 31:193–200
Rigas B, Goldman IS, Levine L (1993) Altered eicosanoid levels in human colon cancer. J Lab Clin Med 122:518–523
Sales KJ, Katz AA, Davis M, Hinz S, Soeters RP, Hofmeyr MD, Millar RP, Jabbour HN (2001) Cyclooxygenase-2 expression and prostaglandin E2 synthesis are up-regulated in carcinomas of the cervix: a possible autocrine/paracrine regulation of neoplastic cell function via EP2/EP4 receptors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:2243–2249
Sheng H, Shao J, Morrow JD, Beauchamp RD, Dubois RN (1998) Modulation of apoptosis and Bcl-2 expression by prostaglandin E2 in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res 58:326–362
Sheng H, Shao J, Washington MK, Dubois RN (2001) Prostaglandin E2 increases growth and motility of colorectal carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 276:75–81
Toma V, Hauri D, Schmid U, Ackermann D, Maurer R, Alund G, Knönagel H, Rist M, Gasser TC, Sauter G, Roth J (1999) Focal loss of CD44 variant protein expression is related to recurrence in superficial bladder carcinoma. Am J Pathol 155:1427–1432
Wendum D, Masliah J, Trugnan G, Flejou JF (2004) Cyclooxygenase-2 and its role in colorectal cancer development. Virchows Arch 445:327–333
Yano T, Zissel G, Muller-Qernheim J, Shin SJ, Satoh H, Ichikawa T (2002) Prostaglandin E2 reinforces the activation of Ras signal pathway in lung adenocarcinoma cells via EP3. FEBS Lett 518:154–158
Yoshimatsu K, Golijanin D, Paty PB, Soslow RA, Jakobsson PJ, DeLellis RA, Subbaramaiah K, Dannenberg AJ (2001) Inducible microsomal prostaglandin E synthase is overexpressed in colorectal adenomas and cancer. Clin Cancer Res 7:3971–3976
Zha S, Yegnasubramanian V, Nelson WG, Isaacs WB, De Marzo AM (2004) Cyclooxygenases in cancer: progress and perspective. Cancer Lett 215:1–20
Zweifel BS, Davis TW, Ornberg RL, Masferrer JL (2002) Direct evidence for a role of cyclooxygenase 2-derived prostaglandin E2 in human head and neck xenograft tumors. Cancer Res 62:6706–6711
Acknowledgements
We thank Takumi Shimogama and Yoshikazu Tsuji for excellent assistance. This study was supported by in part by grant no. 17791080 from the Japanese Society of the Promotion of Science to Y. Miyata. This study did not receive any funding from any commercial source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was not funded by any commercial organization. It was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid from the Japanese Society of the Promotion of Science.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyata, Y., Ohba, K., Kanda, S. et al. Pathological function of prostaglandin E2 receptors in transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. Virchows Arch 448, 822–829 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-006-0198-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-006-0198-1