Abstract
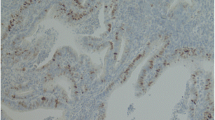
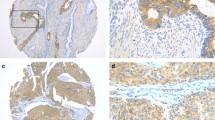
We previously reported the overexpression of cyclins in uterine cervical carcinoma; however, their clinicopathological significance remained undetermined. In the present study, we examined the immunohistochemical expression of cyclins (D1, E, A, B1), p53 and Ki-67 in squamous cell carcinoma (stage Ib+II; 80 cases, stage III+IV; 23 cases). Correlations between the expression of cyclins and clinicopathological parameters and patient survival were statistically evaluated. The results indicated that in the normal squamous epithelium, the expression of cyclins and Ki-67 was sporadically observed in the parabasal layer. Of the 103 cervical carcinomas, overexpression of cyclins D1, E, A, B1 and p53 was observed in 13 (13%), 23 (22%), 25 (24%), 18 (18%) and 23 (22%) cases, respectively, with a slight predominance in advanced stage tumors. The expression of cyclin D1, E, A and p53 significantly correlated with that of Ki-67 (Spearman’s rank correlation). Univariate and multivariate analyses revealed that lymph node metastasis and cyclin A overexpression were independent prognostic factors for unfavorable outcomes in stage Ib+II patients. These findings suggest that the overexpression of various cyclins is involved in the acquisition of the vigorous growth potential of cervical carcinoma cells, and that cyclin A is an independent prognosticator of cervical carcinoma in early stages.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akasofu M, Oda Y (1995) Immunohistochemical detection of p53 in cervical epithelial lesions with or without infection of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18. Virchows Arch 425:593–602
Bae DS, Cho SB, Kim YJ, Whang JD, Song SY, Park CS, Kim DS, Lee JH (2001) Aberrant expression of cyclin D1 is associated with poor prognosis in early stage cervical cancer of the uterus. Gynecol Oncol 81:341–347
Barnes DM (1997) Cyclin D1 in mammary carcinoma. J Pathol 181:267–269
Bosch FX, Manos MM, Munoz N, Sherman M, Jansen AM, Peto J, Schiffman MH, Moreno V, Kurman R, Shah KV (1995) Prevalence of human papillomavirus in cervical cancer: a worldwide perspective. International Biological Study on Cervical Cancer (IBSCC) Study Group. J Natl Cancer Inst 87:796–802
Bosch FX, Lorincz A, Munoz N, Meijer CJ, Shah KV (2002) The causal relation between human papillomavirus and cervical cancer. J Clin Pathol 55:244–265
Brown DC, Cole D, Gatter KC, Mason DY (1988) Carcinoma of the cervix uteri: an assessment of tumour proliferation using the monoclonal antibody Ki67. Br J Cancer 57:178–181
Burger RA, Monk BJ, Kurosaki T, Anton-Culver H, Vasilev SA, Berman ML, Wilczynski SP (1996) Human papillomavirus type 18: association with poor prognosis in early stage cervical cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 88:1361–1368
Cattani P, Hohaus S, Bellacosa A, Genuardi M, Cavallo S, Rovella V, Almadori G, Cadoni G, Galli J, Maurizi M, Fadda G, Neri G (1998) Association between cyclin D1 (CCND1) gene amplification and human papillomavirus infection in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 4:2585–2589
Chen HY, Hsu CT, Lin WC, Tsai HD, Chang WC (2000) Prognostic value of p53 expression in stage IB1 cervical carcinoma. Gynecol Obstet Invest 49:266–271
Cheng WF, Chen CA, Lee CN, Wei LH, Hsieh FJ, Hsieh CY (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor and prognosis of cervical carcinoma. Obstet Gynecol 6:721–726
Cho NH, Kim YB, Park TK, Kim GE, Park K, Song KJ (2003) P63 and EGFR as prognostic predictors in stage IIB radiation-treated cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 91:346–353
Dictor M, Ehinger M, Mertens F, Akervall J, Wennerberg J (1999) Abnormal cell cycle regulation in malignancy. Am J Clin Pathol 112:S40–S52
Dong Y, Sui L, Tai Y, Sugimoto K, Hirao T, Tokuda M (2000) Prognostic significance of cyclin E overexpression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 6:4253–4258
Gerdes J, Lemke H, Baisch H, Wacker HH, Schwab U, Stein H (1984) Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki67. J Immunol 133:1710–1715
Gong J, Ardelt B, Traganos F, Darzynkiewicz Z (1994) Unscheduled expression of cyclin B1 and cyclin E in several leukemic and solid tumor cell lines. Cancer Res 54:4285–4288
Guadagno TM, Ohtsubo M, Roberts JM, Assoian RK (1993) A link between cyclin A expression and adhesion-dependent cell cycle progression. Science 262:1572–1575
Ho DM, Hsu CY, Chiang H (2000) MIB-1 labeling index as a prognostic indicator for survival in patients with FIGO stage IB squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix. Gynecol Oncol 76:97–102
Hsieh JK, Yap D, O’Connor DJ, Fogal V, Fallis L, Chan F, Zhong S, Lu X (2002) Novel function of the cyclin A binding site of E2F in regulating p53-induced apoptosis in response to DNA damage. Mol Cell Biol 22:78–93
Hui AM, Li X, Shi YZ, Takayama T, Torzilli G, Makuuchi M (2000) Cyclin D1 overexpression is a critical event in gallbladder carcinogenesis and independently predicts decreased survival for patients with gallbladder carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 6:4272–4277
Hunt CR, Hale RJ, Buckley CH, Hunt J (1996) p53 expression in carcinoma of the cervix. J Clin Pathol 49:971–974
Isacson C, Kessis TD, Hedrick L, Cho KR (1996) Both cell proliferation and apoptosis increase with lesion grade in cervical neoplasia but do not correlate with human papillomavirus type. Cancer Res 56:669–674
Kanai M, Shiozawa T, Xin L, Nikaido T, Fujii S (1998) Immunohistochemical detection of sex steroid receptors, cyclins, and cyclin-dependent kinases in the normal and neoplastic squamous epithelia of the uterine cervix. Cancer 82:1709–1719
Krivak TC, McBroom JW, Elkas JC (2002) Cervical and vaginal cancer. In: Berek JS (ed) Novak’s gynecology, 13th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 1199–1211
Krtolica A, Ludlow JW (1996) Hypoxia arrests ovarian carcinoma cell cycle progression, but invasion is unaffected. Cancer Res 56:1168–1173
Krtolica A, Krucher NA, Ludlow JW (1999) Molecular analysis of selected cell cycle regulatory proteins during aerobic and hypoxic maintenance of human ovarian carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer 80:1875–1883
Michalides R, van Veelen N, Hart A, Loftus B, Wientjens E, Balm A (1995) Overexpression of cyclin D1 correlates with recurrence in a group of forty-seven operable squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Cancer Res 55:975–978
Michalides R, van Tinteren H, Balkenende A, Vermorken JB, Benraadt J, Huldij J, van Diest P (2002) Cyclin A is a prognostic indicator in early stage breast cancer with and without tamoxifen treatment. Br J Cancer 86:402–408
Nozoe T, Korenaga D, Futatsugi M, Saeki H, Ohga T, Sugimachi K (2002) Cyclin A expression in superficial squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus and coexisting infiltrated lymphocyte follicle. Cancer Lett 188:221–229
Oka K, Arai T (1996) MIB1 growth fraction is not related to prognosis in cervical squamous cell carcinoma treated with radiotherapy. Int J Gynecol Pathol 15:23–27
Porter PL, Malone KE, Heagerty PJ, Alexander GM, Gatti LA, Firpo EJ, Daling JR, Roberts JM (1997) Expression of cell-cycle regulators p27Kip1 and cyclin E, alone and in combination, correlate with survival in young breast cancer patients. Nat Med 3:222–225
Sherr CJ (1993) Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell 73:1059–1065
Sherr CJ (1994) G1 phase progression: cyclin on cue. Cell 79:551–555
Shih HC, Shiozawa T, Kato K, Imai T, Miyamoto T, Uchikawa J, Nikaido T, Konishi I (2003) Immunohistochemical expression of cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, tumor-suppressor gene products, Ki-67, and sex steroid receptors in endometrial carcinoma: positive staining for cyclin A as a poor prognostic indicator. Hum Pathol 34:471–478
Shioazawa T, Li SF, Nakayama K, Nikaido T, Fujii S (1996) Relationship between the expression of cyclins/cyclin-dependent kinases and sex steroid receptors/Ki67 in normal human endometrial glands and stroma during the menstrual cycle. Mol Hum Reprod 2:745–752
Skomedal H, Kristensen GB, Lie AK, Holm R (1999) Aberrant expression of the cell cycle associated proteins TP53, MDM2, p21, p27, cdk4, cyclin D1, RB, and EGFR in cervical carcinomas. Gynecol Oncol 73:223–228
Southern SA, Herrington CS (1998) Differential cell cycle regulation by low- and high-risk human papillomaviruses in low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions of the cervix. Cancer Res 58:2941–2945
Takeno S, Noguchi T, Kikuchi R, Uchida Y, Yokoyama S, Muller W (2002) Prognostic value of cyclin B1 in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 94:2874–881
Takeuchi H, Ozawa S, Ando N, Shih CH, Koyanagi K, Ueda M, Kitajima M (1997) Altered p16/MTS1/CDKN2 and cyclin D1/PRAD-1 gene expression is associated with the prognosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Clin Cancer Res 3:2229–2236
Van de Putte G, Kristensen GB, Lie AK, Baekelandt M, Holm R (2004) Cyclins and proliferation markers in early squamous cervical carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 92:40–46
Volm M, Koomagi R, Mattern J, Stammler G (1997) Cyclin A is associated with an unfavourable outcome in patients with non-small-cell lung carcinomas. Br J Cancer 75:1774–1778
Wright TC, Ferenczy A, Kurman RJ (2002) Carcinoma and other tumors of the cervix. In: Kurman RJ (ed) Blaustein’s pathology of the female genital tract, 5th edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 325–346
Yasmeen A, Berdel WE, Serve H, Muller-Tidow C (2003) E- and A-type cyclins as markers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 3:617–633
Zerfass K, Schulze A, Spitkovsky D, Friedman V, Henglein B, Jansen-Durr P (1995) Sequential activation of cyclin E and cyclin A gene expression by human papillomavirus type 16 E7 through sequences necessary for transformation. J Virol 69:6389–6399
Zhai YL, Nikaido T, Shiozawa T, Orii A, Fujii S (1999) Expression of cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases in smooth muscle tumors of the uterus. Int J Cancer 84:244–250
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture (No. 12671583 and No.14370527), Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiohara, S., Shiozawa, T., Miyamoto, T. et al. Expression of cyclins, p53, and Ki-67 in cervical squamous cell carcinomas: overexpression of cyclin A is a poor prognostic factor in stage Ib and II disease. Virchows Arch 446, 626–633 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-005-1252-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-005-1252-0