Abstract
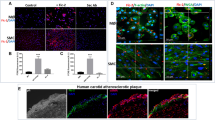
To elucidate the molecular mechanism inducing monocyte/macrophage infiltration in the atherosclerotic lesion, we measured the monocyte chemotactic capacity in the extracts of aortic lesions. Five out of seven extracts exhibited significant chemotactic activities. Immunohistochemical examination with an anti-CD68 monoclonal antibody demonstrated that the five positive lesions possessed obvious monocyte/macrophage infiltrations at the intima, whereas the two negative lesions did so at significantly lower intensities. We subjected the chemotactic extracts to immunological analyses to identify the monocyte chemoattractant in them. The monocyte chemotactic capacities of all positive extracts were removed with anti-S19 ribosomal protein (RP S19) antibody beads and antimonocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) antibody beads. In three of the five extracts, the anti-RP S19 antibody beads were more effective than the anti-MCP-1 antibody beads for removal, while in the remaining two extracts, the opposite was observed. A combined immunoabsorption with these beads depleted the monocyte chemotactic capacity of a representative sample of each group. Consistently, the chemotactic capacity of an apparently RP S19 dimer-predominant extract was strongly inhibited by the presence of a C5a receptor antagonist. These results suggest that the RP S19 dimer and MCP-1 play a major role in the monocyte/macrophage infiltration of the atherosclerotic vascular lesion.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aquel NM, Ball RY, Waldman H, Mitchinson MJ (1985) Identification of macrophages and smooth muscle cells in human atherosclerosis using monoclonal amtibodies. J Pathol 146:197–204
Cianciolo GJ, Snyderman R (1981) Monocyte responsiveness to chemotactic stimuli in a property of subpopulation of cells that can respond to multiple chemoattractants. J Clin Invest 67:60–68
Edwards RJ, Singleton AM, Boobis AR, Davies DS (1989) Cross-reaction of antibodies to coupling groups used in the production of anti-peptide antibodies. J Immunol Methods 117:215–220
Fernandez HN, Henson PM, Otani A, Hugli TE (1978) Chemotactic response to human C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins. I. Evaluation of C3a and C5a leukotaxis in vitro and under stimulated in vivo conditions. J Immunol 120:109–115
Horino K, Nishiura H, Ohsako T, Shibuya Y, Hiraoka T, Kitamura N, Yamamoto T (1998) A monocyte chemotactic factor, S19 ribosomal protein dimer, in phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells. Lab Invest 78:603–617
Kockx MM, Herman AG (1998) Apoptosis in atherogenesis: implications for plaque destabilization (review). Eur Heart J 19(Suppl G):G23–G28
Kondoh N, Schweinfest CW, Henderson KW, Papas TS (1992) Differential expression of S19 ribosomal protein, laminin-binding protein, and human lymphocyte antigen class I messenger RNAs associated with colon carcinoma progression and differentiation. Cancer Res 52:791–796
Matsubara S, Yamamoto T, Tsuruta T, Takagi K, Kambara T (1991) Complement C4-derived monocyte-directed chemotaxis-inhibitory factor: a molecular mechanism to cause polymorphonuclear leukocyte-predominant infiltration in rheumatoid arthritis synovial cavities. Am J Pathol 138:1279–1291
Nishimura T, Horino K, Nishiura H, Shibuya Y, Hiraoka T, Tanase S, Yamamoto T (2001) Apoptotic cells of an epithelial cell line, AsPC-1, release monocyte chemotactic S19 ribosomal protein dimer. J Biochem 129:445–454
Nishiura H, Shibuya Y, Matsubara S, Tanase S, Kambara T, Yamamoto T (1996) Monocyte chemotactic factor in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue: probably a cross-linked derivative of S19 ribosomal protein. J Biol Chem 271:878–882
Nishiura H, Shibuya Y, Yamamoto T (1998) S19 ribosomal protein cross-linked dimer causes monocyte-predominant infiltration by means of molecular mimicry to complement C5a. Lab Invest 78:1615–1623
Nishiura H, Tanase S, Shibuya Y, Nishimura T, Yamamoto T (1999) Determination of the cross-linked residues in homo-dimerization of S19 ribosomal protein concomitant with exhibition of monocyte chemotactic activity. Lab Invest 79:915–923
Okura Y, Brink M, Itabe H, Scheidegger KJ, Kalangos A, Delafontaine P (2000) Oxidized low-density lipoprotein is associated with apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells in human atherosclerotic plaques. Circulation 102:2680–2686
Shibuya Y, Shiokawa M, Nishiura H, Nishimura T, Nishimura T, Nishino N, Okabe H, Takagi K, Yamamoto T (2001) Identification of receptor binding sites of monocyte chemotactic S19 ribosomal protein dimer. Am J Pathol 159:2293–2301
Shrestha A, Horino K, Nishiura H, Yamamoto T (1999) Acquired immune response as a consequence of the macrophage-dependent apoptotic cell clearance and role of the monocyte chemotactic S19 ribosomal protein dimer in this connection. Lab Invest 79:1629–1642
Shrestha A, Shiokawa M, Nishimura T, Nishiura H, Tanaka Y, Nishino N, Shibuya Y, Yamamoto T (2003) Switch moiety in agonist/antagonist dual effect of S19 ribosomal protein dimer on leukocyte chemotactic C5a receptor. Am J Pathol 162:1381–1388
Shrestha A, Shi L, Tanase S, Tsukamoto M, Nishino N, Tokita K, Yamamoto T (2004) Bacterial chaperon protein, Skp, induces leukocyte chemotaxis via C5a receptor. Am J Pathol 164:763–772
Takeya M, Yoshimura T, Leonard EJ, Takahashi K (1993) Detection of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in human atherosclerotic lesions by an anti-monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 monoclonal antibody. Human Pathol 24:534–539
Umeda Y, Shibuya Y, Semba U, Tokita K, Nishino N, Yamamoto T (2004) Guinea pig ribosomal protein as precursor of C5a receptor-directed monocyte-selected leukocyte chemotactic factor. Inflam Res 53:623–630
Watanabe T, Hirata M, Yoshikawa Y, Nagafuchi Y, Toyoshima H, Watanabe T (1985) Role of macrophages in atherosclerosis. Sequential observation of cholesterol-induced rabbit aortic lesions by the immunoperoxidase technique using monoclonal anti-macrophage antibody. Lab Invest 53:80–90
Yamamoto T (2000) Molecular mechanism of monocyte predominant infiltration in chronic inflammation: mediation by a novel monocyte chemotactic factor, S19 ribosomal protein dimer. Pathol Int 50:863–871
Ylä-Herttura S, Lipton BA, Rosenfeld ME, Särkioja T, Yoshimura T, Leonard EJ, Witztum JL, Steinberg D (1991) Expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in macrophage-rich areas of human and rabbit atherosclerotic lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:5252–5256
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Prof. M. Takeya and Miss T. Kubo of Faculty of Medical and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kumamoto University for helpful suggestions and technical advice, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
L. Shi and S. Tsurusaki contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, L., Tsurusaki, S., Futa, N. et al. Monocyte chemotactic S19 ribosomal protein dimer in atherosclerotic vascular lesion. Virchows Arch 447, 747–755 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-005-0012-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-005-0012-5