Abstract
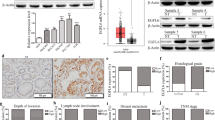
Cbl proteins play important roles in downregulation of growth factor receptors by acting as ubiquitin ligases and multi-adapter proteins. Ligand-induced desensitization of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) has been shown to be controlled by Cbl. In the present study, we examined the expression of Cbl in gastric carcinomas and studied the correlation of Cbl expression with clinicopathological characteristics as well as EGFR expression. Cbl protein was expressed in 67% (82/122) of gastric carcinomas, and diffuse expression of Cbl was detected in 29% (35/122) of the cases. The incidence of cases with diffuse expression of Cbl was significantly higher in advanced cases (28/70, 40%) than in early cases (7/52, 14%) (P=0.0010). Diffuse expression of Cbl was significantly associated with metastasis of tumor cells in lymph nodes (P=0.0318). Diffuse expression of EGFR was significantly associated with depth of invasion (P=0.0057), lymph-node metastasis (P=0.0371) and tumor stages (P=0.0278). As the grades of Cbl expression became stronger, the cases with diffuse EGFR expression increased, the positive correlation being significant (P=0.049). All the cases with diffuse expression of Cbl and EGFR were found to show nodal metastasis and to be at an advanced stage. Moreover, the prognosis of the patients with synchronous diffuse expression of Cbl and EGFR was significantly poorer than that of the patients negative for Cbl and focal or negative for EGFR (P=0.0086). The expression of Cbl protein was clearly induced in gastric carcinoma cell lines by transforming growth factor-α treatment. These results suggest that Cbl in connection with the EGFR system may be associated with stomach carcinogenesis, invasion and metastasis. Cbl may serve as a novel molecular marker for aggressive gastric carcinoma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andoniou C, Thien C, Langdon W (1994) Tumour induction by activated abl involves tyrosine phosphorylation of the product of the cbl oncogene. EMBO J 13:4515–4523
Bolen JB, Veillette A, Schwarts AM, De Seau V, Rosen N (1997) Activation of pp60c-src protein kinase activity in human colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:2251–2255
Di Fiore PP, De Camilli P (2001) Endocytosis and signaling. An inseparable partnership. Cell 106:1–4
Gad H, Ringstad N, Low P, Kjaerulff O, Gustafsson J, Wenk M, Di Paolo G, Nemoto Y, Crun J, Ellisman MH, De Camilli P, Shupliakov O, Brodin L (2000) Fission and uncoating of synaptic clathrin-coated vesicles are perturbed by disruption of interactions with the SH3 domain of endophilin. Neuron 27:301–312
Hopkins C, Gibson A, Shipman M, Miller K (1990) Movement of internalized ligand-receptor complexes along a continuous endosomal reticulum. Nature 346:318–319
Ito R, Kitadai Y, Kyo E, Yokozaki H, Yasui W, Yamashita U, Nikai H andTahara E (1993) Interleukin 1 alpha acts as an autocrine growth stimulator for human gastric carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 53:4102–4106
Japanese Research Society for Gastric Cancer (1995) Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma. 1st English edn. Kanehara & Co., Ltd., Tokyo, pp 38–65
Joazeiro CA, Hunter T (2000) Biochemistry. Ubiquitination—more than two to tango. Science 289:2061–2062
Joazeiro CA, Wing SS, Huang H, Leverson JD, Hunter T, Liu YC (1999) The tyrosine kinase negative regulator c-Cbl as a RING-type, E2-dependent ubiquitin-protein ligase. Science 286:309–312
Kamei T, Machida K, Nimura Y, Senga T, Yamada I, Yoshii S, Matsuda S, Hamaguchi M (2000) C-Cbl protein in human cancer tissues is frequently tyrosine phosphorylated in a tumor-specific manner. Int J Oncol 17:335–339
Kitadai Y, Yasui W, Yokozaki H, Kuniyasu H, Ayhan A, Haruma K, Kajiyama G, Johnson GR, Tahara E (1993) Expression of amphiregulin, a novel gene of the epidermal growth factor family, in human gastric carcinomas. Jpn J Cancer Res 84:879–884
Kuniyasu H, Yoshida K, Yokozaki H, Yasui W, Ito H, Toge T, Ciardiello F, Persico MG, Saeki T, Salomon DS, et al (1991) Expression of cripto, a novel gene of the epidermal growth factor family, in human gastrointestinal carcinomas. Jpn J Cancer Res 82:969–973
Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J (1998) Transmembrane signaling by receptor oligomerization. Methods Mol Biol 84:49–71
Levkowitz G, Waterman H, Ettenberg SA, Katz M, Tsygankov AY, Alroy I, Lavi S, Iwai K, Reiss Y, Ciechanover A, Lipkowitz S, Yarden Y (1999) Ubiquitin ligase activity and tyrosine phosphorylation underlie suppression of growth factor signaling by c-Cbl/Sli-1. Mol Cell 4:1029–1040
Ochiai A, Yasui W, Tahara E (1985) Growth-promoting effect of gastrin on human gastric carcinoma cell line TMK-1. Jpn J Cancer Res 76:1064–1071
Ottenhoff-Kalff AE, Rijiksen G, van Bewrden EA, Hennipman A, Michels AA, Staal GE (1992) Characterization of protein tyrosine kinases from human breast cancer. Cancer Res 52:4773–4778
Oue N, Shigeishi H, Kuniyasu H, Yokozaki H, Kuraoka K, Ito R, Yasui W (2001) Promoter hypermethylation of MGMT is associated with protein loss in gastric carcinoma. Int J Cancer 93:805–809
Petrelli A, Gilestro GF, Lanzardo S, Comoglio PM, Migone N, Giordano S (2002) The endophilin-CIN85-Cbl complex mediates ligand-dependent downregulation of c-Met. Nature 416:187–190
Ringstad N, Gad H, Low P, Di Paolo G, Brodin L, Shupliakov O, De Camilli P (1999) Endophilin/SH3p4 is required for the transition from early to late stages in clathrin-mediated synaptic vesicle endocytosis. Neuron 24:143–154
Schmidt A, Wolde M, Thiele C, Fest W, Kratzin H, Podtelejnikov AV, Witke W, Huttner WB, Soling HD (1999) Endophilin I mediates synaptic vesicle formation by transfer of arachidonate to lysophosphatidic acid. Nature 401:133–141
Simpson F, Hussain NK, Qualmann B, Kelly RB, Kay BK, McPherson PS, Schmid SL (1999) SH3-domain-containing proteins function at distinct steps in clathrin-coated vesicle formation. Nat Cell Biol 1:119–124
Soubeyran P, Kowanetz K, Szymkiewicz I, Langdon WY, Dikic I (2002) Cbl-CIN85-endophilin complex mediates ligand-induced downregulation of EGF receptors. Nature 416:183–187
Take H, Watanabe S, Takeda K, Yu ZX, Iwata N, Kajigaya S (2000) Cloning and characterization of a novel adaptor protein, CIN85, that interacts with c-Cbl. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 268:321–328
Takekura N, Yasui W, Yoshida K, Tsujino T, Nakayama H, Kameda T, Yokozaki H, Nishimura Y, Ito H, Tahara E (1990) pp60c-src protein kinase activity in human gastric carcinomas. Int J Cancer 45:847–851
Thien CB, Langdon WY (1997) EGF receptor binding and transformation by v-cbl is ablated by the introduction of a loss-of-function mutation from the Caenorhabditis elegans sli-1 gene. Oncogene 14:2239–2249
Thien CB, Langdon WY (2001) Cbl: many adaptations to regulate protein tyrosine kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:294–307
Ullirich A, Schlessinger J (1990) Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell 61:203–212
Waterman H, Yarden Y (2001) Molecular mechanisms underlying endocytosis and sorting of ErbB receptor tyrosine kinases. FEBS Lett 490:142–152
Yasui W, Hata J, Yokozaki H, Nakatani H, Ochiai A, Ito H, Tahara E (1988) Interaction between epidermal growth factor and its receptor in progression of human gastric carcinoma. Int J Cancer 41:211–217
Yasui W, Sumiyoshi H, Hata J, Kameda T, Ochiai A, Ito H, Tahara E (1988) Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor in human gastric and colonic carcinomas. Cancer Res 48:137–141
Yokouchi M, Kondo T, Houghton A, Bartkiewicz M, Horne WC, Zhang H, Yoshimura A, Baron R (1999) Ligand-induced ubiquitination of the epidermal growth factor receptor involves the interaction of the c-Cbl RING finger and UbcH7. J Biol Chem 274:31707–31712
Yokozaki H (2000) Molecular characteristics of eight gastric cancer cell lines established in Japan. Pathol Int 50:767–777
Yoshida K, Tsujino T, Yasui W, Kameda T, Sano T, Nakayama H, Toge T, Tahara E (1990) Induction of growth factor-receptor and metalloproteinase genes by epidermal growth factor and/or transforming growth factor-alpha in human gastric carcinoma cell line MKN-28. Jpn J Cancer Res 81:793–798
Acknowledgements
This work was supported, in part, by Grants-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, and Technology of Japan, and the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare of Japan. The authors thank Masayoshi Takatani and Mutsumi Ueda for their skillful technical assistance. The authors are also grateful to Noriko Sagawa for her secretarial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, R., Nakayama, H., Yoshida, K. et al. Expression of Cbl linking with the epidermal growth factor receptor system is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis of human gastric carcinoma. Virchows Arch 444, 324–331 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-004-0982-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-004-0982-8