Abstract
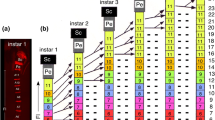
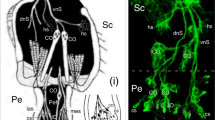
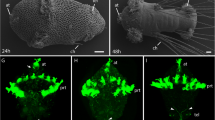
The nervous system of the antenna of the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria consists of two nerve tracts in which sensory cells project their axons to the brain. Each tract is pioneered early in embryogenesis by a pair of identified cells located apically in the antennal lumen. The pioneers are thought to originate in the epithelium of the antenna and then delaminate into the lumen where they commence axogenesis. However, unambiguous molecular identification of these cells in the epithelium, of an identifiable precursor, and of their mode of generation has been lacking. In this study, we have used immunolabeling against neuron-specific horseradish peroxidase and against Lachesin, a marker for differentiating epithelial cells, in combination with the nuclear stain DAPI, to identify the pioneers within the epithelium of the early embryonic antenna. We then track their delamination into the lumen as differentiated neurons. The pioneers are not labeled by the mesodermal/mesectodermal marker Mes3, consistent with an epithelial (ectodermal) origin. Intracellular dye injection, as well as labeling against the mitosis marker phospho-histone 3, identifies precursor cells in the epithelium, each associated with a column of cells. Culturing with the S-phase label 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) shows that both a precursor and its column have incorporated the label, confirming a lineage relationship. Each set of pioneers can be shown to belong to a separate lineage of such epithelial cells, and the precursors remain and are proliferative after generating the pioneers. Analyses of mitotic spindle orientation then enable us to propose a model in which a precursor generates its pioneers asymmetrically via self-renewal.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams RR, Maiato H, Earnshaw W, Carmena M (2001) Essential roles of Drosophila inner centromere protein (INCENP) and aurora B in histone H3 phosphorylation, metaphase chromosome alignment, kinetochore disjunction, and chromosome segregation. J Cell Biol 153:865–879
Anderson DT (1973) Embryology and phylogeny in annelids and arthropods. Pergamon Press, Oxford, New York
Anderson H, Tucker RP (1988) Pioneer neurones use basal lamina as a substratum for outgrowth in the embryonic grasshopper limb. Development 104:601–608
Anderson H, Tucker RP (1989) Spatial and temporal variation in the structure of the basal lamina in embryonic grasshopper limbs during pioneer neurone outgrowth. Development 106:185–194
Apitz H, Salecker I (2014) A challenge of numbers and diversity: neurogenesis in the Drosophila optic lobe. J Neurogen 28:233–249
Ball EE, de Couet HG, Horn PL, Quinn JMA (1987) Haemocytes secrete basement membrane components in embryonic locusts. Development 99:255–259
Bastiani MJ, du Lac S, Goodman CS (1985) The first growth cones in insect embryos: model system for studying the development of neuronal specificity. In: Selverston AI (ed) Model neural networks and behaviour. Plenum Press, New York, pp. 149–174
Bate CM (1976) Embryogenesis of an insect nervous system I. A map of the thoracic and abdominal neuroblasts in Locusta migratoria. J Embryol Exp Morphol 35:107–123
Bellaïche Y, Schweisguth F (2001) Lineage diversity in the Drosophila nervous system. Curr Opin Gen Dev 11:418–423
Bentley D, O’Connor TP (1992) Guidance and steering of peripheral growth cones in grasshopper embryos. In: Letourneau C, Kater SB, Macagno ER (eds) The nerve growth cone. Raven Press, New York, pp. 265–282
Bentley D, Keshishian H, Shankland M, Torian-Raymond A (1979) Quantitative staging of embryonic development of the grasshopper, Schistocerca nitens. J Embryol Exp Morphol 54:47–74
Berlot J, Goodman CS (1984) Guidance of peripheral pioneer neurons in the grasshopper: adhesive hierarchy of epithelial and neuronal surfaces. Science 223:493–496
Bier E, Jan LY, Jan YN (1990) rhomboid, a gene required for dorsoventral axis establishment and peripheral nervous system development in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev 4:190–203
Bodmer R, Jan YN (1987) Morphological differentiation of the embryonic peripheral neurons in Drosophila. Roux’s Arch Dev Biol 196:69–77
Boyan GS, Ehrhardt EE (2015) Pioneer neurons of the antennal nervous system project to protocerebral pioneers in the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria. Dev Genes Evol 225:377–382
Boyan GS, Williams JLD (2004) Embryonic development of the sensory innervation of the antenna of the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria. Arthr Struct Dev 33:381–397
Boyan GS, Williams JLD (2007) Embryonic development of a peripheral nervous system: nerve tract associated cells and pioneer neurons in the antenna of the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria. Arthr Struct Dev 36:336–350
Boyan GS, Williams JLD (2008) Evidence that the peripheral brain commissure is pioneered by neurons with a peripheral-like ontogeny in the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria. Arth Struct Dev 37:186–198
Campos-Ortega JA, Hartenstein V (1985) The embryonic development of Drosophila melanogaster. Springer, Berlin
Casares F, Mann RS (1998) Control of antennal versus leg development in Drosophila Nature 392:723–726
Chapman RF (1982) The insects: structure and function. Hodder and Stoughton, London
Chapman RF (2002) Development of phenotypic differences in sensillum populations on the antennae of a grasshopper, Schistocerca americana. J Morphol 254:186–194
Dambey-Chaudiere C, Jamet E, Burri M, Bopp D, Basler K, Hafen E, Dumont N, Spielmann P, Ghysen A, Noel M (1992) The paired box gene pox-neuro—a determinant of poly-innervated sense organs in Drosophila. Cell 69:159–172
Dickson BJ (2002) Molecular mechanisms of axon guidance. Science 298:1959–1964
Doe CQ (2008) Neural stem cells: balancing self-renewal with differentiation. Development 135:1575–1587
Doe CQ, Goodman CS (1985a) Early events in insect neurogenesis. I. Development and segmental differences in the pattern of neuronal precursor cells. Dev Biol 111:193–205
Doe CQ, Goodman CS (1985b) Early events in insect neurogenesis. II. The role of cell interactions and cell lineage in the determination of neuronal precursor cells. Dev Biol 111:206–219
Ehrhardt E, Kleele T, Boyan GS (2015b) A method for immunolabeling neurons in intact cuticularized insect appendages. Dev Genes Evol 225:187–194
Ehrhardt E, Liu Y, Boyan GS (2015a) Axogenesis in the antennal nervous system of the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria revisited: the base pioneers. Dev Genes Evol 225:39–45
Ehrhardt EE, Graf P, Kleele T, Liu Y, Boyan GS (2016) Fates of identified pioneer cells in the developing antennal nervous system of the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria. Arth Struct Dev 45:23–30
Ganfornina MD, Sánchez D, Bastiani MJ (1995) Lazarillo, a new GPI-linked surface lipocalin, is restricted to a subset of neurons in the grasshopper embryo. Development 121:123–134
Gibson G, Gehring WJ (1988) Head and thoracic transformation caused by ectopic expression of Antennapedia during Drosophila development. Development 102:657–675
Goodman CS (1996) Mechanisms and molecules that control growth cone guidance. Ann Rev Neurosci 19:341–377
Goodman CS, Doe CQ (1994) Embryonic development of the Drosophila central nervous system. In: Bate M, Martinez-Arias A (eds) The development of Drosophila, vol 1. Cold Spring Harbor Press, New York, pp. 1131–1206
Götz M, Huttner WB (2005) The cell biology of neurogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:777–788
Gupta BP, Rodrigues V (1997) Atonal is a proneural gene for a subset of olfactory sense organs in Drosophila. Genes Cells 2:225–233
Hartenstein V (1987) The influence of segmental compartmentalization on the development of the larval peripheral nervous system in Drosophila melanogaster. Roux’s Arch Dev Biol 196:101–112
Heathcote RD (1981) Differentiation of an identified sensory neuron (SR) and associated structures (CTO) in grasshopper embryos. J Comp Neurol 202:1–18
Hendzel M, Wie Y, Mancini MA, Van Hooser A, Ranali T, Brinkley BR, Bazett-Jones DP, Allis CD (1997) Mitosis-specific phosphorylation of histone H3 initiates primarily within pericentromeric heterochromatin during G2 and spreads in an ordered fashion coincident with mitotic chromosome condensation. Chromosoma 106:348–360
Higginbotham HR, Gleeson JG (2007) The centrosome in neuronal development. Trends Neurosci 30:276–283
Ho RK, Goodman CS (1982) Peripheral pathways are pioneered by an array of central and peripheral neurones in grasshopper embryos. Nature 297:404–406
Jan LY, Jan YN (1982) Antibodies to horseradish-peroxidase as specific neuronal markers in Drosophila and grasshopper embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 79:2700–2704
Jan YN, Jan LY (1990) Genes required for specifying cell fates in Drosophila embryonic sensory nervous system. Trends Neurosci 13:493–498
Jarman AP (2014) Development of the auditory organ (Johnston’s organ) in Drosophila. In: Romand R, Varela-Nieto I (eds) Development of auditory and vestibular systems. Academic Press, pp 31–63
Jarman AP, Sun Y, Jan LY, Jan YN (1995) Role of the proneural gene, atonal, in formation of Drosophila chordotonal organs and photoreceptors. Development 121:2019–2030
Karlstrom RO, Wilder LP, Bastiani MJ (1993) Lachesin: an immunoglobulin superfamily protein whose expression correlates with neurogenesis in grasshopper embryos. Development 118:509–522
Keil TA (1992) Fine structure of a developing insect olfactory organ: morphogenesis of the silkmoth antenna. Microsc Res Tech 22:351–371
Keil TA (1997) Comparative morphogenesis of sensilla: a review. Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 26:151–160
Keil TA, Steiner C (1990) Morphogenesis of the antenna of the male silkmoth, Antheraea polyphemus. II. Differential mitoses of ‘dark’ precursor cells create the Anlagen of sensilla. Tissue Cell 22:705–720
Keshishian H (1980) The origin and morphogenesis of pioneer neurons in the grasshopper metathoracic leg. Dev Biol 80:388–397
Keshishian H, Bentley D (1983) Embryogenesis of peripheral nerve pathways in grasshoppers legs. I. The initial nerve pathway to the CNS. Dev Biol 96:89–102
Kotrla KJ, Goodman CS (1984) Transient expression of a surface antigen on a small subset of neurones during embryonic development. Nature 311:151–153
Lefcort F, Bentley D (1989) Organization of cytoskeletal elements and organelles preceding growth cone mergence from an identified neuron in situ. J Cell Biol 108:1737–1749
Locke M, Huie P (1981) Epidermal feet in insect morphogenesis. Nature 293:733–735
Meier T, Chabaud F, Reichert H (1991) Homologous patterns in the embryonic development of the peripheral nervous system in the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria and the fly Drosophila melanogaster. Development 112:241–253
Mueller BK (1999) Growth cone guidance: first steps towards a deeper understanding. Ann Rev Neurosci 22:351–388
Naimski P, Bierzyimageski A, Fikus M (1980) Quantitative fluorescent analysis of different conformational forms of DNA bound to the dye 4′,6-diamidine-2-phenylindole, and separated by gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem 106:471–475
Neumüller RA, Knoblich JA (2009) Dividing cellular asymmetry: asymmetric cell division and its implications for stem cells and cancer. Genes Dev 23:2675–2699
Ramón y Cajal S (1890) A quelle epoque aparaissent les expansion des cellule neurveuses de la moelle epinere du poulet. Anat Anz 5:609–613
Sánchez D, Ganfornina MD, Bastiani MJ (1995) Developmental expression of the lipocalin Lazarillo and its role in axonal pathfinding in the grasshopper embryo. Development 121:135–147
Seidel C, Bicker G (2000) Nitric oxide and cGMP influence axogenesis of antennal pioneer neurons. Development 127:4541–4549
Sousa-Nunes R, Yee LL, Gould AP (2011) Fat cells reactivate quiescent neuroblasts via TOR and glial insulin relays in Drosophila. Nature 471:508–513
Takagi A, Kurita K, Terasawa T, Nakamura T, Bando T, Moriyama Y, Mito T, Noji S, Ohuchi H (2012) Functional analysis of the role of eye absent and sine oculis in the developing eye of the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus. Develop Growth Differ 54:227–240
Tessier-Lavigne M, Goodman CS (1996) The molecular biology of axon guidance. Science 274:1123–1133
Uemura T, Shepherd S, Ackerman L, Jan LY, Jan YN (1989) numb, a gene required in determination of cell fate during sensory organ formation in Drosophila embryos. Cell 58:349–360
Yamashiki N (1981) The role of the spindle body in unequal division of the grasshopper neuroblast. Zool Mag 90:93–101
Yamashiki N, Kawamura KY (1986a) Microdissection studies on the polarity of unequal division in grasshopper neuroblasts. I. Subsequent divisions in neuroblast-type cells produced against the polarity by micromanipulation. Exp Cell Res 166:127–138
Yamashiki N, Kawamura KY (1986b) Microdissection studies on the polarity of unequal division in grasshopper neuroblasts. II. Cell division in binucleate neuroblasts. Develop Growth Differ 28:603–609
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Sanchez and Ganfornina for the gift of the Lazarillo antibody, Dr. Goodman for the gift of the Mes3 antibody, and Dr. Bastiani for the gift of the Lachesin antibody. We thank Dr. Yu Liu for the critical reading of the manuscript and Karin Fischer for the excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experiments were performed in accordance with the guidelines for animal welfare as laid down by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Funding
Both authors received support for this study from the Graduate School of Systemic Neuroscience, University of Munich.
Additional information
Communicated by Claude Desplan
Both authors contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boyan, G., Ehrhardt, E. Ontogeny of pioneer neurons in the antennal nervous system of the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria . Dev Genes Evol 227, 11–23 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-016-0565-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-016-0565-0