Abstract
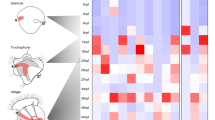
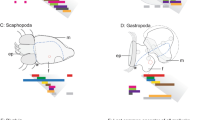
Hox transcription factors, a subfamily of homeobox genes, are expressed in distinct, often overlapping domains along the anterior–posterior body axis of animal embryos. Here, we report the sequence and expression pattern of Hox2, Hox3, Hox4, Hox5, Lox5, Hox7, Lox4, and Lox2 in different larval stages during the encapsulated development of the marine gastropod Gibbula varia. Our results show that all Gva-Hox genes are expressed in ectoderm-derived cells. Hox2, Hox3, Hox4, Hox5, and Hox7 are expressed in overlapping patterns in the pedal, pleural, oesophageal, and visceral ganglia, supporting the ancestral role of Hox genes in the neurogenesis processes in bilaterians. Gva-Hox1, Gva-Post2, and Gva-Post1 genes are involved in shell morphogenesis and have apparently lost their role in neurogangliogenesis. Lox5, Lox4, and Lox2 are expressed in different cells of the apical organ during the earlier larval stage (trochophore) and the cerebral ganglia during later larval stages (veliger). These results support the hypothesis that apical organ neurosensory cells contribute to the formation of cerebral ganglia commissures during metamorphosis. Gva-Hox7 and Gva-Lox4 are additionally expressed in the prototroch of the trochophore and in the velar area of the veliger larvae. This contradicts with the expression of these genes in the annelids, where most of Hox genes are expressed in the posttrochal area and are involved in segmental determination. Therefore, expression of Hox genes may serve as an example of co-option and plasticity of gene function during evolution of gastropods.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aisemberg GO, Macagno ER (1994) Lox1, an Antennapedia-class homeobox gene, is expressed during leech gangliogenesis in both transient and stable central neurons. Dev Biol 161:455–465
Aisemberg GO, Wysocka-Diller J, Wong VY, Macagno ER (1993) Antennapedia-class homebox genes define diverse neuronal sets in the embryonic CNS of the leech. J Neurobiol 24:1423–1432
Aronowitcz J, Lowe CJ (2006) Hox gene expression in the hemichordate Saccoglossus kowalevskii and the evolution of deuterostome nervous system. Integ Comp Biol 46(6):890–901
Balavoine G, de Rosa R, Adoutte A (2002) Hox clusters and bilaterian phylogeny. Mol Phylogenet Evol 24:366–373
Barlow LA, Trueman JW (1992) Patterns of serotonin and SPC immunoreactivity during metamophosis of the nervous system of the red abalone, Haliotis rufescens. J Neurobiol 23:829–844
Barucca M, Olmo E, Canapa A (2003) Hox and paraHox genes in bivalve molluscs. Gene 317:97–102
Biscotti MA, Canapa A, Olmo E, Barucca M (2007) Hox genes in the antarctic polyplacophoran Nuttallochiton mirandus. J Experiment Zool (Mol Dev Evol) 308B:507–513
Brusca RC, Brusca GJ (2002) Phylum Mollusca. In: Invertebrates, 2nd edn. Sinauer, Sunderland, pp 701–769
Callaerts P, Lee PN, Hartmann B, Farfan C, Choy DWY, Ikeo K, Fischbach K, Gehring WJ, de Couet HG (2002) Hox genes in the sepiolid squid Euprymna scolopes: implications for the evolution of complex body plans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(4):2088–2093
Canapa A, Biscotti MA, Olmo E, Barucca M (2005) Isolation of Hox and ParaHox genes in the bivalve Pecten maximus. Gene 348:83–88
de Rosa R, Grenier JK, Andreeva T, Cook CE, Adoutte A, Akam M, Carroll SB, Guillaume Balavoine G (1999) Hox genes in brachiopods and priapulids and protostome evolution. Nature 399:772–776
Dickinson AJG, Croll RP (2003) Development of the larval nervous system of the gastropod Ilyanassa obsoleta. J Comp Neurol 466:197–218
Duboule D (1994) Temporal colinearity and the phylotypic progression: a basis for the stability of a vertebrate Bauplan and the evolution of morphologies through heterochrony. Dev Suppl 135–142
Duboule D, Dollé P (1989) The structural and functional organization of the murine HOX gene family resembles that of Drosophila homeotic genes. EMBO J 8(5):1497–1505
Ferrier DE, Minguillon C (2003) Evolution of the Hox/ParaHox gene clusters. Int J Dev Biol 47(7–8):605–611
Fröbius AC, Matus DQ, Seaver EC (2008) Genomic organization and expression demonstrate spatial and temporal Hox gene colinearity in the Lophotrochozoan Capitella sp. I. PLoS ONE 3(12):e4004. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0004004
Garcia-Fernàndez J (2005) The genesis and evolution of homeobox gene clusters. Nat Rev Genet 6:881–892
Gifondorwa DJ, Leise EM (2006) Programmed cell death in the apical ganglion during larval metamorphosis of the marine mollusc Ilyanassa obsoleta. Biol Bull 210:109–120
Gionti M, Ristoratore F, Di Gregorio A, Aniello F, Branno M, Di Lauro R (1998) Cihox5, a new Ciona intestinalis Hox-related gene, is involved in regionalization of the spinal cord. Dev Genes Evol 207(8):515–523
Giusti AF, Hinman VF, Degnan SM, Degnan BM, Morse DE (2000) Expression of a Scr/Hox5 gene in the larval central nervous system of the gastropod Haliotis, a non-segmented spiralian lophotrochozoan. Evol Dev 2:294–302
Graham A, Papalopulu N, Krumlauf R (1989) The murine and Drosophila homeobox gene complexes have common features of organization and expression. Cell 57:367–378
Hadfield MG, Meleshkevitch EA, Boudko DY (2000) The apical sensory organ of a gastropod veliger is a receptor for settlement cues. Biol Bull 198:67–76
Hejnol A, Martindale MQ (2009) Coordinated spatial and temporal expression of Hox genes during embryogenesis in the acoel Convolutriloba longifissura. BMC Biol 7:65
Hinman VF, O’Brien EK, Richards GS, Degnan BM (2003) Expression of anterior Hox genes during larval development of the gastropod Haliotis asinina. Evol Dev 5:508–521
Holland PW (2001) Beyond the Hox: how widespread is homeobox gene clustering? J Anatomy 199:13–24
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17:754–755
Iijima M, Akiba N, Sarashina I, Kuratani S, Endo K (2006) Evolution of Hox genes in molluscs: a comparison among seven morphologically diverse classes. J Molluscan Stud 72:259–266
In der Rieden PM, Mainguy G, Woltering JM, Durston AJ (2004) Homeodomain to hexapeptide or PBC-interaction-domain distance: size apparently matters. Trends Genet 20:76–79
Irvine SQ, Martindale MQ (2000) Expression patterns of anterior Hox genes in the polychaete Chaetopterus: correlation with morphological boundaries. Dev Biol 217:333–351
Jones DT, Taylor WR, Thornton JM (1992) The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Comput Appl Biosci 8:275–282
Keys DN, Lee BI, Di Gregorio A, Harafuji N, Detter JC, Wang M, Kahsai O, Ahn S, Zhang C, Doyle SA, Satoh N, Satou Y, Saiga H, Christian AT, Kourakis MJ, Master VA, Lokhorst DK, Nardelli-Haefliger D, Wedeen CJ, Martindale MQ, Shankland M (1997) Conserved anterior boundaries of Hox gene expression in the central nervous system of the leech Helobdella. Dev Biol 190:284–300
Kourakis MJ, Master VA, Lokhorst DK, Nardelli-Haefliger D, Wedeen CJ, Martindale MQ, Shankland M (1997) Conserved anterior boundaries of Hox gene expression in the central nervous system of the leech Helobdella. Dev Biol 190:284–300
Kulakova M, Bakalenko N, Novikova E, Cook CE, Eliseeva E, Steinmetz PR, Kostyuchenko RP, Dondua A, Arendt D, Akam M, Andreeva T (2007) Hox gene expression in larval development of the polychaetes Nereis virens and Platynereis dumerilii (Annelida, Lophotrochozoa). Dev Genes Evol 217(1):39–54
Le Gouar M, Guillou A, Vervoort A (2004) Expression of a SoxB and a Wnt2/13 gene during the development of the mollusc Patella vulgata. Dev Genes Evol 214:250–256
Lee PN, Callaerts P, de Couet HG, Martindale MQ (2003) Cephalopod Hox genes and the origin of morphological novelties. Nature 424:1061–1065
Lespinet O, Nederbragt AJ, Cassan M, Dictus WJAG, van Loon AE, Adoutte A (2002) Characterization of two snail genes in the gastropod mollusc Patella vulgata: implications for understanding the ancestral function of the snail-related genes in Bilateria. Dev Genes Evol 212:186–195
Lewis EB (1978) A gene complex controlling segmentation in Drosophila. Nature 276(5688):565–570
Marois R, Carew TJ (1997a) Fine structure of the apical ganglion and its serotonergic cells in the larva of Aplysia californica. Biol Bull 192:388–398
Marois R, Carew TJ (1997b) Ontogeny of serotonergic neurons in Aplysia californica. J Comp Neurol 386:477–490
Marois R, Carew TJ (1997c) Projection patterns and target tissues of the serotonergic cells in larval Aplysia californica. J Comp Neurol 386:491–506
Merabet S, Hudry B, Saadaoui M, Graba Y (2009) Classification of sequence signatures: a guide to Hox protein function. BioEssays 31:500–511
Moreno E, Nadal M, Baguñé J, Martínez P (2009) Tracking the origins of the bilaterian Hox patterning system: insights from the acoel flatworm Symsagittifera roscoffensis. Evol Dev 11(5):574–581
Murtha MT, Leckman JF, Ruddle FH (1991) Detection of homeobox genes in development and evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10711–10715
Nardelli-Haefliger D, Bruce AEE, Shankland M (1994) An axial domain of HOM/Hox gene expression is formed by morphogenetic alignment of independently specified cell lineages in the leech Helobdella. Development 120:1839–1849
Nederbragt AJ, te Welscher P, van den Driesche S, van Loon AE, Dictus WJAG (2002) Novel and conserved roles for orthodenticle/otx and orthopedia/otp orthologs in the gastropod mollusc Patella vulgata. Dev Genes Evol 212:330–337
Page LR, Parries SC (2000) Comparative study of the apical ganglion in planktotrophic caenogastropod larvae: ultrastructure and immunoreactivity to serotonin. J Comp Neurol 418:383–401
Papillon D, Perez Y, Fasano L, Le Parco Y, Caubit X (2005) Restricted expression of a median Hox gene in the central nervous system of chaetognaths. Dev Genes Evol 215:369–373
Passamaneck YJ, Halanych KM (2004) Evidence from Hox genes that bryozoans are lophotrochozoans. Evol Dev 4:275–281
Pendleton JW, Nagai BK, Murtha MT, Ruddle FH (1993) Expansion of the Hox gene family and the evolution of chordates. PNAS 90(13):6300–6304
Pérez-Parallé ML, Carpintero P, Pazos A, Abad M, Sánchez J (2005) The HOX gene cluster in the bivalve mollusc Mytilus galloprovincialis. Biochem Genet 43(7/8):417–424
Pernice M, Deutsch JS, Andouche A, Boucher-Rodoni R, Bonnaud L (2006) Unexpected variation of Hox genes’ Homeodomains in Cephalopods. Mol Phylogenet Evol 40(3):872–879
Raven CP (1966) Morphogenesis: the analysis of Molluscan development, 2nd edn. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Rokhsar DS, Hawkins TL, Levine M, Richardson PM (2005) A saturation screen for cis-acting regulatory DNA in the Hox genes of Ciona intestinalis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(3):679–683
Ruthensteiner B, Schaefer K (2002) The cephalic sensory organ in veliger larvae of pulmonates (Gastropoda: Mollusca). J Morphol 251:93–102
Samadi L, Steiner G (2009) Involvement of Hox genes in shell morphogenesis in the encapsulated development of a top shell gastropod (Gibbula varia L.). Dev Genes Evol 219:523–530
Samadi L, Steiner G (2010) Conservation of ParaHox genes’ function in patterning of the digestive tract of the marine gastropod Gibbula varia. BMC Dev Biol 10:74. doi:10.1186/1471-213X-10-74
Schramm G, Bruchhaus I, Roeder T (2000) A simple and reliable 5´-RACE approach. Nucleic Acids Res 28(22):96–99
Seo HC, Edvardsen RB, Maeland AD, Bjordal M, Jensen MF, Hansen A, Flaat M, Weissenbach J, Lehrach H, Wincker P, Reinhardt R, Chourrout D (2004) Hox cluster disintegration with persistent anteroposterior order of expression in Oikopleura dioica. Natur 431(7004):67–71
Wada H, Garcia-Fernandez J, Holland PW (1999) Colinear and segmental expression of amphioxus Hox genes. Dev Biol 213(1):131–141
Wong VY, Aisemberg GO, Gan WB, Macagno ER (1995) The leech homeobox gene Lox4 may determine segmental differentiation of identified neurons. J Neurosci 15:5551–5559
Wysocka-Diller JW, Aisemberg GO, Baumgarten M, Levine M, Macagno ER (1989) Characterization of a homologue of bithorax-complex genes in the leech Hirudo medicinalis. Nature 341:760–763
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments. Leyli Samadi was supported by an EC fellowship within the MOLMORPH network under the 6th Framework Programme “Marie Curie Fellowships for Early Stage Research Training (EST)” (contract number MEST-CT-2005-020542). We are grateful to Prof. Michael Stachowitsch for improving the English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D.A. Weisblat
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 447 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samadi, L., Steiner, G. Expression of Hox genes during the larval development of the snail, Gibbula varia (L.)—further evidence of non-colinearity in molluscs. Dev Genes Evol 220, 161–172 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-010-0338-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-010-0338-0