Abstract
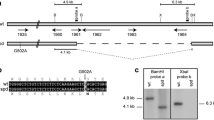
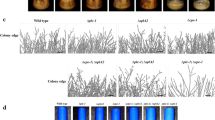
Transcription factor Dd-STATa, a functional Dictyostelium homologue of metazoan signal transducers and activators of transcription proteins, is necessary for culmination during development. We have isolated more than 18 putative multicopy suppressors of Dd-STATa using genetic screening. One was hssA gene, whose expression is known to be G-box-binding-factor-dependent and which was specific to prestalk A (pstA) cells, where Dd-STATa is activated. Also, hssA mRNA was expressed in pstA cells in the Dd-STATa-null mutant. At least 40 hssA-related genes are present in the genome and constitute a multigene family. The tagged HssA protein was translated; hssA encodes an unusually high-glycine-serine-rich small protein (8.37 kDa), which has strong homology to previously reported cyclic-adenosine-monophosphate-inducible 2C and 7E proteins. Overexpression of hssA mRNA as well as frame-shifted versions of hssA RNA suppressed the phenotype of the partially active Dd-STATa strain, suggesting that translation is not necessary for suppression. Although overexpression of prespore-specific genes among the family did not suppress the parental phenotype, prestalk-specific family members did. Although overexpression of the hssA did not revert the expression of Dd-STATa target genes, and although its suppression mechanism remains unknown, morphological reversion implies functional relationships between Dd-STATa and hssA.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoshima R, Hiraoka R, Shimada N, Kawata T (2006) Analysis of a homologue of the adducin head gene which is a potential target for the Dictyostelium STAT protein Dd-STATa. Int J Dev Biol 50:523–532
Araki T, Gamper M, Early A, Fukuzawa M, Abe T, Kawata T, Kim E, Firtel RA, Williams JG (1998) Developmentally and spatially regulated activation of a Dictyostelium STAT protein by a serpentine receptor. EMBO J 17:4018–4028
Chisholm RL, Gaudet P, Just EM, Pilcher KE, Fey P, Merchant SN, Kibbe WA (2006) dictyBase, the model organism database for Dictyostelium discoideum. Nucleic Acids Res 34(Database issue):D423–D427
Darnell JE Jr (1997) STATs and gene regulation. Science 277:1630–1635
Dingermann T, Reindl N, Werner H, Hildebrandt M, Nellen W, Harwood A, Williams J Nerke K (1989) Optimization and in situ detection of Escherichia coli β-galactosidase gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum. Gene 85:353–362
Eichinger L, Pachebat JA, Glockner G, Rajandream MA, Sucgang R, Berriman M, Song J, Olsen R, Szafranski K, Xu Q, Tunggal B, Kummerfeld S, Madera M, Konfortov BA, Rivero F, Bankier AT, Lehmann R, Hamlin N, Davies R, Gaudet P, Fey P, Pilcher K, Chen G, Saunders D, Sodergren E, Davis P, Kerhornou A, Ni X, Hall N, Anjard C, Hemphill L, Bason N, Farbrother P, Desany B, Just E, Morio T, Rost R, Churcher C, Cooper J, Haydock S, van Driessche N, Cronin A, Goodhead I, Muzny D, Mourier T, Pain A, Lu M, Harper D, Lindsay R, Hauser H, James K, Quiles M, Madan Babu M, Saito T, Buchrieser C, Wardroper A, Felder M, Thangavelu M, Johnson D, Knights A, Loulseged H, Mungall K, Oliver K, Price C, Quail MA, Urushihara H, Hernandez J, Rabbinowitsch E, Steffen D, Sanders M, Ma J, Kohara Y, Sharp S, Simmonds M, Spiegler S, Tivey A, Sugano S, White B, Walker D, Woodward J, Winckler T, Tanaka Y, Shaulsky G, Schleicher M, Weinstock G, Rosenthal A, Cox EC, Chisholm RL, Gibbs R, Loomis WF, Platzer M, Kay RR, Williams J, Dear PH, Noegel AA, Barrell B, Kuspa A (2005) The genome of the social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum. Nature 435:43–57
Escalante R, Loomis WF (1995) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of cell-type-specific mRNAs in Dictyostelium. Dev Biol 43:262–266
Fukuzawa M, Williams JG (2000) Analysis of the promoter of the cudA gene reveals novel mechanisms of Dictyostelium cell type differentiation. Development 127:2705–2713
Fukuzawa M, Araki T, Adrian I, Williams JG (2001) Tyrosine phosphorylation-independent nuclear translocation of a Dictyostelium STAT in response to DIF signaling. Mol Cell 7:779–788 Erratum in: Mol Cell (2002) 9:919
Gao Q, Hua J, Kimura R, Headd JJ, Fu XY, Chin YE (2004) Identification of the linker-SH2 domain of STAT as the origin of the SH2 domain using two-dimensional structural alignment. Mol Cell Proteomics 3:704–714
Girard KD, Chaney C, Delannoy M, Kuo SC, Robinson DN (2004) Dynacortin contributes to cortical viscoelasticity and helps define the shape changes of cytokinesis. EMBO J 23:1536–1546
Iranfar N, Fuller D, Loomis WF (2006) Transcriptional regulation of post-aggregation genes in Dictyostelium by a feed-forward loop involving GBF and LagC. Dev Biol 290:460–469
Kawata T, Shevchenko A, Fukuzawa M, Jermyn KA, Totty NF, Zhukovskaya NV, Sterling AE, Mann M, Williams JG (1997) SH2 signaling in a lower eukaryote: a STAT protein that regulates stalk cell differentiation in Dictyostelium. Cell 89:909–916
Kay RR (1997) Dictyostelium development: lower STATs. Curr Biol 7:R723–R725
Kim HS, Lee MS (2007) STAT1 as a key modulator of cell death. Cell Signal 19:454–465
Kuspa A, Loomis WF (1992) Tagging developmental genes in Dictyostelium by restriction enzyme-mediated integration of plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:8803–8807
Kuwayama H, Snippe H, Derks M, Roelofs J, van Haastert PJM (2001) Identification and characterization of DdPDE3, a cGMP-selective phosphodiesterase from Dictyostelium. Biochem J 353:635–644
Lal K, Field MC, Carlton JM, Warwicker J, Hirt RP (2005) Identification of a very large Rab GTPase family in the parasitic protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 143:226–235
Maeda M, Kuwayama H, Yokoyama M, Nishio K, Morio T, Urushihara H, Katho M, Tanaka Y, Saito T, Ochiai H, Takemoto K, Yasukawa H, Takeuchi I (2000) Developmental changes in the spatial expression of genes involved in myosin function in Dictyostelium. Dev Biol 43:114–119
Maeda M, Sakamoto H, Maruo T, Ogihara S, Iranfar N, Fuller D, Morio T, Urushihara H, Tanaka Y, Loomis WF (2003) Changing patterns of gene expression in prestalk cell subtypes of Dictyostelium recognised by in situ hybridisation with genes from microarray analyses. Eukaryot Cell 2:638–645
Maruo T, Sakamoto H, Iranfar N, Fuller D, Morio T, Urushihara H, Tanaka Y, Maeda M, Loomis WF (2004) Control of cell type proportioning in Dictyostelium discoideum by differentiation-inducing factor as determined by in situ hybridization. Eukaryot Cell 3:1241–1248
Mohanty S, Jermyn KA, Early A, Kawata T, Aubry L, Ceccarelli A, Schaap P, Williams JG, Firtel RA (1999) Evidence that the Dictyostelium Dd-STATa protein is a repressor that regulates commitment to stalk cell differentiation and is also required for efficient chemotaxis. Development 126:3391–3405
Mui AL-F (1999) The role of STATs in proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 55:1547–1558
Muramoto T, Suzuki K, Shimizua H, Kohara Y, Kohriki E, Obara S, Tanaka Y, Urushihara H (2003) Construction of a gamete-enriched gene pool and RNAi-mediated functional analysis in Dictyostelium discoideum. Mech Dev 120:965–975
Octtaviani E, Effler JC, Robinson DN (2006) Enlazin, a natural fusion of two classes of canonical cytoskeletal proteins, contributes to cytokinesis dynamics. Mol Biol Cell 17:5275–5286
Prelich G (1999) Suppression mechanisms: themes from variations. Trends Genet 15:261–266
Ramji DP, Richards AJ, Jagger P, Bleasby A, Hames BD (1990) Two cyclic AMP-regulated genes from Dictyostelium discoideum encode homologous proteins. Mol Microbiol 4:129–135
Richards AJ, Corney AJ, Hames BD (1990) Cell-type-specific genes expressed late in Dictyostelium development show markedly different responses to 3′5′ cyclic AMP. Mol Microbiol 4:1279–1291
Rivero F, Dislich H, Glöckner G, Noegel AA (2001) The Dictyostelium discoideum family of Rho-related proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 29:1068–1079
Robinson DN, Spudich JA (2000) Dynacortin, a genetic link between equatorial contractility and global shape control discovered by library complementation of a Dictyostelium discoideum cytokinesis mutant. J Cell Biol 150:823–838
Schilde C, Araki T, Williams H, Harwood A, Williams JG (2004) GSK3 is a multifunctional regulator of Dictyostelium development. Development 131:4555–4565
Seager JHJ, Stevens BA, McCaffery I, Hames BD (2001) Identification of novel elements which regulate the cell-type specificity of Dictyostelium 7E gene expression. Differentiation 68:22–30
Shaulsky G, Escalante R, Loomis WF (1996) Developmental signal transduction pathways uncovered by genetic suppressors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:15260–15265
Shimada N, Kawata T (2007) Evidence that noncoding RNA dutA is a multicopy suppressor of Dictyostelium STAT protein Dd-STATa. Eukaryot Cell 6:1030–1040
Shimada N, Nishio K, Maeda M, Urushihara H, Kawata T (2004a) Extracellular matrix family proteins that are potential targets of Dd-STATa in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Plant Res 117:345–353
Shimada N, Maeda M, Urushihara H, Kawata T (2004b) Identification of new modes of Dd-STATa regulation of gene expression in Dictyostelium by in situ hybridisation. Int J Dev Biol 48:679–682
Shimada N, Maruo T, Maeda M, Urushihara H, Kawata T (2005) Evidence that the Dictyostelium STAT protein Dd-STATa plays a role in the differentiation of inner basal disc cells and identification of a promoter element essential for expression in these cells. Differentiation 73:50–60
Silva CM (2004) Role of STATs as downstream signal transducers in Src family kinase-mediated tumorigenesis. Oncogene 23:8017–8123
Spann TP, Brock DA, Lindsey DF, Wood SA, Gomer RH (1996) Mutagenesis and gene identification in Dictyostelium by shotgun antisense. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5003–5007
St Johnston D (2002) The art and design of genetic screens: Drosophila melanogaster. Nature Rev Genet 3:176–188
Yoshida H, Kumimoto H, Okamoto K (1994) dutA RNA functions as an untranslatable RNA in the development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Nucl Acids Res 22:41–46
Zhukovskaya NV, Fukuzawa M, Tsujioka M, Jermyn KA, Kawata T, Abe T, Zvelebil M, Williams JG (2004) Dd-STATb, a Dictyostelium STAT protein with a highly aberrant SH2 domain, functions as a regulator of gene expression during growth and early development. Development 131:447–458
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Faculty of Science Special Grant for Promoting Scientific Research at Toho University to T. Kawata (301-12) and by a Grant-in-Aid from Japanese Society for the Promotion of Science (JSTS) Fellowships for Young Scientists to N. Shimada (#17.2751). N.S. is a JSTS Research Fellow. We thank Prof. Jeffrey G. Williams for comments related to the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M.Q. Martindale
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimada, N., Kanno-Tanabe, N., Minemura, K. et al. GBF-dependent family genes morphologically suppress the partially active Dictyostelium STATa strain. Dev Genes Evol 218, 55–68 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-008-0202-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-008-0202-7