Abstract
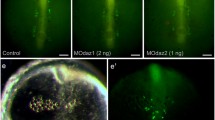
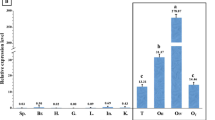
To investigate the germ cell specification in urodeles, we cloned a DAZ-like sequence from the Japanese newt Cynops pyrrhogaster, Cydazl, and raised antibodies specific to Cydazl. Cydazl is a homologue of the human DAZ (deleted in azoospermia), DAZL, and Xenopus dazl genes, which are involved in gametogenesis or germ cell specification. During gametogenesis, expression of Cydazl mRNA and Cydazl protein was detected at first in the small previtellogenic oocytes in females but was not localized as seen in Xenopus and was restricted to secondary spermatogonia prior to meiosis in males. During early embryogenesis, maternal stores of the Cydazl transcript and protein were present in the entire embryos, not localized in any specific region. The zygotic expression was detected in hatching larvae (stage 50) by RT-PCR analysis whereas specific cells expressing Cydazl could not be determined by in situ hybridization at this stage. Strong expression of Cydazl and Cydazl were detected in primordial germ cells (PGCs) that had entered the gonadal rudiment at late stage 59. These results suggest that Cydazl does not function early in development, for the specification of germ cells, but functions later for differentiation of germ cells in the developing gonads during embryogenesis and for meiotic regulation, supporting the previous idea of an intermediate germ cell formation mode in urodeles.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akita Y, Wakahara M (1985) Cytological analyses of factors which determine the number of primordial germ cells (PGCs) in Xenopus laevis. J Embryol Exp Morphol 90:251–265
Ariizumi T, Moriya N, Uchiyama H, Asashima M (1991a) Concentration-dependent inducing activity of activin A. Roux’s Arch Dev Biol 200:230–233
Ariizumi T, Sawanuma K, Uchiyama H, Asashima M (1991b) Dose and time dependent mesoderm induction and out-growth formation by activin A in Xenopus laevis. Int J Dev Biol 35:407–411
Beetschen JC, Gautier J (1989) Oogenesis. In: Armstrong JB, Malacinski GM (eds) Developmental biology of the axolotl. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 25–35
Cooke HJ, Lee M, Kerr S, Fuggiu M (1996) A murine homologue of the human DAZ gene is autosomal and expressed only in male and female gonads. Hum Mol Genet 5:513–526
Czolovska R (1969) Observations on the origin of the ‘germinal cytoplasm’ in Xenopus laevis. J Embryol Exp Morphol 22:229–251
Dixon KE (1994) Evolutionary aspects of primordial germ cell formation. In: Germline development. Ciba Foundation symposium 182. Wylie, Chichester, pp 92–120
Dumont JN (1972) Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol 136:153–179
Eberhart CG, Maines JZ, Wasserman SA (1996) Meiotic cell cycle requirement for a fly homologue of human Deleted in Azoospermia. Nature 381:783–785
Eddy EM, Hahnal AC (1983) Establishment of the germ cell line in mammals. In: McLaren A, Wylie CC (eds) Current problems in germ cell differentiation. Cambridge University Press, London, pp 41–69
Extavour CG, Akam M (2003) Mechanisms of germ cell specification across the metazoans: epigenesis and preformation. Development 130:5869–5884
Guan KL, Dixon JE (1991) Eukaryotic proteins expressed in Escherichia coli: an improved thrombin cleavage and purification procedure of fusion proteins with glutathione S-transferase. Anal Biochem 192:262–267
Hall BK (1999) Evolutionary developmental biology, 2nd edn. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Hamashima N, Kotani M (1977) Ultrastructural observations on the primordial germ cells in the newt, Triturus pyrrhogaster. Zool Mag 86:239–245
Heasmann J, Quarmby J, Wylie CC (1984) The mitochondrial cloud of Xenopus oocytes: the source of germinal granule material. Dev Biol 105:458–469
Hirai T, Yamashita M, Yoshikuni M, Lou YH, Nagahama Y (1992) Cyclin B in fish oocytes: Its cDNA and amino acid sequences, appearance during maturation, and induction of p34cdc2 activation. Mol Reprod Dev 33:131–140
Houston DW, King ML (2000) A critical role for Xdazl, a germ plasm-localized RNA, in the differentiation of primordial germ cells in Xenopus. Development 127:447–456
Houston DW, Zhang J, Maines JZ, Wasserman SA, King ML (1998) A Xenopus DAZ-like gene encodes an RNA component of germ plasm and is a functional homologue of Drosophila boule. Development 125:171–180
Ikenishi K (1998) Germ plasm in Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila and Xenopus. Dev Growth Differ 40:1–10
Ikenishi K, Kotani M (1975) Ultrastructure of the ‘germinal plasm’ in Xenopus embryos after cleavage. Dev Growth Differ 17:101–110
Ikenishi K, Nieuwkoop PD (1978) Location and ultrastructure of primordial germ cells (PGCs) in Ambystoma mexicanum. Dev Growth Differ 20:1–9
Ikenishi K, Nakazato S, Okuda T (1986) Direct evidence for the presence of germ cell determinant in vegetal pole cytoplasm of Xenopus laevis and in a subcellular fraction of it. Dev Growth Differ 28:563–568
Johnson AD, Bachvarova RF, Drum M, Masi T (2001) Expression of axolotl Dazl RNA, a marker of germ plasm: widespread maternal RNA and onset of expression in germ cells approaching to the gonad. Dev Biol 234:402–415
Johnson AD, Drum M, Bachvarova RF, Masi T, White ME, Crother BI (2003) Evolution of predetermined germ cells in vertebrate embryos: implications for macroevolution. Evol Dev 5:414–431
Kamimura M, Ikenishi K, Kotani M, Matsuno T (1976) Observation and proliferation of gonocytes in Xenopus laevis. J Embryol Exp Morphol 36:197–207
Karashima T, Sugimoto A, Yamamoto M (2000) Caenorhabditis elegans homologue of the human azoospermia factor DAZ is required for oogenesis but not for spermatogenesis. Development 127:1069–79
King ML (2003) Germ cells and germ plasm. In: Hall BK, Olson WM (eds) Keywords and concepts in evolutionary developmental biology. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Mass., pp 155–161
Kocher-Becker U, Tiedemann H (1971) Induction of mesodermal and endodermal structures and primordial germ cells in Triturus ectoderm by vegetalizing factor from chick embryos. Nature 233:65–66
Kotani M (1957) On the formation of primordial germ cells from the presumptive ectoderm of Triturus gastrulae. J Inst Polytech Osaka City Univ Ser D 8:145–159
Kotani M (1958) The formation of germ cells after extirpation of the presumptive lateral plate of Triturus gastrulae. J Inst Polytech Osaka City Univ Ser D 9:195–209
Lawson KA, Hage WJ (1994) Clonal analysis of the origin of primordial germ cells in the mouse. In: Germline development. Ciba Foundation symposium 182. Wylie, Chichester, pp 68–91
Lehmann R, Ephrussi A (1994) Germ plasm formation and germ cell determination in Drosophila. In: Germline development. Ciba Foundation symposium 182. Wylie, Chichester, pp 282–300
Lesimple M, Dournon C, Houillon C (1990) Melanin as a natural germ cell marker for intraspecific transplantation experiments in Ambystoma mexicanum (Urodela, Amphibia). Roux’s Arch Dev Biol 198:420–429
Maegawa S, Yasuda K, Inoue K (1999) Maternal mRNA localization of zebrafish DAZ-like gene. Mech Dev 81:223–226
Mahowald AP (1968) Polar granules of Drosophila. II. Ultrastructural changes during early embryogenesis. J Exp Zool 167:237–262
Mahowald AP, Boswell RE (1983) Germ plasm and germ cell development in invertebrates. In: McLaren A, Wylie CC (eds) Current problems in germ cell differentiation. Cambridge University Press, London, pp 3–17
Michael P (1984) Are the primordial germ cell (PGCs) in urodela formed by the inductive action of the vegetative yolk mass? Dev Biol 103:109–116
Mita K, Yamashita M (2000) Expression of Xenopus Daz-like protein during gametogenesis and embryogenesis. Mech Dev 94:251–255
Moriya N, Uchiyama H, Asashima M (1993) Induction of pronephric tubules by activin and retinoic acid in presumptive ectoderm of Xenopus laevis. Dev Growth Differ 35:123–128
Nieuwkoop PD, Sutasurya LA (1979) Primordial germ cells in the chordates. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Nieuwkoop PD, Sutasurya LA (1981) Primordial germ cells in the invertebrates. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Okada Y, Ichikawa M (1947) Normal table of Triturus (Cynops) pyrrhogaster. Jpn J Exp Morphol 3:1–6
Reijo RA, Lee TY, Salo P, Alagappan R, Brown LG, Rosenberg M, Rozen S, Jaffe T, Straus D, Hovatta O et al. (1995) Diverse spermatogenic defects in humans caused by Y chromosome deletions encompassing a novel RNA-binding protein. Nat Genet 10:383–393
Ruggiu M, Speed R, Taggart M, Mckay SJ, Kilanowski F, Saunders P, Dorin J, Cooke HJ (1997) The mouse Dazla gene encodes a cytoplasmic protein essential for gametogenesis. Nature 389:73–77
Saxena R, Brown LG, Hawkins T, Alagappan RK, Skaletsky H, Reeve MP, Reijo R, Rozen S, Dinulos MB, Disteche CM, Page DC (1996) The DAZ gene cluster on the human Y chromosome arose from an autosomal gene that was transposed, repeatedly amplified and pruned. Nat Genet 14:292–9
Sekizaki H, Takahashi S, Tanegashima K, Onuma Y, Haramoto Y, Asashima M (2004) Tracing of Xenopus tropicalis germ plasm and presumptive primordial germ cells with the Xenopus tropicalis DAZ-like gene. Dev Dyn 229:367–372
Smith LD, Michael P, Williams MA (1983) Does a predetermined germ line exist in amphibians?. In: McLaren A, Wylie CC (eds) Current problems in germ cell differentiation. Cambridge University Press, London, pp 19–39
Strome S, Garvin C, Paulsen J, Capowski E, Martin P, Beanan M (1994) Specification and development of the germline in Caenorhabditis elegans. Ciba Foundation symposium 182. Wylie, Chichester, pp 31–51
Sutasurya LA, Nieuwkoop PD (1974) The induction of the primordial germ cells in the urodeles. Wilhelm Roux’ Arch Entwicklungsmech Org 175:199–220
Takabatake T, Takahashi TC, Inoue K, Ogawa M, Takeshima K (1996) Activation of two Cynops genes, fork head and sonic hedgehog, in animal cap explants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 218:395–401
Wakahara M (1977) Partial characterization of ‘primordial germ cell-forming activity’ localized in vegetal cytoplasm in anuran egg. J Embryol Exp Morphol 39:221–233
Wakahara M (1978) Induction of supernumerary primordial germ cells by injecting vegetal pole cytoplasm into Xenopus eggs. J Exp Zool 203:159–164
Wakahara M (1990) Cytoplasmic localization of and organization of germ-cell determinants. In: Malacinski GM (eds) Cytoplasmic organization system. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 219–242
Wakahara M (1996) Primordial germ cell development: is the urodele pattern closer to mammals than to anurans? Int J Dev Biol 40:653–659
Whitington P, Dixon KE (1975) Quantitative studies of germ plasm and germ cells during early embryogenesis of Xenopus laevis. J Embryol Exp Morphol 33:57–74
Williams MA, Smith LD (1971) Ultrastructure of the ‘germinal plasm’ during maturation and early cleavage in Rana pipiens. Dev Biol 25:568–580
Xu EY, Moore FL, Reijo RA (2001) A gene family required for human germ cell development evolved from an ancient meiotic gene conserved in metazoans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:7414–7419
Yamashita M, Yoshikuni M, Hirai T, Fukada S, Nagahama Y (1991) A monoclonal antibody against the PSTAIR sequence of p34cdc2, catalytic subunit of maturation-promoting factor and key regulator of the cell cycle. Dev Growth Differ 33:617–624
Acknowledgements
This work partly was supported by the Sasakawa Scientific Research Grant from The Japan Science Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by N. Satoh
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamori, Y., Iwai, T., Mita, K. et al. Spatio-temporal expression of a DAZ-like gene in the Japanese newt Cynops pyrrhogaster that has no germ plasm. Dev Genes Evol 214, 615–627 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-004-0443-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-004-0443-z