Abstract
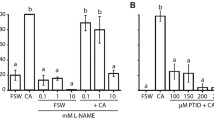
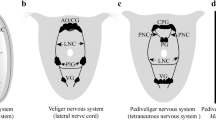
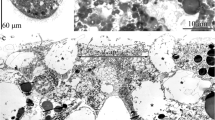
The primitive nervous system in planula larvae of Hydractinia echinata (Cnidaria) has sensory neurons containing LWamide or RFamide neuropeptides. LWamides have been shown to induce metamorphosis of planula larvae into adult polyps. We report here that RFamides act antagonistically to LWamides. RFamides inhibit metamorphosis when applied to planula larvae during metamorphosis induction by treatment with LWamides (or other inducing agents such as CsCl ions, diacylglycerol and bacterial inducers). Our results show further that RFamides act downstream of LWamide release, presumably directly on target cells mediating metamorphosis. These observations support a model in which metamorphosis in H. echinata is regulated by sensory neurons secreting LWamides and RFamides in response to environmental cues.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berking S, Walther M (1994) Control of metamorphosis in the hydroid Hydractinia. In: Davey KG, Peter RE, Tobe SS (eds) Perspectives in comparative endocrinology. Research Council of Canada, Ottawa, pp 381–388
Bode HR (1992) Continuous conversion of neuron phenotype in Hydra. Trends Genet 8: 279–284
Bode H, Berking S, David CN, Gierer A, Schaller H, Trenkner E (1973) Quantitative analysis of cell types during growth and morphogenesis in hydra. Wilhelm Roux’ Archiv Entwicklungsmech Org 171:269–285
Di Guglielmo GM, Drake PG, Baass PC, Authier F, Posner BI, Bergeron JJ (1998) Insulin receptor internalization and signaling. Mol Cell Biochem 182:59–63
Dunne JF, Javois LC, Huang LW, Bode HR (1985) A subset of cells in the nerve net of Hydra oligactis defined by a monoclonal antibody: its arrangement and development. Dev Biol 109:41–53
Gajewski M, Leitz T, Schlossherr J, Plickert G (1996) LWamides from Cnidaria constitute a novel family of neuropeptides with morphogenetic activity. Roux’s Arch Dev Biol 205: 232–242
Gajewski M, Schmutzler C, Plickert G (1998) Structure of neuropeptide precursors in cnidarian. Ann NY Acad Sci 839:311–315
Grimmelikhuijzen CJP (1985) Antisera to the sequence Arg-Phe-amide visualize neuronal centralization in hydroid polyps. Cell Tissue Res 241:171–182
Kroiher M, Berking S (1999) On natural metamorphosis inducers of the cnidarians Hydractinia echinata (Hydrozoa) and Aurelia aurita (Scyphozoa). Helgol Mar Res 53:118–121
Law PY, Loh HH (1999) Regulation of opioid receptor activities. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289:607–624
Leitz T (1993) Biochemical and cytological bases of metamorphosis in Hydractinia echinata. Mar Biol 116:559–564
Leitz T (1998a) Metamorphosin A and related compounds: a novel family of neuropeptides with morphogenetic activity. Ann New York Acad Sci 839:105–110
Leitz T (1998b) Induction of metamorphosis of the marine hydrozoan Hydractinia echinata Fleming, 1828. Biofouling 12:173–187
Leitz T, Lay M (1995) Metamorphosin A is a neuropeptide. Roux’s Arch Dev Biol 204:276–279
Leitz T, Müller WA (1987) Evidence for the involvement of PI-signaling and diacylglycerol second messengers in the initiation of metamorphosis in the hydroid Hydractinia echinata Fleming. Dev Biol 121:82–89
Leitz T, Wagner T (1993) The marine bacterium Alteromonas espejiana induces metamorphosis of the hydroid Hydractinia echinata. Mar Biol 115:173–178
Leitz T, Morand K, Mann M (1994) Metamorphosin A: a novel peptide controlling development of the lower metazoan Hydractinia echinata (Coelenterata, Hydrozoa). Dev Biol 163:440–446
Moosler A, Rinehart KL, Grimmelikhuijzen CJP (1996) Isolation of four novel neuropeptides, the hydra-RFamide I-IV, from Hydra magnipapillata. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 229:596–602
Müller WA (1973) Metamorphose-Induktion bei Planulalarven. I. Der bakterielle Induktor. Wilhelm Roux’ Archiv Entwicklungsmech Org 173:107–121
Müller WA, Buchal G (1973) Metamorphose-Induktion bei Planulalarven. II. Induktion durch monovalente Kationen: die Bedeutung des Gibbs-Donnan-Verhältnisses und der Na+/K+-ATPase. Wilhelm Roux’ Archiv Entwicklungsmech Org 173:122–135
Plickert G (1989) Proportion-altering factor (PAF) stimulates nerve cell formation in Hydractinia echinata. Cell Differ Dev 26:19–28
Plickert G, Kroiher M, Munck A (1988) Cell proliferation and early differentiation during embryonic development and metamorphosis of Hydractinia echinata. Development 103:795–803
Schmich J, Rudolf R, Trepel S, Leitz T (1998a) Immunohistochemical studies of GLWamides in cnidaria. Cell Tissue Res 294:169–177
Schmich J, Trepel S, Leitz T (1998b) The role of GLWamides in metamorphosis of Hydractinia echinata. Dev Genes Evol 208:267–273
Schwartz AL (1995) Receptor cell biology: receptor-mediated endocytosis. Pediatr Res 38:835–843
Schwoerer-Böhning B, Kroiher M, Müller W (1990) Signal transmission and covert repattern in the metamorphosis of Hydractinia echinata (Hydrozoa). Roux’s Arch Dev Biol 198:245–251
Takahashi T, Muneoka Y, Lohmann J, Lopez de Haro MS, Solleder G, Bosch TCG, David CN, Bode HR, Koizumi O, Shimizu H, Hatta M, Fujisawa T, Sugiyama T (1997) Systematic isolation of peptide signal molecules regulating development in hydra: LWamide and PW families. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:1241–1246
Takahashi T, Koizumi O, Ariura Y, Romanovitch A, Bosch TCG, Kobayakawa Y, Mohri S, Bode HR, Yum S, Hatta M, Fujisawa T (2000) A novel neuropeptide, Hym-355, positively regulates neuron differentiation in Hydra. Development 127:997–1005
Yum S, Takahashi T, Hatta M, Fujisawa T (1998) The structure and expression of a preprohormone of a neuropeptide, Hym-176 in Hydra magnipapillata. FEBS Lett 439:31–34
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Y. Muneoka and T. Takahashi for a gift of hydra peptides, Dr. T. Leitz for a gift of A. espejiana culture, Drs. T. Fujisawa and M. Hatta for valuable discussions, and Ms. A. Zychlinski for enthusiastic technical assistance. T.S. was a recipient of the Alexander von Humboldt-Foundation Research Award, which enabled him to initiate this project in the laboratory of C.N.D. This work was supported in part by grants from Sumitomo Foundation and Yamada Science Foundation to T.S. and by grants from the German Science Foundation (DFG) to C.N.D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by D. Tautz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katsukura, Y., David, C.N., Grimmelikhuijzen, C.J.P. et al. Inhibition of metamorphosis by RFamide neuropeptides in planula larvae of Hydractinia echinata . Dev Genes Evol 213, 579–586 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-003-0361-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-003-0361-5