Abstract.
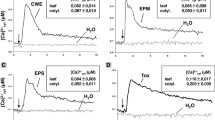
The source of Ca2+ involved in transducing an oxidative-burst defense signal was examined in aequorin-transformed tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) cells using modulators of Ca2+ entry. Treatments that either increased or decreased the influx of Ca2+ from external stores were found to have little effect on the magnitude or kinetics of an osmotically stimulated oxidative burst. In contrast, treatments that reduced the discharge of Ca2+ from internal stores inhibited dilution-activated H2O2 production. Curiously, most of the modulators commonly employed in animal studies as internal Ca2+-release inhibitors were neither effective in blocking discharge of intracellular Ca2+ nor in preventing the oxidative burst. When three different biochemical elicitors of the oxidative burst were similarly examined, both the H2O2 production and Ca2+ fluxes stimulated were found to be sensitive to modulators of internal Ca2+ release, but neither was impacted by alterations in externally derived Ca2+ influx. We hypothesize, therefore, that the oxidative burst does not depend on the influx of external Ca2+, but instead may generally be mediated by the release of internal Ca2+ in a manner that depends on the proper function of kinases and anion channels. These Ca2+ pulses trigger downstream signaling events that include the activation of Ca2+-regulated protein kinases, which are required for stimulation of the oxidative burst.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cessna, S.G., Low, P.S. Activation of the oxidative burst in aequorin-transformed Nicotiana tabacum cells is mediated by protein kinase- and anion channel-dependent release of Ca2+ from internal stores. Planta 214, 126–134 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250100596
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250100596