Abstract
Main conclusion
Transcriptional activation of subfamily II PHT1 members in roots is associated with the enhanced phosphorus use efficiency and growth promotion of barley seedlings inoculated with Glomus species.
Abstract
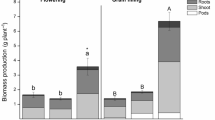
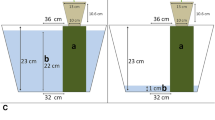
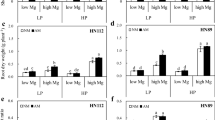
The arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi symbiotic associations in cereal crops are known to regulate growth in cultivar-specific manner and induce phosphate (Pi) transporters (PHT1) in roots. In the present study, we observed that both AM colonization of roots by Glomus species and phosphate starvation enhanced phosphorus use efficiency (PUE) in barley seedlings. Our search for the full complement of PHT1 members in the recently sequenced barley genome identified six additional genes, totaling their number to 17. Both AM colonization and Pi starvation triggered activation of common as well as different PHT1s. Pi starvation led to the robust upregulation of HvPHT1;6.2/6.3 at 7d and weak activation of HvPHT1;1 in shoots at 3d time-point. In roots, only HvPHT1;1, HvPHT1;6.2/6.3, HvPHT1;7, HvPHT1;8, HvPHT1;11.2 and HvPHT12 were induced at least one of the time-points. AM colonization specifically upregulated HvPHT1;11, HvPHT1;11.2, HvPHT1;12 and HvPHT1;13.1/13.2, members belonging to subfamily II, in roots. Sucrose availability seems to be obligatory for the robust activation of HvPHT1;1 as unavailability of this metabolite generally weakened its upregulation under Pi starvation. Intriguingly, lack of sucrose supply also led to induction of HvPHT1;5, HvPHT1;8, and HvPHT1;11.2 in either roots or shoot or both. The mRNA levels of HvPHT1;5 and HvPHT1;11.2 were not severely affected under combined deficiency of Pi and sucrose. Taken together, this study not only identify additional PHT1 members in barley, but also ascertain their AM, Pi and sucrose-specific transcript accumulation. The beneficial role of AM fungi in the promotion of PUE and barley seedlings' growth is also demonstrated.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The authors declare that no new data were generated in this article.
Abbreviations
- AM:
-
Arbuscular mycorrhiza
- IAP:
-
Intracellular acid phosphatase
- PHT:
-
Phosphate transporters
- Pi:
-
Inorganic phosphate
- PSI:
-
Phosphorus starvation inducible
- PUE:
-
Phosphorus use efficiency
- SAP:
-
Secretory acid phosphatase
References
Agarwal N, Minj DK, Rani K (2015) Estimation of total carbohydrate present in dry fruits. IOSR J Environ Sci 1:24–27
Ai P, Sun S, Zhao J (2009) Two rice phosphate transporters, OsPht1;2 and OsPht1;6, have different functions and kinetic properties in uptake and translocation. Plant J 57:798–809
Akash PA, Srivastva A, Mathur S et al (2021) Identification, evolutionary profiling, and expression analysis of F-box superfamily genes under phosphate deficiency in tomato. Plant Physiol Biochem 162:349–362
Baon JB, Smith SE, Alston AM (1993) Mycorrhizal responses of barley cultivars differing in P efficiency. Plant Soil 157:97–105
Bernaola L, Stout MJ (2021) The effect of mycorrhizal seed treatments on rice growth, yield, and tolerance to insect herbivores. J Pest Sci 94:375–392
Bray RH, Kurtz LT (1945) Determination of total, organic, and available forms of phosphorus in soils. Soil Sci 59:39–46
Bruce A (1966) Assay of inorganic phosphate, total phosphate and phosphatases. Methods Enzymol 8:115–118
Bun-Ya M, Nishimura M, Harashima S, Oshima Y (1991) The PHO84 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes an inorganic phosphate transporter. Mol Cell Biol 11:3229–3238
Clarke C, Mosse B (1981) Plant growth responses to vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza XII. Field inoculation responses of barley at two soil P levels. New Phytol 87:695–703
Ditusa SF, Fontenot EB, Wallace RW et al (2016) A member of the phosphate transporter 1 (Pht1) family from the arsenic-hyperaccumulating fern Pteris vittata is a high-affinity arsenate transporter. New Phytol 209:762–772
Doerner P (2008) Phosphate starvation signaling: a threesome controls systemic Pi homeostasis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:536–540
Druka A, Muehlbauer G, Druka I et al (2006) An atlas of gene expression from seed to seed through barley development. Funct Integr Genom 6:202–211
Fester T, Maier W, Strack D (1999) Accumulation of secondary compounds in barley and wheat roots in response to inoculation with an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and co-inoculation with rhizosphere bacteria. Mycorrhiza 8:241–246
Grace EJ, Cotsaftis O, Tester M et al (2009) Arbuscular mycorrhizal inhibition of growth in barley cannot be attributed to extent of colonization, fungal phosphorus uptake or effects on expression of plant phosphate transporter genes. New Phytol 181:938–949
Gu M, Chen A, Sun S, Xu G (2016) Complex regulation of plant phosphate transporters and the gap between molecular mechanisms and practical application: what is missing? Mol Plant 9:396–416
Hammond JP, White PJ (2008) Sucrose transport in the phloem: Integrating root responses to phosphorus starvation. J Exp Bot 59:93–109
Huang X, Zhu W, Dai S et al (2008) The involvement of mitochondrial phosphate transporter in accelerating bud dormancy release during chilling treatment of tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa). Planta 228:545–552
Huang CY, Shirley N, Genc Y et al (2011) Phosphate utilization efficiency correlates with expression of low-affinity phosphate transporters and noncoding RNA, IPS1, in barley. Plant Physiol 156:1217–1229
Jensen A (1982) Influence of four vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on nutrient uptake and growth in barley (Hordeum vulgare). New Phytol 90:45–50
Karandashov V, Bucher M (2005) Symbiotic phosphate transport in arbuscular mycorrhizas. Trends Plant Sci 10:22–29
Karthikeyan AS, Varadarajan DK, Jain A et al (2007) Phosphate starvation responses are mediated by sugar signaling in Arabidopsis. Planta 225:907–918
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M et al (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547
Lapis-Gaza HR, Jost R, Finnegan PM (2014) Arabidopsis PHOSPHATE TRANSPORTER 1 genes PHT1;8 and PHT1;9 are involved in root-to-shoot translocation of orthophosphate. BMC Plant Biol 14:334
Leggewie G, Willmitzer L, Riesmeier JW (1997) Two cDNAs from potato are able to complement a phosphate uptake-deficient yeast mutant: Identification of phosphate transporters from higher plants. Plant Cell 9:381–392
Li HY, Zhu YG, Marschner P et al (2005) Wheat responses to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in a highly calcareous soil differ from those of clover, and change with plant development and P supply. Plant Soil 277:221–232
Liao H, Yan X (1999) Seed size is closely related to phosphorus use efficiency and photosynthetic phosphorus use efficiency in common bean. J Plant Nutr 22:877–888
Liu C, Muchhal US, Uthappa M et al (1998a) Tomato phosphate transporter genes are differentially regulated in plant tissues by phosphorus. Plant Physiol 116:91–99
Liu H, Trieu AT, Blaylock LA, Harrison MJ (1998b) Cloning and characterization of two phosphate transporters from Medicago truncatula roots: Regulation in response to phospate and to colonization by arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 11:14–22
Liu J, Uhde-Stone C, Li A et al (2001) A phosphate transporter with enhanced expression in proteoid roots of white lupin (Lupinus albus L.). Plant Soil 237:257–266
Liu TY, Huang TK, Yang SY et al (2016) Identification of plant vacuolar transporters mediating phosphate storage. Nat Commun 7:1–11
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lorenzo-Orts L, Couto D, Hothorn M (2020) Identity and functions of inorganic and inositol polyphosphates in plants. New Phytol 225:637–652
Loth-Pereda V, Orsini E, Courty PE et al (2011) Structure and expression profile of the phosphate Pht1 transporter gene family in mycorrhizal Populus trichocarpa. Plant Physiol 156:2141–2154
Mascher M, Gundlach H, Himmelbach A et al (2017) A chromosome conformation capture ordered sequence of the barley genome. Nature 544:427–433
Mayer KFX, Waugh R, Langridge P et al (2012) A physical, genetic and functional sequence assembly of the barley genome. Nature 491:711
Młodzińska E, Zboińska M (2016) Phosphate uptake and allocation: a closer look at Arabidopsis thaliana L. and Oryza sativa L. Front Plant Sci 7:1198
Mohammad MJ, Malkawi HI, Shibli R (2003) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphorus fertilization on growth and nutrient uptake of barley grown on soils with different levels of salts. J Plant Nutr 26:125–137
Muchhal US, Pardo JM, Raghothama KG (1996) Phosphate transporters from the higher plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10519–10523
Nagy R, Karandashov V, Chague V et al (2005) The characterization of novel mycorrhiza-specific phosphate transporters from Lycopersicon esculentum and Solanum tuberosum uncovers functional redundancy in symbiotic phosphate transport in solanaceous species. Plant J 42:236–250
Nagy R, Vasconcelos MJV, Zhao S et al (2006) Differential regulation of five Pht1 phosphate transporters from maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Biol 8:186–197
Nakagawa T, Imaizumi-Anraku H (2015) Rice arbuscular mycorrhiza as a tool to study the molecular mechanisms of fungal symbiosis and a potential target to increase productivity. Rice 8:1–9
Nussaume L (2011) Phosphate import in plants: focus on the PHT1 transporters. Front Plant Sci 2:83
Paszkowski U, Kroken S, Roux C, Briggs SP (2002) Rice phosphate transporters include an evolutionarily divergent gene specifically activated in arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:13324–13329
Phillips JM, Hayman DS (1970) Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection. Trans Br Mycol Soc 55:158–161
Powell CL (1981) Inoculation of barley with efficient mycorrhizal fungi stimulates seed yield. Plant Soil 3:487–489
Preuss CP, Huang CY, Tyerman SD (2011) Proton-coupled high-affinity phosphate transport revealed from heterologous characterization in Xenopus of barley-root plasma membrane transporter, HvPHT1;1. Plant Cell Environ 34:681–689
Rae AL, Cybinski DH, Jarmey JM, Smith FW (2003) Characterization of two phosphate transporters from barley; evidence for diverse function and kinetic properties among members of the Pht1 family. Plant Mol Biol 53:27–36
Raghothama KG, Karthikeyan AS (2005) Phosphate acquisition. Plant Soil 274:37–49
Sawers RJH, Svane SF, Quan C et al (2017) Phosphorus acquisition efficiency in arbuscular mycorrhizal maize is correlated with the abundance of root-external hyphae and the accumulation of transcripts encoding PHT1 phosphate transporters. New Phytol 214:632–643
Sawers RJH, Ramírez-Flores MR, Olalde-Portugal V, Paszkowski U (2018) The impact of domestication and crop improvement on arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis in cereals: insights from genetics and genomics. New Phytol 220:1135–1140
Schachtman DP, Reid RJ, Ayling SM et al (1998) Phosphorus uptake by plants: from soil to cell. Plant Physiol 116:447–453
Schünmann PHD, Richardson AE, Smith FW, Delhaize E (2004a) Characterization of promoter expression patterns derived from the Pht1 phosphate transporter genes of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J Exp Bot 55:855–865
Schünmann PHD, Richardson AE, Vickers CE, Delhaize E (2004b) Promoter analysis of the barley Pht1;1 phosphate transporter gene identifies regions controlling root expression and responsiveness to phosphate deprivation. Plant Physiol 136:4205–4214
Seo HM, Jung Y, Song S et al (2008) Increased expression of OsPT1, a high-affinity phosphate transporter, enhances phosphate acquisition in rice. Biotechnol Lett 30:1833–1838
Shin H, Shin HS, Dewbre GR, Harrison MJ (2004) Phosphate transport in Arabidopsis: Pht1;1 and Pht1;4 play a major role in phosphate acquisition from both low- and high-phosphate environments. Plant J 39:629–642
Sisaphaithong T, Kondo D, Matsunaga H et al (2012) Expression of plant genes for arbuscular mycorrhiza-inducible phosphate transporters and fungal vesicle formation in sorghum, barley, and wheat roots. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 76:2364–2367
Smith TF (1980) The effect of season and crop rotation on the abundance of spores of vesicular-arbuscular (V-A) mycorrhizal endophytes. Plant Soil 57:475–489
Smith FW, Hawkesford MJ, Ealing PM et al (1997) Regulation of expression of a cDNA from barley roots encoding a high affinity sulphate transporter. Plant J 12:875–884
Smith FW, Rae AL, Hawkesford MJ (2000) Molecular mechanisms of phosphate and sulphate transport in plants. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Biomembr 1465:236–245
Srivastava R, Akash et al (2020) Identification, structure analysis, and transcript profiling of purple acid phosphatases under Pi deficiency in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) and its wild relatives. Int J Biol Macromol 165:2253–2266
Stribley DP, Tinker PB, Snellgrove RC (1980) Effect of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the relations of plant growth, internal phosphorus concentration and soil phosphate analyses. J Soil Sci 31:655–672
Tawaraya K (2003) Arbuscular mycorrhizal dependency of different plant species and cultivars. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 5:655–668
Teng W, Zhao YY, Zhao XQ et al (2017) Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of PHT1 phosphate transporters in wheat. Front Plant Sci 8:543
Walder F, Brulé D, Koegel S et al (2015) Plant phosphorus acquisition in a common mycorrhizal network: regulation of phosphate transporter genes of the Pht1 family in sorghum and flax. New Phytol 205:1632–1645
Wang L, Lu S, Zhang Y et al (2014) Comparative genetic analysis of Arabidopsis purple acid phosphatases AtPAP10, AtPAP12, and AtPAP26 provides new insights into their roles in plant adaptation to phosphate deprivation. J Integr Plant Biol 56:299–314
Wang L, Xiao L, Yang H et al (2020) Genome-wide identification, expression profiling, and evolution of phosphate transporter gene family in green algae. Front Genet 11:590947
Weber MJ, Edlin G (1971) Phosphate transport, nucleotide pools, and ribonucleic acid synthesis in growing and in density-inhibited 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem 6:1828–1833
Willmann M, Gerlach N, Buer B et al (2013) Mycorrhizal phosphate uptake pathway in maize: Vital for growth and cob development on nutrient poor agricultural and greenhouse soils. Front Plant Sci 4:533
Xiao K, Liu J, Dewbre G et al (2006) Isolation and characterization of root-specific phosphate transporter promoters from Medicago truncatula. Plant Biol 8:439–449
Yamaji N, Takemoto Y, Miyaji T et al (2017) Reducing phosphorus accumulation in rice grains with an impaired transporter in the node. Nature 541:92–95
Zhang R, Mu Y, Li X et al (2020) Response of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi diversity and community in maize and soybean rhizosphere soil and roots to intercropping systems with different nitrogen application rates. Sci Total Environ 740:139810
Zhu YG, Smith FA, Smith SE (2003) Phosphorus efficiencies and responses of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi grown in highly calcareous soil. Mycorrhiza 13:93–100
Acknowledgements
Research at RK lab is supported by grants received from the Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India (Grant No. BT/PR31630/AGIII/103/1119/2019), Council of Industrial and Scientific Research, Govt. of India (Grant No.38/1482/19/EMR-II) and Science and Engineering Research Board, Govt. of India (Grant No. CRG/2018/001033) and IoE, MHRD (RC1-20-018). RK acknowledge assistance from the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, under Funds for Infrastructure in Science and Technology (FIST), Level II, and from University Grants Commission under Special Assistance Programme (UGC-SAP-DRS-II) to the Department of Plant Sciences, University of Hyderabad (UoH). RK also acknowledges the financial support to UoH-IoE by MHRD (F11/9/2019-U3(A)). RS thanks the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Govt. of India, for the JRF and SRF fellowships. PS thanks MHRD for JRF and SRF fellowship. HC thank IIT Roorkee for financial support through FIG-100677. RS thanks Mr. Suvajit Basu for his help in initial bioinformatics analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest or financial conflicts to disclose.
Additional information
Communicated by Dorothea Bartels.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, R., Sirohi, P., Chauhan, H. et al. The enhanced phosphorus use efficiency in phosphate-deficient and mycorrhiza-inoculated barley seedlings involves activation of different sets of PHT1 transporters in roots. Planta 254, 38 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03687-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03687-0